Current, Resistance and Circuits
... copper wire are in random motion at speeds of the order of 106 m/s. If you pass a hypothetical plane through such a wire, conduction electrons pass through it in both directions at the rate of many billions per second—but there is no net transport of charge and thus no current through the wire. Howe ...
... copper wire are in random motion at speeds of the order of 106 m/s. If you pass a hypothetical plane through such a wire, conduction electrons pass through it in both directions at the rate of many billions per second—but there is no net transport of charge and thus no current through the wire. Howe ...
Calculate Inductor AC Flux Density
... To determine which formula to use, consider what contributes to flux in the core. When the inductance is the primary of a transformer (1) should be used (this includes current transformers 1). The only flux in the core of a transformer is due to the magnetizing current arising from the primary volta ...
... To determine which formula to use, consider what contributes to flux in the core. When the inductance is the primary of a transformer (1) should be used (this includes current transformers 1). The only flux in the core of a transformer is due to the magnetizing current arising from the primary volta ...
File
... series with an ammeter and a 3 V battery. The ammeter reading is 0.15 A. (a) Determine the resistance of the wire. (b) The length of the wire is doubled and its cross-sectional area halved. Determine the new resistance and hence ...
... series with an ammeter and a 3 V battery. The ammeter reading is 0.15 A. (a) Determine the resistance of the wire. (b) The length of the wire is doubled and its cross-sectional area halved. Determine the new resistance and hence ...
Manufacturing Processes - Philadelphia University Jordan
... grains; such materials are termed polycrystalline. Various stages in the solidification of a polycrystalline specimen are represented schematically in Fig. 2-20. Initially, small crystals or nuclei form at various positions. These have random crystallographic orientations, as indicated by the square ...
... grains; such materials are termed polycrystalline. Various stages in the solidification of a polycrystalline specimen are represented schematically in Fig. 2-20. Initially, small crystals or nuclei form at various positions. These have random crystallographic orientations, as indicated by the square ...
Introduction to Semiconductor Devices
... (d) For each doping level in (a) vary temperature (T) from 200 K to 500K. (e) For each doping level in (b) vary temperature (T) from 200K to 500K. (f) Plot μn vs T and μp vs T at different doping levels. Why does mobility increase with decreasing temperature? Concept: Diffusion Q3) Consider a Si sla ...
... (d) For each doping level in (a) vary temperature (T) from 200 K to 500K. (e) For each doping level in (b) vary temperature (T) from 200K to 500K. (f) Plot μn vs T and μp vs T at different doping levels. Why does mobility increase with decreasing temperature? Concept: Diffusion Q3) Consider a Si sla ...
Name___________________________________ February 15
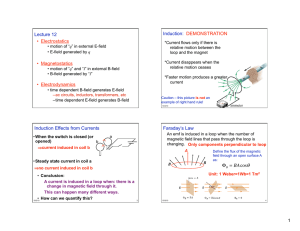
... 19. One of the advantages of an electromagnet over a bar magnet is that an electromagnet a) can easily be turned on and off. b) can be moved from place to place. c) has no magnetic field. d) has a north pole and a south pole. ...
... 19. One of the advantages of an electromagnet over a bar magnet is that an electromagnet a) can easily be turned on and off. b) can be moved from place to place. c) has no magnetic field. d) has a north pole and a south pole. ...
Conductors
... Also, if the surface is an equipotential (from 4), then, since gradient of V, it is perpendicular to surface ...
... Also, if the surface is an equipotential (from 4), then, since gradient of V, it is perpendicular to surface ...
Metallic Crystal Structure
... electrons; furthermore, the nature of the bond depends on the electron structures of the constituent atoms. Secondary or physical forces and energies are also found in many solid materials; they are weaker than the primary ones, but nonetheless influence the physical properties of some materials. Me ...
... electrons; furthermore, the nature of the bond depends on the electron structures of the constituent atoms. Secondary or physical forces and energies are also found in many solid materials; they are weaker than the primary ones, but nonetheless influence the physical properties of some materials. Me ...
N - PembyPhysics
... magnetic field. These currents produce an undesirable by-product—heat in the iron. Energy loss in a transformer can be reduced by using thinner laminations, very “soft” (low-carbon) iron and wire with a larger cross section, or by winding the primary and secondary circuits with conductors that have ...
... magnetic field. These currents produce an undesirable by-product—heat in the iron. Energy loss in a transformer can be reduced by using thinner laminations, very “soft” (low-carbon) iron and wire with a larger cross section, or by winding the primary and secondary circuits with conductors that have ...
lecture 29 motional emf
... a wingspan of L = 39.9 m and flies at constant altitude in a northerly direction with a speed of v = 240 m/s. If the vertical component of the Earth’s magnetic field is Bv = 5.0 × 10-6 T, and its horizontal component is Bh = 1.4 × 10-6 T, what is the induced emf between the wing ...
... a wingspan of L = 39.9 m and flies at constant altitude in a northerly direction with a speed of v = 240 m/s. If the vertical component of the Earth’s magnetic field is Bv = 5.0 × 10-6 T, and its horizontal component is Bh = 1.4 × 10-6 T, what is the induced emf between the wing ...
Document
... the induced emf. If a blood vessel is 2 mm in diameter and a 0.08 T magnetic field causes an induced emf of 0.1 mv, what is the flow velocity of the blood? OSE: = B ℓ v v = / (B ℓ) In Figure 21-11 (the figure for this example), B is applied to the blood vessel, so B is to v. The ions flow ...
... the induced emf. If a blood vessel is 2 mm in diameter and a 0.08 T magnetic field causes an induced emf of 0.1 mv, what is the flow velocity of the blood? OSE: = B ℓ v v = / (B ℓ) In Figure 21-11 (the figure for this example), B is applied to the blood vessel, so B is to v. The ions flow ...
Electromigration

Electromigration is the transport of material caused by the gradual movement of the ions in a conductor due to the momentum transfer between conducting electrons and diffusing metal atoms. The effect is important in applications where high direct current densities are used, such as in microelectronics and related structures. As the structure size in electronics such as integrated circuits (ICs) decreases, the practical significance of this effect increases.