Biology 232
... odorants bind to receptors on olfactory cilia, which produce receptor potentials threshold potential produces an action potential, which propagates along the olfactory nerve, through cribriform plate (olfactory threshold is low – as little as 4 odorant molecules) olfactory nerves (cranial nerve I) s ...
... odorants bind to receptors on olfactory cilia, which produce receptor potentials threshold potential produces an action potential, which propagates along the olfactory nerve, through cribriform plate (olfactory threshold is low – as little as 4 odorant molecules) olfactory nerves (cranial nerve I) s ...
The Psychopathology of Pain
... Glia-Neuron Interaction • Toll-Like Receptors (TLR2 and TLR4) – Innate immune receptors that respond to diverse pathogens and pathogen- or damage-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs & DAMPs) as well as endogenous signals such as IL-1b, TNFα, IL-6 and nitric oxide – Activation of TLRs results in imm ...
... Glia-Neuron Interaction • Toll-Like Receptors (TLR2 and TLR4) – Innate immune receptors that respond to diverse pathogens and pathogen- or damage-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs & DAMPs) as well as endogenous signals such as IL-1b, TNFα, IL-6 and nitric oxide – Activation of TLRs results in imm ...
Neuroanatomy Part 2
... cells or synapse directly with the ganglion cells. Step Five: The ganglion depolarizes and initiates a nerve impulse. Step Six: The nerve impulses are passed on the optic nerve and the pulse travels to the thalamus. Step Seven: The thalamus relays the impulse to the occipital lobe where the image is ...
... cells or synapse directly with the ganglion cells. Step Five: The ganglion depolarizes and initiates a nerve impulse. Step Six: The nerve impulses are passed on the optic nerve and the pulse travels to the thalamus. Step Seven: The thalamus relays the impulse to the occipital lobe where the image is ...
A Prelude to AChemS XXIX
... of the symposium is how olfactory bulb output is translated into an integrated olfactory perception. It brings together multidisciplinary, comparative approaches to the basic questions of odor perception and memory. Neural coding in the chemical senses: This symposium will focus on gustatory and o ...
... of the symposium is how olfactory bulb output is translated into an integrated olfactory perception. It brings together multidisciplinary, comparative approaches to the basic questions of odor perception and memory. Neural coding in the chemical senses: This symposium will focus on gustatory and o ...
Neuro Physiology 1
... A synapse is the anatomical site where nerve cells communicate with other nerves, muscle and glands. There are two types which have been identified, either a chemical or electrical synapse. In electrical synapses, the membranes of the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons come close together, and gap ...
... A synapse is the anatomical site where nerve cells communicate with other nerves, muscle and glands. There are two types which have been identified, either a chemical or electrical synapse. In electrical synapses, the membranes of the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons come close together, and gap ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... • Afferent (Sensory) Neurons carry messages from tissues and sensory organs to the brain and spinal cord for processing ...
... • Afferent (Sensory) Neurons carry messages from tissues and sensory organs to the brain and spinal cord for processing ...
Visual Field - Warren`s Science Page
... Receptor axons lead into one of two olfactory bulbs In these small brain structures, axons synapse with cells that sort out scent Then, information flows along olfactory tract to cerebrum, where further processed ...
... Receptor axons lead into one of two olfactory bulbs In these small brain structures, axons synapse with cells that sort out scent Then, information flows along olfactory tract to cerebrum, where further processed ...
PDF
... During early development, embryonic cells can form derivatives of all three embryonic layers. This pluripotency, which is regulated by a gene regulatory network that includes the transcription factors Oct4 and Nanog, is lost in mouse embryos between about E7.5 and E8.5. Here (p. 2288), Rodrigo Osorn ...
... During early development, embryonic cells can form derivatives of all three embryonic layers. This pluripotency, which is regulated by a gene regulatory network that includes the transcription factors Oct4 and Nanog, is lost in mouse embryos between about E7.5 and E8.5. Here (p. 2288), Rodrigo Osorn ...
Synapses and neurotransmitters
... • Allows flow of ions from one neuron to another • Bi directional • Used when you need very fast reaction, say for defensive beahviour, that sort of thing • No receptor or binding site, but a connexon ...
... • Allows flow of ions from one neuron to another • Bi directional • Used when you need very fast reaction, say for defensive beahviour, that sort of thing • No receptor or binding site, but a connexon ...
Neurons - Holterman
... 4. The sodium-potassium pump pushes 3 Na and 2 K against their concentration gradients using 1 ATP. It restores and maintains the resting potential by pushing more Na out of neuron and pushing more K into neuron. (But overall, it pushes more positive charges out of the cell than it brings in.) 5. T ...
... 4. The sodium-potassium pump pushes 3 Na and 2 K against their concentration gradients using 1 ATP. It restores and maintains the resting potential by pushing more Na out of neuron and pushing more K into neuron. (But overall, it pushes more positive charges out of the cell than it brings in.) 5. T ...
Nervous System Communication
... effector cells • Nerve impulse must cross gap (electrical signal is changed to a chemical signal) ...
... effector cells • Nerve impulse must cross gap (electrical signal is changed to a chemical signal) ...
nuclear receptors - SBI
... • Nuclear receptors are soluble proteins that can bind to specific DNA regulatory elements (response elements or REs) and act as cell typeand promoter-specific regulators of transcription. • In contrast to other transcription factors, the activity of nuclear receptors can be modulated by binding to ...
... • Nuclear receptors are soluble proteins that can bind to specific DNA regulatory elements (response elements or REs) and act as cell typeand promoter-specific regulators of transcription. • In contrast to other transcription factors, the activity of nuclear receptors can be modulated by binding to ...
4/12 - bio.utexas.edu
... At the synapse the electrical signal is converted to a chemical signal: ...
... At the synapse the electrical signal is converted to a chemical signal: ...
Ch 49 Pract Test Nervous System
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
Nervous System
... 1. The diagram below is of a nerve cell or neuron. i. Add the following labels to the diagram. Axon; Myelin sheath; Cell body; Dendrites; Muscle fibers; ii. If you like, colour in the diagram as suggested below. Axon - purple; Myelin sheath - yellow; Cell body - blue; ...
... 1. The diagram below is of a nerve cell or neuron. i. Add the following labels to the diagram. Axon; Myelin sheath; Cell body; Dendrites; Muscle fibers; ii. If you like, colour in the diagram as suggested below. Axon - purple; Myelin sheath - yellow; Cell body - blue; ...
The Nervous System
... impulses away from the cell body is the axon – Ends in a series of small areas called axon terminals – Some axons have an insulating membrane called the myelin sheath • The sheath leaves exposed parts of the axon called nodes where a nerve impulse can “jump” from one node to the next ...
... impulses away from the cell body is the axon – Ends in a series of small areas called axon terminals – Some axons have an insulating membrane called the myelin sheath • The sheath leaves exposed parts of the axon called nodes where a nerve impulse can “jump” from one node to the next ...
Quiz 6 study guide
... consistent with neuron A releasing GABA as its neurotransmitter? Why or why not? b. If neuron A fires a second action potential shortly after its first one, neuron E does not fire a second action potential. Why not? c. If neuron D is firing action potentials, neuron E will not fire action potentials ...
... consistent with neuron A releasing GABA as its neurotransmitter? Why or why not? b. If neuron A fires a second action potential shortly after its first one, neuron E does not fire a second action potential. Why not? c. If neuron D is firing action potentials, neuron E will not fire action potentials ...
CHAPTER10B
... www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/histology/slide.php?image_name=myelin&slide_file=images/histology/nervous_tissue/display/schwann3.jpg&image_id=1058 ...
... www.mc.vanderbilt.edu/histology/slide.php?image_name=myelin&slide_file=images/histology/nervous_tissue/display/schwann3.jpg&image_id=1058 ...
Chp 7 (part 1)
... 5. Found in sensory neurons in PNS ganglia 7. Physiology a. Neurons have 2 major functional Properties 1. Irritability: ability to respond to a stimulus 2. Conductivity: ability to transmit an impulse b. Polarized: a resting neuron with fewer + ions inside its membrane than outside 1. Mainly K+ insi ...
... 5. Found in sensory neurons in PNS ganglia 7. Physiology a. Neurons have 2 major functional Properties 1. Irritability: ability to respond to a stimulus 2. Conductivity: ability to transmit an impulse b. Polarized: a resting neuron with fewer + ions inside its membrane than outside 1. Mainly K+ insi ...
The Neuron: Building Block of the Nervous System
... Synaptic Transmission Synaptic Transmission – Sequence of events in which ...
... Synaptic Transmission Synaptic Transmission – Sequence of events in which ...
Chp 8 the senses
... •Sclera = White connective tissue layer seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” •Cornea –Transparent, central anterior portion –Allows for light to pass through –Repairs itself easily –The only human tissue that can be transplanted without fear of rejection Choroid Layer •Blood-rich nutritive tuni ...
... •Sclera = White connective tissue layer seen anteriorly as the “white of the eye” •Cornea –Transparent, central anterior portion –Allows for light to pass through –Repairs itself easily –The only human tissue that can be transplanted without fear of rejection Choroid Layer •Blood-rich nutritive tuni ...
CASE 45
... protein, gustducin, which stimulates phosphodiesterase and decreases cAMP and cyclic guanine monophosphate (cGMP) levels. In these cells cAMP and cGMP lead to hyperpolarization, and so their degradation produces depolarization. In addition, other G protein-coupled receptors stimulate the IP3 pathway ...
... protein, gustducin, which stimulates phosphodiesterase and decreases cAMP and cyclic guanine monophosphate (cGMP) levels. In these cells cAMP and cGMP lead to hyperpolarization, and so their degradation produces depolarization. In addition, other G protein-coupled receptors stimulate the IP3 pathway ...
NMSI - 1 Intro to the Nervous System
... reading the question and ending with marking an answer. a. interneurons motor neurons sensory neurons effectors b. effectors sensory neurons interneurons motor neurons c. sensory neurons interneurons motor neurons effectors d. interneurons sensory neurons motor neurons effect ...
... reading the question and ending with marking an answer. a. interneurons motor neurons sensory neurons effectors b. effectors sensory neurons interneurons motor neurons c. sensory neurons interneurons motor neurons effectors d. interneurons sensory neurons motor neurons effect ...
Slide ()
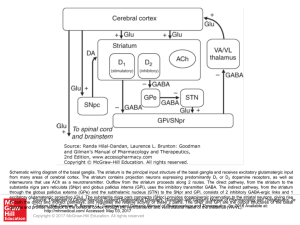
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...