Ch 2 Cognition & the Brain
... Caption: Basic components of the neuron. The one on the left contains a receptor, which is specialized to receive information from the environment (in this case, pressure that would occur from being touched on the skin). This neuron synapses on the neuron on the right, which has a cell body instead ...
... Caption: Basic components of the neuron. The one on the left contains a receptor, which is specialized to receive information from the environment (in this case, pressure that would occur from being touched on the skin). This neuron synapses on the neuron on the right, which has a cell body instead ...
WARM UP 3/4 - KENYON'S CLASS
... Physical symptoms such as muscle tension, involuntary teeth clenching, nausea, blurred vision, rapid eye movement, faintness, and chills or sweating. ...
... Physical symptoms such as muscle tension, involuntary teeth clenching, nausea, blurred vision, rapid eye movement, faintness, and chills or sweating. ...
The Nervous System - Appoquinimink High School
... ˃ Align along nerve fibers ˃ Provide the insulating layer of myelin – myelin sheath ...
... ˃ Align along nerve fibers ˃ Provide the insulating layer of myelin – myelin sheath ...
Read the perspective by Temel and Jahanshahi here.
... the mouse brain. Four weeks later, magnetic nanoparticles were injected into the same region, where they were detected in the extracellular space (whether they are internalized by any cell in vivo remains to be shown). Mice were then exposed to an external alternating magnetic field that caused the ...
... the mouse brain. Four weeks later, magnetic nanoparticles were injected into the same region, where they were detected in the extracellular space (whether they are internalized by any cell in vivo remains to be shown). Mice were then exposed to an external alternating magnetic field that caused the ...
DOC
... Neurons communicate using chemical messengers called NEUROTRANSMITTERS. A neuron sends an electrical signal that triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. Like a lock and key, the chemical attaches to a special receptor on another neuron. The message is sent. Some neurotransmitters tell the next n ...
... Neurons communicate using chemical messengers called NEUROTRANSMITTERS. A neuron sends an electrical signal that triggers the release of a neurotransmitter. Like a lock and key, the chemical attaches to a special receptor on another neuron. The message is sent. Some neurotransmitters tell the next n ...
CH. 2 (BIOLOGY)
... travels through the body and is absorbed by the organs and tissues being studied. Next, you will be asked to lie down on a flat examination table that is moved into the center of a PET scanner—a doughnut-like shaped machine. This machine detects and records the energy given off by the tracer substan ...
... travels through the body and is absorbed by the organs and tissues being studied. Next, you will be asked to lie down on a flat examination table that is moved into the center of a PET scanner—a doughnut-like shaped machine. This machine detects and records the energy given off by the tracer substan ...
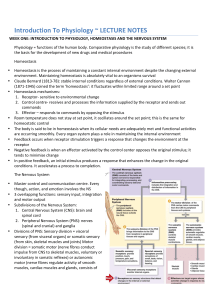
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
... (1871-‐1945) coined the term ‘homeostasis’: it fluctuates within limited range around a set point Homeostasis mechanisms: 1. Receptor-‐ sensitive to environmental change 2. Control centre-‐ receives and processes ...
Neurons
... Classification of Neurons • Classification based on Structural differences: • Bipolar neurons • Unipolar neurons • Multipolar neurons ...
... Classification of Neurons • Classification based on Structural differences: • Bipolar neurons • Unipolar neurons • Multipolar neurons ...
Reports Tab Components - Computer Science & Engineering
... Design Overview Conclusion and Future Work ...
... Design Overview Conclusion and Future Work ...
The Brain: It`s All In Your Mind
... changes in our environment and can be internal or external. ...
... changes in our environment and can be internal or external. ...
The Brain - Misty Cherie
... • Sends feedback signals to the motor cortex to regulate balance and posture • Monitors and coordinates complex skilled movements, such as speaking, dancing, juggling, riding a bicycle, skipping, flipping a pancake, playing a musical instrument, hitting a baseball, playing a video game, skating, etc ...
... • Sends feedback signals to the motor cortex to regulate balance and posture • Monitors and coordinates complex skilled movements, such as speaking, dancing, juggling, riding a bicycle, skipping, flipping a pancake, playing a musical instrument, hitting a baseball, playing a video game, skating, etc ...
The Nervous System - Primary Home Care
... The brain fits inside our skull and weighs about three pounds in an adult. The soft, wavy material we associate with the word brain is called the cerebrum or cerebral cortex. This is the largest part of the brain, and it controls all the functions associated with thinking and voluntary activity. Dec ...
... The brain fits inside our skull and weighs about three pounds in an adult. The soft, wavy material we associate with the word brain is called the cerebrum or cerebral cortex. This is the largest part of the brain, and it controls all the functions associated with thinking and voluntary activity. Dec ...
E.4 Neurotransmitters and Synapses
... cerebellum. •The basal ganglia controls unconscious muscle movements, which is another reason why motor coordination is impaired when under the influence of marijuana ...
... cerebellum. •The basal ganglia controls unconscious muscle movements, which is another reason why motor coordination is impaired when under the influence of marijuana ...
Neural Control II
... ligand-gated channels for Cl-, diffuses into neuron, makes the inside of the membrane more negative than it is at rest – Hyperpolarization; called an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) ...
... ligand-gated channels for Cl-, diffuses into neuron, makes the inside of the membrane more negative than it is at rest – Hyperpolarization; called an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) ...
The Nervous System- Nervous Tissue
... in the PNS creating a neurilemma around them. Neurilemma allows for potential regeneration of damaged axons • creates myelin sheath around most axons of PNS ...
... in the PNS creating a neurilemma around them. Neurilemma allows for potential regeneration of damaged axons • creates myelin sheath around most axons of PNS ...
Self as a function of the brain
... 3 souls: vegetative or plant soul (growth), an animal soul (response), philosopher’s soul (mind) – but these concepts lost their reference. Michał Heller: we had Galileo case, now Darwin, and sooner or later neuroscience case, theologians should not be satisfied with ...
... 3 souls: vegetative or plant soul (growth), an animal soul (response), philosopher’s soul (mind) – but these concepts lost their reference. Michał Heller: we had Galileo case, now Darwin, and sooner or later neuroscience case, theologians should not be satisfied with ...
Brain Anatomy
... Newer neural networks within the cerebrum – the two large hemispheres that contribute 85% of brain’s weight are associated with: Perceptions, Thinking, Speaking ...
... Newer neural networks within the cerebrum – the two large hemispheres that contribute 85% of brain’s weight are associated with: Perceptions, Thinking, Speaking ...
Brain
... Consists of sensory and motor neurons that transmit messages to and from the central nervous system Without the PNS, our brains would be isolated from the world ...
... Consists of sensory and motor neurons that transmit messages to and from the central nervous system Without the PNS, our brains would be isolated from the world ...
{ How Neurosciences help us to understand some (psycho)therapeutic processes
... During psychotherapy the “attachment quality” of the therapeutic relationship is critical. Experimental evidence suggests that secure attachment, is associated with reduction in amygdala firing (lessening anxiety) and increases in nucleus accumbens activity (possibly related to enhanced reward repr ...
... During psychotherapy the “attachment quality” of the therapeutic relationship is critical. Experimental evidence suggests that secure attachment, is associated with reduction in amygdala firing (lessening anxiety) and increases in nucleus accumbens activity (possibly related to enhanced reward repr ...
The Nervous System
... • d) Know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting impulses • e) Know the role of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation, thought, and response ...
... • d) Know the functions of the nervous system and the role of neurons in transmitting impulses • e) Know the role of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation, thought, and response ...
Nervous system - Lancaster High School
... 3 divisions in vertebrates (embryo) Hindbrain Cerebellum, medulla oblongata, pons Midbrain Forebrain Cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, limbic system ...
... 3 divisions in vertebrates (embryo) Hindbrain Cerebellum, medulla oblongata, pons Midbrain Forebrain Cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, limbic system ...
Document
... Even infants who receive sterilized formula suffer from more meningitis and infection of the gut, ear, respiratory tract and urinary tract than do breast-fed youngsters ...
... Even infants who receive sterilized formula suffer from more meningitis and infection of the gut, ear, respiratory tract and urinary tract than do breast-fed youngsters ...
biology lecture notes chapter 2
... of depolarization, an action potential occurs. VISUAL: Hold up Electrical wire—similarities to axon (insulation, send electrical impulse) and the main difference: no continuous signals/bursts of activity with periods to reset the chemicals involved Student activity—complete the map of the neuron by ...
... of depolarization, an action potential occurs. VISUAL: Hold up Electrical wire—similarities to axon (insulation, send electrical impulse) and the main difference: no continuous signals/bursts of activity with periods to reset the chemicals involved Student activity—complete the map of the neuron by ...
Brain

The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. Only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain; diffuse or localised nerve nets are present instead. The brain is located in the head, usually close to the primary sensory organs for such senses as vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell. The brain is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a typical human, the cerebral cortex (the largest part) is estimated to contain 15–33 billion neurons, each connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons communicate with one another by means of long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells.Physiologically, the function of the brain is to exert centralized control over the other organs of the body. The brain acts on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated responses to changes in the environment. Some basic types of responsiveness such as reflexes can be mediated by the spinal cord or peripheral ganglia, but sophisticated purposeful control of behavior based on complex sensory input requires the information integrating capabilities of a centralized brain.The operations of individual brain cells are now understood in considerable detail but the way they cooperate in ensembles of millions is yet to be solved. Recent models in modern neuroscience treat the brain as a biological computer, very different in mechanism from an electronic computer, but similar in the sense that it acquires information from the surrounding world, stores it, and processes it in a variety of ways, analogous to the central processing unit (CPU) in a computer.This article compares the properties of brains across the entire range of animal species, with the greatest attention to vertebrates. It deals with the human brain insofar as it shares the properties of other brains. The ways in which the human brain differs from other brains are covered in the human brain article. Several topics that might be covered here are instead covered there because much more can be said about them in a human context. The most important is brain disease and the effects of brain damage, covered in the human brain article because the most common diseases of the human brain either do not show up in other species, or else manifest themselves in different ways.