8 The Most Complex Object in the Known Universe
... the donor synapse) and can simultaneously involve any ad hoc group of synapses, which leads to an immense number of possible firing configurations. Being essentially wave functions, the brain’s data-mediating ions are able to link up and communicate with any synapse and establish collaborative reson ...
... the donor synapse) and can simultaneously involve any ad hoc group of synapses, which leads to an immense number of possible firing configurations. Being essentially wave functions, the brain’s data-mediating ions are able to link up and communicate with any synapse and establish collaborative reson ...
1. The axons of certain neurons are covered by a layer of fatty tissue
... exactly but have something close, don’t sweat it. Use these as tools of info going forward! ) 1) You could simply write “chemically.” Or the specific answer is: A neuron fires when excitatory inputs exceed inhibitory inputs by a sufficient threshold. When the resulting impulse reaches the axom’s en ...
... exactly but have something close, don’t sweat it. Use these as tools of info going forward! ) 1) You could simply write “chemically.” Or the specific answer is: A neuron fires when excitatory inputs exceed inhibitory inputs by a sufficient threshold. When the resulting impulse reaches the axom’s en ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves The Brain
... Superior colliculi vision reflex center Inferior colliculi auditory reflex center ...
... Superior colliculi vision reflex center Inferior colliculi auditory reflex center ...
The Nervous System
... brain formed by a partial crossing over of optic nerves • Olfactory bulb: Structure located in the forebrain that receives neural input regarding smell ...
... brain formed by a partial crossing over of optic nerves • Olfactory bulb: Structure located in the forebrain that receives neural input regarding smell ...
The Nervous System
... and midbrain. – Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
... and midbrain. – Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
Ch. 35 Nervous System ppt - Jamestown Public Schools
... The sensory division of the PNS transmits impulses from sense organs to the CNS The motor division transmits impulses from the CNS to the muscles or glands The somatic nervous system regulates activities that are under conscious control, such as movement of the skeletal muscles ...
... The sensory division of the PNS transmits impulses from sense organs to the CNS The motor division transmits impulses from the CNS to the muscles or glands The somatic nervous system regulates activities that are under conscious control, such as movement of the skeletal muscles ...
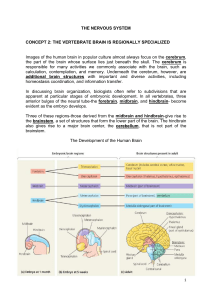
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN
... The midbrain contains centers for receiving and integrating several types of sensory information. It also sends coded sensory information along neurons to specific regions of the forebrain. All sensory axons involved in hearing either terminate in the midbrain or pass through it on their way to the ...
... The midbrain contains centers for receiving and integrating several types of sensory information. It also sends coded sensory information along neurons to specific regions of the forebrain. All sensory axons involved in hearing either terminate in the midbrain or pass through it on their way to the ...
The Nervous System
... and midbrain. – Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
... and midbrain. – Medulla oblongata controls involuntary activities such as heart rate and breathing – Pons and midbrain act as pathways connecting various part of the brain with each other. ...
CNS Brain 241North
... (sensory info. filter) & hypothalamus (eating & drinking reflexes) • Mesencephalon: Visual and Auditory reflex centers (head-turning) • Pons: Relay station for sensory info. ...
... (sensory info. filter) & hypothalamus (eating & drinking reflexes) • Mesencephalon: Visual and Auditory reflex centers (head-turning) • Pons: Relay station for sensory info. ...
Myers AP - Unit 3B
... Figure 3B.14 New technology shows the brain in action This fMRI (functional MRI) scan shows the visual cortex in the occipital lobes activated (color representation of increased bloodflow) as a research participant looks at a photo. When the person stops looking, the region instantly calms down. ...
... Figure 3B.14 New technology shows the brain in action This fMRI (functional MRI) scan shows the visual cortex in the occipital lobes activated (color representation of increased bloodflow) as a research participant looks at a photo. When the person stops looking, the region instantly calms down. ...
NOTES FOR CHAPTER 13
... synapse = space between the axon of a neuron and the dendrites or cell body of another neuron (also between axons and muscle cells) neurotransmitter = chemical stored at the ends of axons that is responsible for transmission across a synapse (can stimulate or inhibit responses) ...
... synapse = space between the axon of a neuron and the dendrites or cell body of another neuron (also between axons and muscle cells) neurotransmitter = chemical stored at the ends of axons that is responsible for transmission across a synapse (can stimulate or inhibit responses) ...
Basal nuclei
... • Controls the overall degree of cortical alertness => ability to direct attention • Helps the cerebellum to regulate muscle tones & generate smooth movements ...
... • Controls the overall degree of cortical alertness => ability to direct attention • Helps the cerebellum to regulate muscle tones & generate smooth movements ...
Classifications of Neurons 1. Function 2. Structure 3. Shape
... A. Cervical spinal cord B. Thoracic spinal cord C. Lumbar spinal cord D. Lumbo-sacral spinal cord ...
... A. Cervical spinal cord B. Thoracic spinal cord C. Lumbar spinal cord D. Lumbo-sacral spinal cord ...
neurotransmitters.
... biology underlies our mental & behavior processes. Biological Psychologists study the links between biological activity and psychological events. ...
... biology underlies our mental & behavior processes. Biological Psychologists study the links between biological activity and psychological events. ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam2_180117_final
... This can occur in the presynaptic neuron or in neighboring glial cells. Itself serves as metabolic precursor for the major inhibitory neurotransmitter ____________________________, via the action of the enzyme ____ ______________________________________. It binds to four families of cell surface rec ...
... This can occur in the presynaptic neuron or in neighboring glial cells. Itself serves as metabolic precursor for the major inhibitory neurotransmitter ____________________________, via the action of the enzyme ____ ______________________________________. It binds to four families of cell surface rec ...
L03 Brain Script Addendum
... The hindbrain is connected to the spinal cord and it is the oldest brain region. The structures in the hindbrain control heart rate, breathing, arousal, and other basic functions for survival. The three main parts of the hindbrain are the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. The medulla regulates breathin ...
... The hindbrain is connected to the spinal cord and it is the oldest brain region. The structures in the hindbrain control heart rate, breathing, arousal, and other basic functions for survival. The three main parts of the hindbrain are the medulla, pons, and cerebellum. The medulla regulates breathin ...
Nervous system - Effingham County Schools
... • Unmyelinated fibers conduct impulses slower. • Myelinated fibers conduct impulses faster – Nodes of Ranvier (short region of exposed axon between Schwann cells on neurons) – The more myelin the faster the impulse ...
... • Unmyelinated fibers conduct impulses slower. • Myelinated fibers conduct impulses faster – Nodes of Ranvier (short region of exposed axon between Schwann cells on neurons) – The more myelin the faster the impulse ...
brain - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... called glia, actually makes up a whopping 85 percent of brain cells. For a long time, scientists thought that glia simply held neurons together. (Indeed, “glia” take their name from the Greek word for glue.) But recent research by Fields, Bukalo’s colleague at the National Institutes of Child Health ...
... called glia, actually makes up a whopping 85 percent of brain cells. For a long time, scientists thought that glia simply held neurons together. (Indeed, “glia” take their name from the Greek word for glue.) But recent research by Fields, Bukalo’s colleague at the National Institutes of Child Health ...
Printable version
... 2. responsible for integration; impulses are sent to the CNS, which decides what to do and sends instructions to the effectors B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 1. consists of two types of nerves a. cranial - extend directly from the brain b. spinal - extend from the spinal cord to the rest of the ...
... 2. responsible for integration; impulses are sent to the CNS, which decides what to do and sends instructions to the effectors B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 1. consists of two types of nerves a. cranial - extend directly from the brain b. spinal - extend from the spinal cord to the rest of the ...
File
... Motor vs. Sensory vs. Intermediate Neuron Structure Motor Neuron • Cell body lies in spinal cord or brain • Many dendrites coming off of cell body ...
... Motor vs. Sensory vs. Intermediate Neuron Structure Motor Neuron • Cell body lies in spinal cord or brain • Many dendrites coming off of cell body ...
Peripheral Nervous System - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... distinct brain regions (i.e., functional localization). Involves artificially stimulating distinct regions and assessing changes in behaviour. Electrical stimulation is delivered through electrodes; the electrical current increases the firing of neurons at the tip of the electrode. ...
... distinct brain regions (i.e., functional localization). Involves artificially stimulating distinct regions and assessing changes in behaviour. Electrical stimulation is delivered through electrodes; the electrical current increases the firing of neurons at the tip of the electrode. ...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... NOTE: You may be asked to identify any structure, cell, tissue, or organ labeled in the figures/pictures within this lab manual. In addition, you may be asked to name one function of each labeled item and one location within the human body where it can be found. You are only responsible for the spec ...
... NOTE: You may be asked to identify any structure, cell, tissue, or organ labeled in the figures/pictures within this lab manual. In addition, you may be asked to name one function of each labeled item and one location within the human body where it can be found. You are only responsible for the spec ...
file - Athens Academy
... responsible for ridding the brain of debris and foreign substances – it acts as an immune system for the nervous system. ...
... responsible for ridding the brain of debris and foreign substances – it acts as an immune system for the nervous system. ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.