P38
... the filamentary structure were made from the collapsed arcade, and had upward velocities by the released energy of the emerging flux. ・These results of our simulations suggest that the converging motion which can destabilize the sheared arcade field may be due to the flux emergence which has been ob ...
... the filamentary structure were made from the collapsed arcade, and had upward velocities by the released energy of the emerging flux. ・These results of our simulations suggest that the converging motion which can destabilize the sheared arcade field may be due to the flux emergence which has been ob ...
Computing the gravitational and magnetic anomalies - U
... irrelevant and can be set to any value. The algorithm does not include the effects of demagnetization (Grant and West, 1965), and thus it is not suited for modeling the anomalies due to bodies whose magnetic susceptibility exceeds about 0.01 emu. Although rocks rarely have magnetic susceptibilities ...
... irrelevant and can be set to any value. The algorithm does not include the effects of demagnetization (Grant and West, 1965), and thus it is not suited for modeling the anomalies due to bodies whose magnetic susceptibility exceeds about 0.01 emu. Although rocks rarely have magnetic susceptibilities ...
Sample Pages
... themselves does not produce any useful work; it’s the effects that the moving electrons have on the loads they flow through that are important. The effects of electron movement are the same regardless of the direction of the current flow. Figure 16–1 ...
... themselves does not produce any useful work; it’s the effects that the moving electrons have on the loads they flow through that are important. The effects of electron movement are the same regardless of the direction of the current flow. Figure 16–1 ...
Induced electric fields
... Origin of electromotive force is of non-electrostatic nature (similar to battery → chemical) Charges are brought to a higher potential Concept can be generalized to conductors of any shape and in any field (can be non-uniform, but not varying with time) ...
... Origin of electromotive force is of non-electrostatic nature (similar to battery → chemical) Charges are brought to a higher potential Concept can be generalized to conductors of any shape and in any field (can be non-uniform, but not varying with time) ...
M106 Vibrating Sample Magnetometry
... field will grow at the cost of domains with energetically more unfavorable magnetization alignment. As a consequence domain walls move through the sample and the overall magnetization increases in field direction. In magnetically soft materials, domain walls are broad and the movement of the walls r ...
... field will grow at the cost of domains with energetically more unfavorable magnetization alignment. As a consequence domain walls move through the sample and the overall magnetization increases in field direction. In magnetically soft materials, domain walls are broad and the movement of the walls r ...
The Hall Effect - Ryerson Department of Physics
... An electric charge moving perpendicular to a magnetic field B will experience a magnetic force. This also applies to the current flowing in a conductor placed in a magnetic field. The magnetic force will tend to move the charge carriers to one edge of the conductor leaving a deficiency of charge car ...
... An electric charge moving perpendicular to a magnetic field B will experience a magnetic force. This also applies to the current flowing in a conductor placed in a magnetic field. The magnetic force will tend to move the charge carriers to one edge of the conductor leaving a deficiency of charge car ...
Abstract - Iraqi Cultural Attache
... in the magnetic topology of the field occurs-facilitated by the process of ‘magnetic reconnection’. A great deal of research has been focussed on understanding the reconnection ;process and we now appreciate that the 3D process is critically different from early 2D models. The magnetic field in many ...
... in the magnetic topology of the field occurs-facilitated by the process of ‘magnetic reconnection’. A great deal of research has been focussed on understanding the reconnection ;process and we now appreciate that the 3D process is critically different from early 2D models. The magnetic field in many ...
4th Grade Physical Science- Magnetism and Electricity CA Focus
... • How you make the two lights in a series circuit brighter? Part 2: Building Parallel Circuits • How can you light two bulbs brightly with just one battery? • How are series and parallel circuits the same? different? Part 3: The String-of-Lights Problem • How can you design a string of lights that w ...
... • How you make the two lights in a series circuit brighter? Part 2: Building Parallel Circuits • How can you light two bulbs brightly with just one battery? • How are series and parallel circuits the same? different? Part 3: The String-of-Lights Problem • How can you design a string of lights that w ...
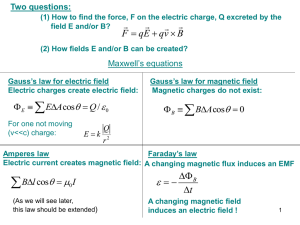
Magnetic flux Induced emf Faraday`s Law Lenz`s Law Motional EMF
... A square coil of wire with side 5.00 cm contains 100 loops and is positioned perpendicular to an uniform 0.60-T magnetic field as shown. It is quickly and uniformly pulled from the field (moving perpendicular to B) to a region where B drops abruptly to zero. At t=0, the right edge of the coil is the ...
... A square coil of wire with side 5.00 cm contains 100 loops and is positioned perpendicular to an uniform 0.60-T magnetic field as shown. It is quickly and uniformly pulled from the field (moving perpendicular to B) to a region where B drops abruptly to zero. At t=0, the right edge of the coil is the ...
magnetostriction with the michelson interferometer
... additionally subdivided in Weiss molecular magnetic fields consisting of many molecules which form the elementary dipoles (*). ...
... additionally subdivided in Weiss molecular magnetic fields consisting of many molecules which form the elementary dipoles (*). ...
Your Magnet Safety Team - Center for In Vivo Microscopy
... General MRI Hazards • An MRI scanner creates a magnetic field that is 30,000-150,000 times stronger than the earth’s magnetic field and is always on • While hazards to people with pace-makers and implants tend to be emphasized, projectile hazards are most worrisome for us • Within a few feet of the ...
... General MRI Hazards • An MRI scanner creates a magnetic field that is 30,000-150,000 times stronger than the earth’s magnetic field and is always on • While hazards to people with pace-makers and implants tend to be emphasized, projectile hazards are most worrisome for us • Within a few feet of the ...
lecture13
... The first transformer has a 2:1 ratio of turns, so the voltage doubles. But the second transformer has a 1:2 ratio, so the voltage is halved again. Therefore, the end result is the same as the original voltage. ...
... The first transformer has a 2:1 ratio of turns, so the voltage doubles. But the second transformer has a 1:2 ratio, so the voltage is halved again. Therefore, the end result is the same as the original voltage. ...
MRI glossary
... LONGITUDINAL RELAXATION - return of longitudinal magnetization to its equilibrium value after excitation due to the exchange of energy between the nuclear spins and the lattice. LONGITUDINAL RELAXATION TIME - the time constant, T1, which determines the rate at which excited protons return to equili ...
... LONGITUDINAL RELAXATION - return of longitudinal magnetization to its equilibrium value after excitation due to the exchange of energy between the nuclear spins and the lattice. LONGITUDINAL RELAXATION TIME - the time constant, T1, which determines the rate at which excited protons return to equili ...
PARAMETERS AND SYMBOLS FOR USE IN NUCLEAR
... structure in solution. Its uses also span structure in solids and mobility at the molecular level in all phases. The research literature in the subject is vast and ever-increasing. Unfortunately, many articles do not contain sufficient information for experiments to be repeated elsewhere, and there ...
... structure in solution. Its uses also span structure in solids and mobility at the molecular level in all phases. The research literature in the subject is vast and ever-increasing. Unfortunately, many articles do not contain sufficient information for experiments to be repeated elsewhere, and there ...
Chapter 7 powerpoint
... of Canada, about 1,000 km from the geographic north pole. • Earth’s magnetic poles move slowly with time. • Sometimes Earth’s magnetic poles switch places so that Earth’s south magnetic pole is the southern hemisphere near the geographic south pole. ...
... of Canada, about 1,000 km from the geographic north pole. • Earth’s magnetic poles move slowly with time. • Sometimes Earth’s magnetic poles switch places so that Earth’s south magnetic pole is the southern hemisphere near the geographic south pole. ...
Electromagnetic knots and the magnetic flux in superconductors
... are conserved quantities and they are proportional to the linking numbers of the magnetic and the electric lines, respectively. 4. The evolution in time of an electromagnetic knot imposes that the magnetic helicity is always equal to the electric helicity hm = he = a n. ...
... are conserved quantities and they are proportional to the linking numbers of the magnetic and the electric lines, respectively. 4. The evolution in time of an electromagnetic knot imposes that the magnetic helicity is always equal to the electric helicity hm = he = a n. ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.