Lecture 15: The Brain
... • Ultimately controls the autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Ultimately controls the endocrine system (because it is connected to the pituitary gland via the tiny infundibulum) • Controls body temperature and is thus affected by pyrogens (chemicals produced by an immune response that re-set the ...
... • Ultimately controls the autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Ultimately controls the endocrine system (because it is connected to the pituitary gland via the tiny infundibulum) • Controls body temperature and is thus affected by pyrogens (chemicals produced by an immune response that re-set the ...
Chapter 9 Lesson Two-Nervous System
... Alcohol and Drug Abuse Alcohol can destroy millions of brain cells, which can never be replaced. Other drugs harm the brain by affecting sleeping, breathing, sleeping, and the way your nervous system sends and receives messages. ...
... Alcohol and Drug Abuse Alcohol can destroy millions of brain cells, which can never be replaced. Other drugs harm the brain by affecting sleeping, breathing, sleeping, and the way your nervous system sends and receives messages. ...
PPT
... Split-Brain Patients If the image of an object is presented in their left visual field, they cannot tell the experimenter the identity of the object. This is because this visual information is processed only in the right hemisphere, which cannot produce language. They could pick that object from a ...
... Split-Brain Patients If the image of an object is presented in their left visual field, they cannot tell the experimenter the identity of the object. This is because this visual information is processed only in the right hemisphere, which cannot produce language. They could pick that object from a ...
Figure 4.5 The human nervous system.
... to parasympathetic ganglia close to each internal organ shorter postganglionic fibers then extend from the parasympathetic ganglia in the organs; release acetylcholine ...
... to parasympathetic ganglia close to each internal organ shorter postganglionic fibers then extend from the parasympathetic ganglia in the organs; release acetylcholine ...
BRAIN RESEARCH METHODS
... It is a thin glass tube filled with salty fluid that conducts electricity ...
... It is a thin glass tube filled with salty fluid that conducts electricity ...
How do we see - Austin Community College
... 2. Each of the major parts of the brain has several other structures within it. Locate and identify these structures (listed below) on anatomical models. CEREBRUM: _____ right/left cerebral hemispheres (Sensory areas are involved in the perception of sensory information. Motor areas control muscula ...
... 2. Each of the major parts of the brain has several other structures within it. Locate and identify these structures (listed below) on anatomical models. CEREBRUM: _____ right/left cerebral hemispheres (Sensory areas are involved in the perception of sensory information. Motor areas control muscula ...
Chapter 8 - Cloudfront.net
... other parts of the body to the spinal cord and brain for analysis. • Motor nerve fibers carry messages of action from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and organs. ...
... other parts of the body to the spinal cord and brain for analysis. • Motor nerve fibers carry messages of action from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and organs. ...
Chapter 2 Powerpoint
... border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and ...
... border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and ...
Chapter 2 - Forensic Consultation
... Reticular (“net-like”) Formation The reticular formation is a nerve network in the brainstem. It enables alertness (arousal); stimulating this makes us wide awake. It also filters incoming sensory information and relays it to other brain areas. ...
... Reticular (“net-like”) Formation The reticular formation is a nerve network in the brainstem. It enables alertness (arousal); stimulating this makes us wide awake. It also filters incoming sensory information and relays it to other brain areas. ...
Chicurel2001NatureNV..
... with visual perception and the conscious processing of other types of information4. Last year, Singer’s team showed anaesthetized cats a checked pattern made up of two different sets of stripes moving at right angles to each other.Varying the brightness of the stripes changes the way the overall pat ...
... with visual perception and the conscious processing of other types of information4. Last year, Singer’s team showed anaesthetized cats a checked pattern made up of two different sets of stripes moving at right angles to each other.Varying the brightness of the stripes changes the way the overall pat ...
Aging and Physical Changes
... Psychological consequences: Role of circulatory system in brain and cognitive function – quite a direct impact: jogging is good for health and for mind… ...
... Psychological consequences: Role of circulatory system in brain and cognitive function – quite a direct impact: jogging is good for health and for mind… ...
Nervous System Cells
... • Nerves are bundles of peripheral nerve fibers held together by several layers of ...
... • Nerves are bundles of peripheral nerve fibers held together by several layers of ...
to-BBB and Lundbeck to join forces on brain delivery of
... to-BBB, the Dutch drug brain delivery company, and the pharmaceutical company H. Lundbeck A/S are entering into a research collaboration to evaluate delivery of antibodies to the brain for Central Nervous System (CNS) diseases. This research could provide the backbone of new emerging therapies for u ...
... to-BBB, the Dutch drug brain delivery company, and the pharmaceutical company H. Lundbeck A/S are entering into a research collaboration to evaluate delivery of antibodies to the brain for Central Nervous System (CNS) diseases. This research could provide the backbone of new emerging therapies for u ...
Neurons in the Brain
... According to Piaget, infants do not yet have ideas or concepts about things (nor a memory for people or objects if they are absent)...they only interact with objects at a sensorimotor level (until 18 mos. or 2 yrs of age). ...
... According to Piaget, infants do not yet have ideas or concepts about things (nor a memory for people or objects if they are absent)...they only interact with objects at a sensorimotor level (until 18 mos. or 2 yrs of age). ...
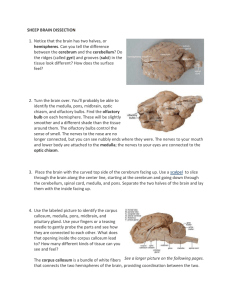
Sheep Brain Dissection Instructions
... The pituitary gland, which produces important hormones, is a sac-like area between the pons and the optic chiasm. This might be harder to locate, especially if it has been punctured. 5. Look closely at the inside of the cerebellum. You should see a branching "tree" of lighter tissue surrounded by da ...
... The pituitary gland, which produces important hormones, is a sac-like area between the pons and the optic chiasm. This might be harder to locate, especially if it has been punctured. 5. Look closely at the inside of the cerebellum. You should see a branching "tree" of lighter tissue surrounded by da ...
The Nervous System - OCPS TeacherPress
... that increases the speed of nerve impulse conductions ...
... that increases the speed of nerve impulse conductions ...
Nervous System (Human): Introduction
... intercommunicate electrochemically via synapses (junctions) between their projecting axons and dendrites – processes whose number and pattern divide neurons into three types: unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar. From unipolar or bipolar receptor neurons, sensory (also called afferent) nerve bundles (n ...
... intercommunicate electrochemically via synapses (junctions) between their projecting axons and dendrites – processes whose number and pattern divide neurons into three types: unipolar, bipolar, and multipolar. From unipolar or bipolar receptor neurons, sensory (also called afferent) nerve bundles (n ...
Glossary - Neurosurgery and Spine Specialists
... the brain and spinal cord. The arachnoid mater is itself separated into two layers, between which (called the subarachnoid space) is cerebrospinal fluid. ...
... the brain and spinal cord. The arachnoid mater is itself separated into two layers, between which (called the subarachnoid space) is cerebrospinal fluid. ...
Adolescents Brain Development
... • Axon – an electricity conducting fiber that carries information away from the cell body • Dendrite – receives messages from other neurons • Synapse – contact point where one neuron “communicates” with another neuron ...
... • Axon – an electricity conducting fiber that carries information away from the cell body • Dendrite – receives messages from other neurons • Synapse – contact point where one neuron “communicates” with another neuron ...
Brain, Cranial Nerves, and Spinal Cord
... – Label parts of a spinal cord given either a silver stained micrograph, an illustration of the spinal cord, or a spinal cord model (use the two slides given here and learn those) – Be able to name the horns (ventral, dorsal, lateral) of the spinal cord and the TYPES of cells found in each horn (mot ...
... – Label parts of a spinal cord given either a silver stained micrograph, an illustration of the spinal cord, or a spinal cord model (use the two slides given here and learn those) – Be able to name the horns (ventral, dorsal, lateral) of the spinal cord and the TYPES of cells found in each horn (mot ...
A Neuron - Gordon State College
... – Spinal cord: slender, tube-shaped part of the (CNS) that connects the brain to the body via the peripheral nervous system The spinal cord transmits information from sensory neurons to the brain, and from the brain to motor neurons that initiate movement. The upper segments of the spinal cord c ...
... – Spinal cord: slender, tube-shaped part of the (CNS) that connects the brain to the body via the peripheral nervous system The spinal cord transmits information from sensory neurons to the brain, and from the brain to motor neurons that initiate movement. The upper segments of the spinal cord c ...
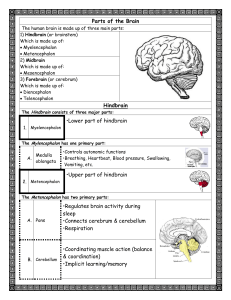
Parts of the Brain Hindbrain •Lower part of hindbrain •Upper part of
... •Regulates brain activity during sleep •Connects cerebrum & cerebellum •Respiration ...
... •Regulates brain activity during sleep •Connects cerebrum & cerebellum •Respiration ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.