Organization and Development of the Nervous System
... In PNS, there are mechanisms for creating collagen around the injury to act as a “bridge” for axons to grow along. ...
... In PNS, there are mechanisms for creating collagen around the injury to act as a “bridge” for axons to grow along. ...
File parts of the brain
... Amygdala- It just sounds scar y. “Amygdala” should be the name of a witch in a horror movie - controls aggression and fear Hippocampus: If you saw a “hippo” on “campus” you would remember involved in memor y Cerebral cor tex: cor tex is Latin for “shell” or “husk” - the cerebral cor tex is out ...
... Amygdala- It just sounds scar y. “Amygdala” should be the name of a witch in a horror movie - controls aggression and fear Hippocampus: If you saw a “hippo” on “campus” you would remember involved in memor y Cerebral cor tex: cor tex is Latin for “shell” or “husk” - the cerebral cor tex is out ...
Nervous System
... The Brain • Adult brain weighs approx. 1.4 kg (~3 lbs) and contains about 100 billion neurons • capable of carrying out many simultaneous operations • made of multiple lobes, parts ...
... The Brain • Adult brain weighs approx. 1.4 kg (~3 lbs) and contains about 100 billion neurons • capable of carrying out many simultaneous operations • made of multiple lobes, parts ...
Document
... 1993: Meeting on Neural Modeling and Functional Brain Imaging • Brought together modelers and functional brain imagers for the first time. • Tried to determine what research questions modelers could address • The four questions: – Relation between neural activity and imaging signals – Effective con ...
... 1993: Meeting on Neural Modeling and Functional Brain Imaging • Brought together modelers and functional brain imagers for the first time. • Tried to determine what research questions modelers could address • The four questions: – Relation between neural activity and imaging signals – Effective con ...
EQ2.5 - major divisions of the nervous system
... What are the major divisions of the nervous system, and what are their basic functions? The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system ...
... What are the major divisions of the nervous system, and what are their basic functions? The two major divisions of the nervous system are the central and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is divided in two parts : the brain and the spinal chord. The Peripheral nervous system ...
CHAPTER 13 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... - because the white matter tracts cross as they enter the brain... The right side of the brain senses and controls the left side of the body and vice versa ...
... - because the white matter tracts cross as they enter the brain... The right side of the brain senses and controls the left side of the body and vice versa ...
reduced size
... - They discovered that cutting the _______ roots produce sensory impairments while cutting the ______ roots produce motor deficits. - Gave rise to the notion that peripheral nerves are bundles of _____________________ that are either sensory or motor, but are generally mixed in peripheral nerves (we ...
... - They discovered that cutting the _______ roots produce sensory impairments while cutting the ______ roots produce motor deficits. - Gave rise to the notion that peripheral nerves are bundles of _____________________ that are either sensory or motor, but are generally mixed in peripheral nerves (we ...
Heidi
... • Consists of medulla, pons, and midbrain • Motor and sensory neurons travel through the brainstem allowing for the relay of signals between the brain and the spinal cord • Deals with breathing, arousal, alertness, blood pressure, digestion, and heart rate ...
... • Consists of medulla, pons, and midbrain • Motor and sensory neurons travel through the brainstem allowing for the relay of signals between the brain and the spinal cord • Deals with breathing, arousal, alertness, blood pressure, digestion, and heart rate ...
History and Methods
... – There is absolutely zero tolerance for cheating and plagiarism in this course. The syllabus contains important information on course and university policies. READ IT. – You must write in your own words. That means no wikipedia or web text. No copy and pasting, period. None. – It is your responsibi ...
... – There is absolutely zero tolerance for cheating and plagiarism in this course. The syllabus contains important information on course and university policies. READ IT. – You must write in your own words. That means no wikipedia or web text. No copy and pasting, period. None. – It is your responsibi ...
The Brain - Wando High School
... --Dendrites: part of the neuron that receives info. from the axon. --Axons: carries messages to dendrites of another neuron. --Synapse: junction point of two or more neurons. --Vesicles: bubble-like containers of neurotransmitters; located at ends of axons. --Neurotransmitters: chemicals in the ends ...
... --Dendrites: part of the neuron that receives info. from the axon. --Axons: carries messages to dendrites of another neuron. --Synapse: junction point of two or more neurons. --Vesicles: bubble-like containers of neurotransmitters; located at ends of axons. --Neurotransmitters: chemicals in the ends ...
Methods in Cognitive Neuroscience I
... Neurosurgery Methods • Direct cortical stimulation – Delivery of a small electric current directly on the cortical surface – Causes temporary disruption or facilitation of function in cortex being stimulated – Used clinically to map function, so that critical regions can be avoided during tissue re ...
... Neurosurgery Methods • Direct cortical stimulation – Delivery of a small electric current directly on the cortical surface – Causes temporary disruption or facilitation of function in cortex being stimulated – Used clinically to map function, so that critical regions can be avoided during tissue re ...
Silencing brain cells with
... Lab and an associate member of the McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT. Boyden’s super silencers are developed from two genes found in different natural organisms such as bacteria and fungi. These genes, called Arch and Mac, encode for light-activated proteins that help the organisms make e ...
... Lab and an associate member of the McGovern Institute for Brain Research at MIT. Boyden’s super silencers are developed from two genes found in different natural organisms such as bacteria and fungi. These genes, called Arch and Mac, encode for light-activated proteins that help the organisms make e ...
The Computational Brain
... Nowhere in nature does a more unbelievable entity exist than what is present in each human. This essential organ is responsible for all bodily and mental functions that neuroscientists and psychologist are learning more and more about each day. Can something so flawless be created? The quest for kno ...
... Nowhere in nature does a more unbelievable entity exist than what is present in each human. This essential organ is responsible for all bodily and mental functions that neuroscientists and psychologist are learning more and more about each day. Can something so flawless be created? The quest for kno ...
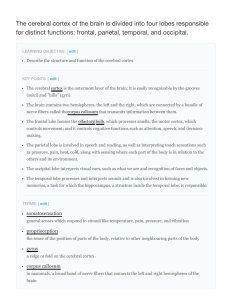
The cerebral cortex of the brain is divided into four lobes
... The parietal lobe is located at the top of the brain. Neurons in the parietal lobe are involved in speech and reading. Two of the parietal lobe's main functions are processing somatosensation(touch sensations such as pressure, pain, heat, cold) and processing proprioception (the sense of how parts o ...
... The parietal lobe is located at the top of the brain. Neurons in the parietal lobe are involved in speech and reading. Two of the parietal lobe's main functions are processing somatosensation(touch sensations such as pressure, pain, heat, cold) and processing proprioception (the sense of how parts o ...
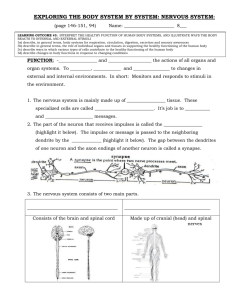
nervous system worksheet
... 3c) describe ways in which various types of cells contribute to the healthy functioning of the human body 3d) describe changes in body functions in response to changing conditions ...
... 3c) describe ways in which various types of cells contribute to the healthy functioning of the human body 3d) describe changes in body functions in response to changing conditions ...
Teacher Guide
... amygdala - part of the brain involved in processing the memory of emotional reactions, notably fear and anger (Sheep Brain Dissection) axon - the neuronal process that sends the signal or message away from the cell body toward target cells or neurons (Connect the Neurons, Close-up of the Nervous Sys ...
... amygdala - part of the brain involved in processing the memory of emotional reactions, notably fear and anger (Sheep Brain Dissection) axon - the neuronal process that sends the signal or message away from the cell body toward target cells or neurons (Connect the Neurons, Close-up of the Nervous Sys ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System and Brain Complete
... 1. Forebrain (= prosencephalon) (smell) 2. Midbrain (= mesencephalon) (vision) 3. Hindbrain (+ rhombencephalon) (hearing and balance) Different vertebrate groups have evolved different kinds of brains over time; Comparison of Vertebrate Brains – see Fig. 33.12 Basic organization of the brain (detail ...
... 1. Forebrain (= prosencephalon) (smell) 2. Midbrain (= mesencephalon) (vision) 3. Hindbrain (+ rhombencephalon) (hearing and balance) Different vertebrate groups have evolved different kinds of brains over time; Comparison of Vertebrate Brains – see Fig. 33.12 Basic organization of the brain (detail ...
nerves
... nerve ring. Within each arm, the radial nerve is linked to a nerve net from which it receives input and to which it sends signals controlling motor activity. ...
... nerve ring. Within each arm, the radial nerve is linked to a nerve net from which it receives input and to which it sends signals controlling motor activity. ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... The cerebral cortex For convenience sake, each hemisphere of the brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions. The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the cor ...
... The cerebral cortex For convenience sake, each hemisphere of the brain is often subdivided into four different lobes—or four different geographic regions. The cerebral cortex provides many functions for the body—some of these functions have been “localized” (i.e., the particular part of the cor ...
Unit10 Nervous Wk 1
... mark is level with the top of the forefinger. 2. Without warning, the first student drops the rule and the second student attempts to catch it between the thumb and forefinger, noting the distance on the ruler just above the forefinger. 3. Repeat several times, so that an average can be calculated. ...
... mark is level with the top of the forefinger. 2. Without warning, the first student drops the rule and the second student attempts to catch it between the thumb and forefinger, noting the distance on the ruler just above the forefinger. 3. Repeat several times, so that an average can be calculated. ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... • The membrane will repolarize when K+ leaves the cell setting the membrane back to resting potential or polarized • This de and repolarization continues down the nerve until it reaches another nerve to pass on the impulse or until it reaches an effector. ...
... • The membrane will repolarize when K+ leaves the cell setting the membrane back to resting potential or polarized • This de and repolarization continues down the nerve until it reaches another nerve to pass on the impulse or until it reaches an effector. ...
Chapter 19 The Neurological System
... A. Cerebrum- is the largest part of the brain (80%). It is divided into two layers and two halves (hemispheres). Each portion of the cerebrum has its own specialized function. a. Cerebral Cortex- points to the unique human abilities of learning, intelligent reasoning, and judgment. This is the outs ...
... A. Cerebrum- is the largest part of the brain (80%). It is divided into two layers and two halves (hemispheres). Each portion of the cerebrum has its own specialized function. a. Cerebral Cortex- points to the unique human abilities of learning, intelligent reasoning, and judgment. This is the outs ...
PAPER #3: EMBARGOED PRESS RELEASE STRICTLY UNDER
... between activation of the ventral subiculum (the brain's addiction center) and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons tha ...
... between activation of the ventral subiculum (the brain's addiction center) and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons tha ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.