Lecture 5 - Course Notes
... • In addition, NaCl will also have certain intrinsic sodium and chlorine vacancy concentration (VNa′ and VCl•) due to Schottky dissociation, depending on the temperature. ΔGNa* is the migration free energy for sodium vacancies [VNa‘] is the sodium vacancy concentration ...
... • In addition, NaCl will also have certain intrinsic sodium and chlorine vacancy concentration (VNa′ and VCl•) due to Schottky dissociation, depending on the temperature. ΔGNa* is the migration free energy for sodium vacancies [VNa‘] is the sodium vacancy concentration ...
conductivity and resistance
... 2a. Definition of Drift Velocity. The charge carrier drift velocity in a conducting material is proportional to the applied electric field strength. We can picture a conducting material as a “lattice” of atoms within which charge carrying particles (conduction electrons) move with a thermal distribu ...
... 2a. Definition of Drift Velocity. The charge carrier drift velocity in a conducting material is proportional to the applied electric field strength. We can picture a conducting material as a “lattice” of atoms within which charge carrying particles (conduction electrons) move with a thermal distribu ...
Electric Fields in Materials - UAH Department of Electrical and
... In reality metals are very good conductors in which the electric field below the skin depth of the conductor is indeed zero. However the skin depth is a frequency dependent function that is usually observed only in high frequency applications. If indeed the skin depth is considered in a problem, the ...
... In reality metals are very good conductors in which the electric field below the skin depth of the conductor is indeed zero. However the skin depth is a frequency dependent function that is usually observed only in high frequency applications. If indeed the skin depth is considered in a problem, the ...
Silicon Deposition
... • Sintering causes some Al to dissolve into the Si • Some Al diffusions are so thin that the Al can erode completely, called contact spiking • CS was first observed in the emitter regions of NPN transistors so CS is also known as emitter punchthrough • CS is minimized by replacing Al with a saturate ...
... • Sintering causes some Al to dissolve into the Si • Some Al diffusions are so thin that the Al can erode completely, called contact spiking • CS was first observed in the emitter regions of NPN transistors so CS is also known as emitter punchthrough • CS is minimized by replacing Al with a saturate ...
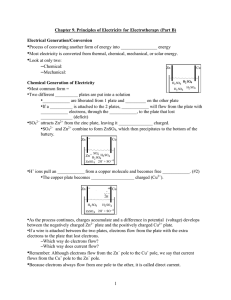
Chapter 9 (Part B)
... •If a wire is attached between the two plates, electrons flow from the plate with the extra electrons to the plate that lost electrons. –Which way do electrons flow? –Which way does current flow? •Remember: Although electrons flow from the Zn− pole to the Cu+ pole, we say that current flows from the ...
... •If a wire is attached between the two plates, electrons flow from the plate with the extra electrons to the plate that lost electrons. –Which way do electrons flow? –Which way does current flow? •Remember: Although electrons flow from the Zn− pole to the Cu+ pole, we say that current flows from the ...
extrinsic semiconductor
... As the temperature is increased more and more the donor atoms are ionized and the fermi level drops. For a particular temperature all donor atoms are ionized, further increase in temperature results in generation of electron hole pairs due to breaking of covalent bonds and materials tends to behav ...
... As the temperature is increased more and more the donor atoms are ionized and the fermi level drops. For a particular temperature all donor atoms are ionized, further increase in temperature results in generation of electron hole pairs due to breaking of covalent bonds and materials tends to behav ...
Lesson 12. Topic “Magnetic effect of an electric current”. Grammar
... constant flow of current. Seven years later the Danish scientist and experimenter, Oersted, decided to establish the relation between a flow of current and a magnetic needle. It took him at least 13 years more to find out that a compass needle is deflected when brought near a wire through which the ...
... constant flow of current. Seven years later the Danish scientist and experimenter, Oersted, decided to establish the relation between a flow of current and a magnetic needle. It took him at least 13 years more to find out that a compass needle is deflected when brought near a wire through which the ...
The Biot-Savart law
... is very strong and very uniform inside the tube, and very weak outside the tube. Let’s consider an ideal solenoid (infinitely long and no space between the windings, for which field is zero outside the solenoid and of constant magnitude inside the solenoid). For a length of solenoid containing windi ...
... is very strong and very uniform inside the tube, and very weak outside the tube. Let’s consider an ideal solenoid (infinitely long and no space between the windings, for which field is zero outside the solenoid and of constant magnitude inside the solenoid). For a length of solenoid containing windi ...
semiconductors
... Up to now we have examined p-type and n-type material separately. However, the properties of these extrinsic semiconductor materials become useful only when the two types are combined in some way. The area where the two types meet is called a pn junction, and the resulting properties allow it to be ...
... Up to now we have examined p-type and n-type material separately. However, the properties of these extrinsic semiconductor materials become useful only when the two types are combined in some way. The area where the two types meet is called a pn junction, and the resulting properties allow it to be ...
Electromigration

Electromigration is the transport of material caused by the gradual movement of the ions in a conductor due to the momentum transfer between conducting electrons and diffusing metal atoms. The effect is important in applications where high direct current densities are used, such as in microelectronics and related structures. As the structure size in electronics such as integrated circuits (ICs) decreases, the practical significance of this effect increases.

![2 Electric current [ ]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001511845_1-c754371f0fc86e182eb4561709dc5dd4-300x300.png)