administering-medications-7th-edition-donna-gauwitz
... Take a field trip to a pharmaceutical company in your area to observe the step-by-step process of manufacturing drugs. Ask students to summarize why, as health care workers, they should understand the drug manufacturing process. Discuss how the company followed drug legislation. Invite a pharmac ...
... Take a field trip to a pharmaceutical company in your area to observe the step-by-step process of manufacturing drugs. Ask students to summarize why, as health care workers, they should understand the drug manufacturing process. Discuss how the company followed drug legislation. Invite a pharmac ...
Chapter 5 Quantitative and Thought Questions 5.1 Patient A`s drug
... of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Therefore, the drug must be acting at a point beyond this kinase (e.g., at the level of the phosphorylated protein mediating this response). 5.4 Not in most cells, because there are other physiological mechanisms by which signals impinging on the cell can increase c ...
... of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Therefore, the drug must be acting at a point beyond this kinase (e.g., at the level of the phosphorylated protein mediating this response). 5.4 Not in most cells, because there are other physiological mechanisms by which signals impinging on the cell can increase c ...
DRUG INTERACTIONS AND ANESTHESIA
... preparations that increase tolerance to mental exhaustion and enhance attention and mental endurance in situations of decreased performance The key point of action of phytoadaptogens appears to be their upregulating and stress-mimetic effects on the "stress-sensor" protein Hsp70, which plays an imp ...
... preparations that increase tolerance to mental exhaustion and enhance attention and mental endurance in situations of decreased performance The key point of action of phytoadaptogens appears to be their upregulating and stress-mimetic effects on the "stress-sensor" protein Hsp70, which plays an imp ...
ROUTES OF DRUG ADMINISTRATION
... membranes and the liver, for the first time, during the absorption process after oral administration. This is also known PreSystemic elimination. h) Drugs interaction may occur if two drugs are given cocurrently. ...
... membranes and the liver, for the first time, during the absorption process after oral administration. This is also known PreSystemic elimination. h) Drugs interaction may occur if two drugs are given cocurrently. ...
click here for presentation
... • Discuss new medications and their impact on the elderly • Discuss new medications, adverse effects, or restrictions for the general population ...
... • Discuss new medications and their impact on the elderly • Discuss new medications, adverse effects, or restrictions for the general population ...
Psychopharmacology
... Down regulated DA system may require antidepressant drugs Lethargy has to be waited out Cold turkey is difficult because of cravings, but ...
... Down regulated DA system may require antidepressant drugs Lethargy has to be waited out Cold turkey is difficult because of cravings, but ...
Protease inhibitors in chronic hepatitis C
... The Canadian Liver Foundation (CLF) was the first organization in the world devoted to providing support for research and education into the causes, diagnoses, prevention and treatment of all liver disease. Through its chapters across the country, the CLF strives to promote liver health, improve pub ...
... The Canadian Liver Foundation (CLF) was the first organization in the world devoted to providing support for research and education into the causes, diagnoses, prevention and treatment of all liver disease. Through its chapters across the country, the CLF strives to promote liver health, improve pub ...
Drugs - Kaleem Rasheed
... the last month and 20% had used illegal drugs in the last year • 13% of boys reported taking drugs in the last month compared to 11% of girls • Use increased with age. Six percent of 11-year-olds had used drugs in the last year compared to 39% of 15-year-olds ...
... the last month and 20% had used illegal drugs in the last year • 13% of boys reported taking drugs in the last month compared to 11% of girls • Use increased with age. Six percent of 11-year-olds had used drugs in the last year compared to 39% of 15-year-olds ...
COMPLICATIONS AND MANAGEMENT 14 JULY 2010
... Patients rarely develop chronic liver disease after an acute severe DILI. Patients with cholestatic/mixed liver disease were more prone to developing chronic injury (9%), than those with the hepatocellular form ...
... Patients rarely develop chronic liver disease after an acute severe DILI. Patients with cholestatic/mixed liver disease were more prone to developing chronic injury (9%), than those with the hepatocellular form ...
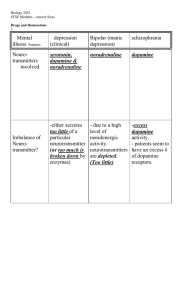
Drugs and Homeostasis STSE Answers File
... - give patients better quality of life - control of symptoms while research for a cure continues ...
... - give patients better quality of life - control of symptoms while research for a cure continues ...
Atenolol bisoprolol conversion
... The team at eInformatics are Medinformatix EHR and RIS experts! From workflow to reporting, from Quality Payment Programs to optical shop. Bisoprolol Fumarate 2.5 mg, 5 mg & 10 mg Tablets - Patient Information Leaflet (PIL) by Actavis UK Ltd The recommendation for first-line therapy for hypertension ...
... The team at eInformatics are Medinformatix EHR and RIS experts! From workflow to reporting, from Quality Payment Programs to optical shop. Bisoprolol Fumarate 2.5 mg, 5 mg & 10 mg Tablets - Patient Information Leaflet (PIL) by Actavis UK Ltd The recommendation for first-line therapy for hypertension ...
UNESCO Course on Benefit and Harm CASE STUDY: USE OF NEW
... The drug is not generally recognized by qualified experts as a safe and effective cancer drug, but various proponents of the drug have claimed that it can cure or control the spread of cancer, or at least can mitigate the symptoms of the disease without curing it. This drug has not been approved by ...
... The drug is not generally recognized by qualified experts as a safe and effective cancer drug, but various proponents of the drug have claimed that it can cure or control the spread of cancer, or at least can mitigate the symptoms of the disease without curing it. This drug has not been approved by ...
Herbal Remedies and Drug Interactions
... two hours after taking other meds. Concurrent use with laxatives and stool softeners should be avoided because of possible potentiation of the laxative effect. ...
... two hours after taking other meds. Concurrent use with laxatives and stool softeners should be avoided because of possible potentiation of the laxative effect. ...
Answers
... 10) Both Ranitidine and Lansoprazole are used to reduce stomach acid production. (15) a) How do these drugs work (explain the mechanism)? b) Which drug is likely to be more effective (explain your conclusion!)? Ranitidine is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist which inhibits histamine-induced gastric ...
... 10) Both Ranitidine and Lansoprazole are used to reduce stomach acid production. (15) a) How do these drugs work (explain the mechanism)? b) Which drug is likely to be more effective (explain your conclusion!)? Ranitidine is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist which inhibits histamine-induced gastric ...
Virtual Screening in Drug Discovery: an Overview
... and leads compounds • Most drugs work by interacting with a protein/DNA at a specific target site. • Drug molecules need to (1) bind tightly to the target site (affinity) and exert the desired activity (potency) (2) have minimal off-target binding (side effects/toxicity) (3 ) can get to the target s ...
... and leads compounds • Most drugs work by interacting with a protein/DNA at a specific target site. • Drug molecules need to (1) bind tightly to the target site (affinity) and exert the desired activity (potency) (2) have minimal off-target binding (side effects/toxicity) (3 ) can get to the target s ...
Tuberculosis
... drugs should never be given alone! They are always used in combination because resistance occurs to one drug alone very rapidly. They are used in combination with each other initially as well as other drugs. Bacilli must become resistant to two drugs in order to remain viable. Statistically, the cha ...
... drugs should never be given alone! They are always used in combination because resistance occurs to one drug alone very rapidly. They are used in combination with each other initially as well as other drugs. Bacilli must become resistant to two drugs in order to remain viable. Statistically, the cha ...
Pharmacology Jeopardy Part 1
... – Occurs in sulfonamides and other drugs that are normally highly bound to albumin in adults ...
... – Occurs in sulfonamides and other drugs that are normally highly bound to albumin in adults ...
dose-response and dose-effect relationships
... dose-response and dose-effect relationships The graph of the relation between dose and the proportion of individuals responding with an all-or-none effect; it is essentially the graph of the probability of an occurrence (or the proportion of a population exhibiting an effect) against dose. Typical e ...
... dose-response and dose-effect relationships The graph of the relation between dose and the proportion of individuals responding with an all-or-none effect; it is essentially the graph of the probability of an occurrence (or the proportion of a population exhibiting an effect) against dose. Typical e ...
drug effects - Grand Saline ISD
... • A receptor is a protein molecule on the surface of or within a cell that recognizes and binds with specific molecules, thereby producing some effect within the cell. – receptor site may have specificity – the affinity is the strength by which a particular chemical messenger binds to its receptor s ...
... • A receptor is a protein molecule on the surface of or within a cell that recognizes and binds with specific molecules, thereby producing some effect within the cell. – receptor site may have specificity – the affinity is the strength by which a particular chemical messenger binds to its receptor s ...
Pharmacokinetics
... • Drug factors include drug solubility, pH, and molecular size • Patient factors include the animal’s age, health, metabolic rate, genetic factors, sex, and species ...
... • Drug factors include drug solubility, pH, and molecular size • Patient factors include the animal’s age, health, metabolic rate, genetic factors, sex, and species ...
Pharm II-Ch 8-PPT
... • PEOPLE TRAVELING TO AN AREA WHERE MALARIA IS ENDEMIC • PATIENTS WHO ARE UNDERGOING GI OR GENITOURINARY SURGERY • PATIENTS WITH KNOWN CARDIAC VALVE DISEASE, VALVE REPLACEMENTS, AND OTHER CONDITIONS REQUIRING INVASIVE PROCEDURES ...
... • PEOPLE TRAVELING TO AN AREA WHERE MALARIA IS ENDEMIC • PATIENTS WHO ARE UNDERGOING GI OR GENITOURINARY SURGERY • PATIENTS WITH KNOWN CARDIAC VALVE DISEASE, VALVE REPLACEMENTS, AND OTHER CONDITIONS REQUIRING INVASIVE PROCEDURES ...
Sedative-Hypnotics
... Benzodiazepines is a class of drugs that have an effect on the brain that, in turn, induces sleep and causes feelings of relief, relaxation and a state of euphoria. Benzodiazepines should only be taken as prescribed by your physician. Although this class of drugs is one of the safest classes of pres ...
... Benzodiazepines is a class of drugs that have an effect on the brain that, in turn, induces sleep and causes feelings of relief, relaxation and a state of euphoria. Benzodiazepines should only be taken as prescribed by your physician. Although this class of drugs is one of the safest classes of pres ...
Drug interaction

A drug interaction is a situation in which a substance (usually another drug) affects the activity of a drug when both are administered together. This action can be synergistic (when the drug's effect is increased) or antagonistic (when the drug's effect is decreased) or a new effect can be produced that neither produces on its own. Typically, interactions between drugs come to mind (drug-drug interaction). However, interactions may also exist between drugs and foods (drug-food interactions), as well as drugs and medicinal plants or herbs (drug-plant interactions). People taking antidepressant drugs such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors should not take food containing tyramine as hypertensive crisis may occur (an example of a drug-food interaction). These interactions may occur out of accidental misuse or due to lack of knowledge about the active ingredients involved in the relevant substances.It is therefore easy to see the importance of these pharmacological interactions in the practice of medicine. If a patient is taking two drugs and one of them increases the effect of the other it is possible that an overdose may occur. The interaction of the two drugs may also increase the risk that side effects will occur. On the other hand, if the action of a drug is reduced it may cease to have any therapeutic use because of under dosage. Notwithstanding the above, on occasion these interactions may be sought in order to obtain an improved therapeutic effect. Examples of this include the use of codeine with paracetamol to increase its analgesic effect. Or the combination of clavulanic acid with amoxicillin in order to overcome bacterial resistance to the antibiotic. It should also be remembered that there are interactions that, from a theoretical standpoint, may occur but in clinical practice have no important repercussions.The pharmaceutical interactions that are of special interest to the practice of medicine are primarily those that have negative effects for an organism. The risk that a pharmacological interaction will appear increases as a function of the number of drugs administered to a patient at the same time.It is possible that an interaction will occur between a drug and another substance present in the organism (i.e. foods or alcohol). Or in certain specific situations a drug may even react with itself, such as occurs with dehydration. In other situations, the interaction does not involve any effect on the drug. In certain cases, the presence of a drug in an individual's blood may affect certain types of laboratory analysis (analytical interference).It is also possible for interactions to occur outside an organism before administration of the drugs has taken place. This can occur when two drugs are mixed, for example, in a saline solution prior to intravenous injection. Some classic examples of this type of interaction include that Thiopentone and Suxamethonium should not be placed in the same syringe and same is true for Benzylpenicillin and Heparin. These situations will all be discussed under the same heading due to their conceptual similarity.Drug interactions may be the result of various processes. These processes may include alterations in the pharmacokinetics of the drug, such as alterations in the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of a drug. Alternatively, drug interactions may be the result of the pharmacodynamic properties of the drug, e.g. the co-administration of a receptor antagonist and an agonist for the same receptor.