
10th-physics-magnetic-effects-of
... 1. The properties of magnetic field lines 2.Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other 3.Draw the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet 4.Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances 5.What precaution should be taken to avoid the over loading of domes ...
... 1. The properties of magnetic field lines 2.Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other 3.Draw the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet 4.Name two safety measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances 5.What precaution should be taken to avoid the over loading of domes ...
Unit IIA Electricity and Magnetism
... Creating electromagnets – Send an electrical current through a coil of wire wrapped around some iron – Current controls the strength of an electromagnet—more current, stronger magnet Uses:Magnetically levitated trains (monorails) and roller coasters ...
... Creating electromagnets – Send an electrical current through a coil of wire wrapped around some iron – Current controls the strength of an electromagnet—more current, stronger magnet Uses:Magnetically levitated trains (monorails) and roller coasters ...
MSPS2
... Conduct an investigation and evaluate the experimental design to provide evidence that fields exist between objects exerting forces on each other even though the objects are not in contact. [Clarification Statement: Examples of this phenomenon could include the interactions of magnets, electrically ...
... Conduct an investigation and evaluate the experimental design to provide evidence that fields exist between objects exerting forces on each other even though the objects are not in contact. [Clarification Statement: Examples of this phenomenon could include the interactions of magnets, electrically ...
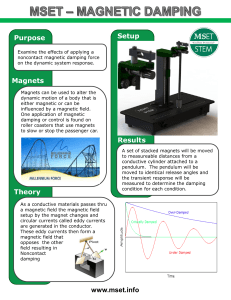
Purpose Magnets Theory Results www.mset.info Setup
... to measureable distances from a conductive cylinder attached to a pendulum. The pendulum will be moved to identical release angles and the transient response will be measured to determine the damping condition for each condition. ...
... to measureable distances from a conductive cylinder attached to a pendulum. The pendulum will be moved to identical release angles and the transient response will be measured to determine the damping condition for each condition. ...
Guided Reading 15.1
... 4. Draw arrows to show the direction of the magnetic force for each type of interaction. In the box underneath each diagram, write “attract” or “repel” to describe the type of interaction. ...
... 4. Draw arrows to show the direction of the magnetic force for each type of interaction. In the box underneath each diagram, write “attract” or “repel” to describe the type of interaction. ...
TCAP Review 2013 – Page 9 – Electromagnetism
... With the electrons in the domain, how must the spin of the electrons align in order for an object to be magnetic? (p. 427) ...
... With the electrons in the domain, how must the spin of the electrons align in order for an object to be magnetic? (p. 427) ...
Magnetism - schoolphysics
... 7. The next diagram shows a demagnetised bar. (a) Write down TWO ways of magnetising it. (b) Draw a diagram to show how the tiny molecular magnets would be arranged when it was completely magnetised. ...
... 7. The next diagram shows a demagnetised bar. (a) Write down TWO ways of magnetising it. (b) Draw a diagram to show how the tiny molecular magnets would be arranged when it was completely magnetised. ...
PHY-ZS-004 Electromagnetic Induction
... oxide of iron). They discovered that the stone always pointed in the same direction. Later, stones of magnetite called “lodestones” were used in navigation. ...
... oxide of iron). They discovered that the stone always pointed in the same direction. Later, stones of magnetite called “lodestones” were used in navigation. ...
Unit 9: Magnetism and Induction Review KEY
... Ørsted discovered that current flowing through a magnet deflected a compass needle. He related the concepts of electricity and magnetism ...
... Ørsted discovered that current flowing through a magnet deflected a compass needle. He related the concepts of electricity and magnetism ...
Magnetism Review game Thursday
... stay up, wrong answers sit down. 4. Team with most players still up at the end wins (3 Extra Credit points on the test) ...
... stay up, wrong answers sit down. 4. Team with most players still up at the end wins (3 Extra Credit points on the test) ...
18-1 Magnetism - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... 5. Based on the arrangement of the iron filings, where on the magnet is the strength of the magnetic field the greatest? ____________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... 5. Based on the arrangement of the iron filings, where on the magnet is the strength of the magnetic field the greatest? ____________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
bar magnets - jfindlay.ca
... Purpose: To see the effects of magnetic fields produced by magnets. ...
... Purpose: To see the effects of magnetic fields produced by magnets. ...
magnets ch.18
... 2. p454 The parts of a magnet where the magnetic effects are strongest are called _______. 3. p454 The magnetic effects are strongest near the ______ of the bar magnet. 4. p 455 The force of repulsion or attraction between the poles of magnets is called the _____. 5. p 456 A ________ _________ exist ...
... 2. p454 The parts of a magnet where the magnetic effects are strongest are called _______. 3. p454 The magnetic effects are strongest near the ______ of the bar magnet. 4. p 455 The force of repulsion or attraction between the poles of magnets is called the _____. 5. p 456 A ________ _________ exist ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.





















![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-300x300.png)
