Cognitive Handout 2 - Connecticut Speech-Language
... We refer to these changes as memories. Experiences are not “stored”; rather, they change the way we perceive, perform, think, and plan. They do so by physically changing the structure of the nervous system, altering neural circuits that participate in perceiving, performing, thinking, and planning. ...
... We refer to these changes as memories. Experiences are not “stored”; rather, they change the way we perceive, perform, think, and plan. They do so by physically changing the structure of the nervous system, altering neural circuits that participate in perceiving, performing, thinking, and planning. ...
The Nervous System
... Neurons are surrounded by a membrane. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". ...
... Neurons are surrounded by a membrane. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". ...
T/F
... T/F The human brain is larger than that of any other animal. T/F A single cell can stretch all the way from your spine to your toe. T/F Messages travel in the brain by means of electricity. T/F A brain cell can send out hundreds of messages each second, and manage to catch some rest in between. T/F ...
... T/F The human brain is larger than that of any other animal. T/F A single cell can stretch all the way from your spine to your toe. T/F Messages travel in the brain by means of electricity. T/F A brain cell can send out hundreds of messages each second, and manage to catch some rest in between. T/F ...
Learning and the Brain - Santa Clara County Office of
... Use the questions hand out in your take away packet. The person holding the picture needs to describe the picture to the person asking the questions. It is a lot more fun if only one of you has seen the picture. (The questioner will hopefully not see the picture.) Goal: Let us see how close you come ...
... Use the questions hand out in your take away packet. The person holding the picture needs to describe the picture to the person asking the questions. It is a lot more fun if only one of you has seen the picture. (The questioner will hopefully not see the picture.) Goal: Let us see how close you come ...
SBI4U - sheep brain dissection REVISED
... the meninges covers the surface of the cerebrum. This has been removed for you. However, note the remnants of the meninges. (b) Name the three membranes that make up the meninges. ...
... the meninges covers the surface of the cerebrum. This has been removed for you. However, note the remnants of the meninges. (b) Name the three membranes that make up the meninges. ...
Chapter Four
... the cerebral cortex; contains the primary visual cortex. Sensory association cortex – receives information from the primary sensory areas. Motor association cortex – those regions of the cerebral cortex that control the primary motor cortex; involved in planning and executing behaviors. Occipi ...
... the cerebral cortex; contains the primary visual cortex. Sensory association cortex – receives information from the primary sensory areas. Motor association cortex – those regions of the cerebral cortex that control the primary motor cortex; involved in planning and executing behaviors. Occipi ...
Bio101Lab13
... – Label parts of a spinal cord given either a silver stained micrograph, an illustration of the spinal cord, or a spinal cord model (use the two slides given here and learn those) – Be able to name the horns (ventral, dorsal, lateral) of the spinal cord and the TYPES of cells found in each horn (mot ...
... – Label parts of a spinal cord given either a silver stained micrograph, an illustration of the spinal cord, or a spinal cord model (use the two slides given here and learn those) – Be able to name the horns (ventral, dorsal, lateral) of the spinal cord and the TYPES of cells found in each horn (mot ...
BIO21012 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS)
... (c)connect areas between hemispheres (d)corpus callosum (4)association fibers (a)within hemispheres (5)projection fibers (a)leave brain to spinal cord (b)form ascending and descending tracts (6)decussation of the pyramids (a)crossing over of projection fibers so that right brain controls muscles on ...
... (c)connect areas between hemispheres (d)corpus callosum (4)association fibers (a)within hemispheres (5)projection fibers (a)leave brain to spinal cord (b)form ascending and descending tracts (6)decussation of the pyramids (a)crossing over of projection fibers so that right brain controls muscles on ...
Addiction and the Brain
... tiny gap, or synapse, to other neurons. Specialized molecules called receptors on the receiving neuron pick up the chemical. The branches on the receiving end of a neuron are called dendrites. Receptors there have special shapes so they can only collect one kind of neurotransmitter. In the dendrite, ...
... tiny gap, or synapse, to other neurons. Specialized molecules called receptors on the receiving neuron pick up the chemical. The branches on the receiving end of a neuron are called dendrites. Receptors there have special shapes so they can only collect one kind of neurotransmitter. In the dendrite, ...
Introducing Your Brain
... tiny gap, or synapse, to other neurons. Specialized molecules called receptors on the receiving neuron pick up the chemical. The branches on the receiving end of a neuron are called dendrites. Receptors there have special shapes so they can only collect one kind of neurotransmitter. In the dendrite, ...
... tiny gap, or synapse, to other neurons. Specialized molecules called receptors on the receiving neuron pick up the chemical. The branches on the receiving end of a neuron are called dendrites. Receptors there have special shapes so they can only collect one kind of neurotransmitter. In the dendrite, ...
Paleontology Zhurnal, 1965, No
... mould about 360-400 cc; consequently the volume of the brain itself was not more than 180-200 cc. This is a very small brain in comparison with the gigantic dimensions of the body. The brain is longitudinally prolate, S-shaped, so that the anterior part was higher than the posterior. The olfactory ...
... mould about 360-400 cc; consequently the volume of the brain itself was not more than 180-200 cc. This is a very small brain in comparison with the gigantic dimensions of the body. The brain is longitudinally prolate, S-shaped, so that the anterior part was higher than the posterior. The olfactory ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
Your Body Is Nothing Without A Brain
... young children, teenagers, and adults constantly placing themselves at risk of compromising their quality of life with a brain injury whose effects could be temporary, permanent, or delayed into the future? This author was able to solve the problem of paraplegic and quadriplegic injuries in young ch ...
... young children, teenagers, and adults constantly placing themselves at risk of compromising their quality of life with a brain injury whose effects could be temporary, permanent, or delayed into the future? This author was able to solve the problem of paraplegic and quadriplegic injuries in young ch ...
Exercises and Tests
... 1. Only glial cells make up the brain. TF 2. Glial cells transmit and receive electro signal to and from the brain. TF 3. The brain contains billions of neurons. TF 4. The number of glial cells is the same as the number of neurons. TF 5. All the neurons have the same size and length. TF 6. The neuro ...
... 1. Only glial cells make up the brain. TF 2. Glial cells transmit and receive electro signal to and from the brain. TF 3. The brain contains billions of neurons. TF 4. The number of glial cells is the same as the number of neurons. TF 5. All the neurons have the same size and length. TF 6. The neuro ...
Document
... The nervous system is one of the 2 control systems in our body. The nervous system is designed for fast action. It coordinates fast or rapid activities, such as muscle movement. Signaling is by electrical impulses, these are rapid, specific and produce an almost immediate response. ...
... The nervous system is one of the 2 control systems in our body. The nervous system is designed for fast action. It coordinates fast or rapid activities, such as muscle movement. Signaling is by electrical impulses, these are rapid, specific and produce an almost immediate response. ...
Nature Versus Nurture
... Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, which are specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks ...
... Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, which are specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks ...
November 13th Notes (Nervous System)
... Fatty protein that covers/insulates most nerves Increases speed of transmission Formed by Schwann cells ...
... Fatty protein that covers/insulates most nerves Increases speed of transmission Formed by Schwann cells ...
Slide ()
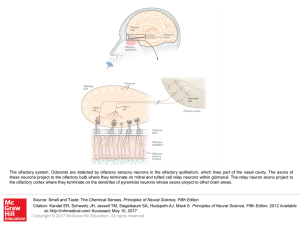
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Nervous System powerpoint new
... Some neurons contain the following additional parts: Myelin Sheath-a white fatty covering that insulates the axon. Schwann cells produce the myelin sheath – Schwann cells- a special kind of glial cell that produces a myelin sheath that wraps around the ...
... Some neurons contain the following additional parts: Myelin Sheath-a white fatty covering that insulates the axon. Schwann cells produce the myelin sheath – Schwann cells- a special kind of glial cell that produces a myelin sheath that wraps around the ...
File - Mr. Downing Biology 30
... Caption: Wearable computing. Male researcher using the prototype fingernail touch sensor he has developed. This affective computer detects each touch of the finger by the change it causes in the colour of the blood capillaries below the nail. Such a system could be used for buttonless controls, for ...
... Caption: Wearable computing. Male researcher using the prototype fingernail touch sensor he has developed. This affective computer detects each touch of the finger by the change it causes in the colour of the blood capillaries below the nail. Such a system could be used for buttonless controls, for ...
The Nervous System
... • Chemoreceptors respond to dissolved chemicals during sensations of taste and smell and to changes in internal body chemistry such as variations of O 2, CO 2, or H + in the blood. • Nociceptors respond to a variety of stimuli associated with tissue damage. The brain interprets the pain. ...
... • Chemoreceptors respond to dissolved chemicals during sensations of taste and smell and to changes in internal body chemistry such as variations of O 2, CO 2, or H + in the blood. • Nociceptors respond to a variety of stimuli associated with tissue damage. The brain interprets the pain. ...
Ch 3 – Biological Bases of Behavior
... 1. sensory neurons are located in the body’s sense organs (for example, the eye, ear, or nose) and send information from these organs to the brain 2. motor neurons– convey information from the nervous system to the body’s organs, glands, and muscles 3. interneurons (association neurons) transmit inf ...
... 1. sensory neurons are located in the body’s sense organs (for example, the eye, ear, or nose) and send information from these organs to the brain 2. motor neurons– convey information from the nervous system to the body’s organs, glands, and muscles 3. interneurons (association neurons) transmit inf ...
intro to psych ch3 biological bases of behavior
... Autonomic Nervous System: glands and organs; “automatic functions” ...
... Autonomic Nervous System: glands and organs; “automatic functions” ...
Neuro 16 Neurotransmitters Student
... May contribute to presence of uncontrolled involuntary movements. ...
... May contribute to presence of uncontrolled involuntary movements. ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.