magnetic dipole
... introduce the concept of an electric field to describe the interaction between the charges. In Ampere’s law, we can define an appropriate field that may be regarded as the means by which currents exert force Lecture 7 ...
... introduce the concept of an electric field to describe the interaction between the charges. In Ampere’s law, we can define an appropriate field that may be regarded as the means by which currents exert force Lecture 7 ...
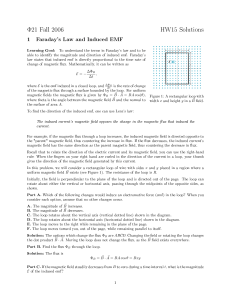
Φ21 Fall 2006 HW15 Solutions 1 Faraday`s Law and Induced EMF
... gives the direction of the magnetic eld generated by this current. In this problem, we will consider a rectangular loop of wire with sides x and y placed in a region where a ~ exists (see Figure 1). The resistance of the loop is R. uniform magnetic eld B Initially, the eld is perpendicular to the ...
... gives the direction of the magnetic eld generated by this current. In this problem, we will consider a rectangular loop of wire with sides x and y placed in a region where a ~ exists (see Figure 1). The resistance of the loop is R. uniform magnetic eld B Initially, the eld is perpendicular to the ...
Analyzing Magnetic Fields with Solenoids - PhysicsEd
... my students to note the number of loops they wrap the wire around the straw in order to discuss the influence of the number of loops on the magnetic field. Other extensions to this activity include ways for students to explore different designs for their solenoids and the effects these designs creat ...
... my students to note the number of loops they wrap the wire around the straw in order to discuss the influence of the number of loops on the magnetic field. Other extensions to this activity include ways for students to explore different designs for their solenoids and the effects these designs creat ...
Magnetism - Rockaway Township School District
... Ask questions that can be investigated within the scope of the classroom, outdoor environment, and museums and other public facilities with available resources and, when appropriate, frame a hypothesis based on observations and scientific principles. Planning and Carrying Out Investigations Plan ...
... Ask questions that can be investigated within the scope of the classroom, outdoor environment, and museums and other public facilities with available resources and, when appropriate, frame a hypothesis based on observations and scientific principles. Planning and Carrying Out Investigations Plan ...
MRI
... Magnetic Resonance Imaging It is energetically more favourable for hydrogen nuclei to return to their original state in the external magnetic field after the RF pulse. As they do so, they re-emit the energy absorbed from the radio wave in about 0.01 to 0.1 seconds. The emitted energy is a radio wav ...
... Magnetic Resonance Imaging It is energetically more favourable for hydrogen nuclei to return to their original state in the external magnetic field after the RF pulse. As they do so, they re-emit the energy absorbed from the radio wave in about 0.01 to 0.1 seconds. The emitted energy is a radio wav ...
electromagnetic induction
... Electromagnetic Induction, continued • The magnetic force acts on moving electric charges. – The force is at its maximum value when the charge moves perpendicularly to the field. – As the angle between the charge’s direction and the direction of the magnetic field decreases, the force on the charge ...
... Electromagnetic Induction, continued • The magnetic force acts on moving electric charges. – The force is at its maximum value when the charge moves perpendicularly to the field. – As the angle between the charge’s direction and the direction of the magnetic field decreases, the force on the charge ...
Force Between Current
... we will observe a form of magnetic levitation. What we will do is send equal current in opposite directions through two parallel wires, one of which is fixed in position. The non-fixed wire will rise as the current increases. We will measure the force on the wire and use this measurement to determin ...
... we will observe a form of magnetic levitation. What we will do is send equal current in opposite directions through two parallel wires, one of which is fixed in position. The non-fixed wire will rise as the current increases. We will measure the force on the wire and use this measurement to determin ...
Slide 1
... developed. It has established a workhorse reputation within many research circles, including thin films and material surface processing, fusion, high-power space propulsion, and academia, filling the role of not only a simply constructed plasma source but also that of a key component… “Theta-pinch d ...
... developed. It has established a workhorse reputation within many research circles, including thin films and material surface processing, fusion, high-power space propulsion, and academia, filling the role of not only a simply constructed plasma source but also that of a key component… “Theta-pinch d ...
Electric Art From Electromagnetism to Electrodynamics
... another, with collinear axes. There was no visible interaction between them when no current was flowing. When there was a constant current flowing along both spirals they attracted or repelled one another, depending upon the directions of the currents. It was in this way that he concluded for the fi ...
... another, with collinear axes. There was no visible interaction between them when no current was flowing. When there was a constant current flowing along both spirals they attracted or repelled one another, depending upon the directions of the currents. It was in this way that he concluded for the fi ...
KS4 Electricity – The Uses of Electromagnetism
... energy at low v______ current is increased in voltage before it is ...
... energy at low v______ current is increased in voltage before it is ...
mri safety - Munson Healthcare
... the inside of the human body. MR imaging uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed three-dimensional pictures of internal body structures. ...
... the inside of the human body. MR imaging uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed three-dimensional pictures of internal body structures. ...
Magnetic Battery Feasibility Study using Flux Switching Topology
... Permanent magnets have long been known to store magnetic energy in the alignment of the magnetic domains within the material. This paper investigates the possibility of constructing a magnetic device which can effectively extract the stored potential energy from permanent magnets and convert that en ...
... Permanent magnets have long been known to store magnetic energy in the alignment of the magnetic domains within the material. This paper investigates the possibility of constructing a magnetic device which can effectively extract the stored potential energy from permanent magnets and convert that en ...
Short Introduction to (Classical) Electromagnetic Theory
... ~ are generated by charges and 1. Electric fields E proportional to total charge 2. Magnetic monopoles do not exist 3. Changing magnetic flux generates circulating electric fields/currents 4.1 Changing electric flux generates circulating magnetic fields 4.2 Static electric current generates circulat ...
... ~ are generated by charges and 1. Electric fields E proportional to total charge 2. Magnetic monopoles do not exist 3. Changing magnetic flux generates circulating electric fields/currents 4.1 Changing electric flux generates circulating magnetic fields 4.2 Static electric current generates circulat ...
Modeling the Effects of Guest Molecules in Metal
... Our computational methodology correctly predicts the changes in the magnetic susceptibility when MOFs undergo thermal spin-crossover. Out of the three guest molecules tested, acetone and water shift the transition temperature to lower values, while a slight shift to higher values is observed for CS2 ...
... Our computational methodology correctly predicts the changes in the magnetic susceptibility when MOFs undergo thermal spin-crossover. Out of the three guest molecules tested, acetone and water shift the transition temperature to lower values, while a slight shift to higher values is observed for CS2 ...
electromagnetic induction
... Electromagnetic Induction, continued • The magnetic force acts on moving electric charges. – The force is at its maximum value when the charge moves perpendicularly to the field. – As the angle between the charge’s direction and the direction of the magnetic field decreases, the force on the charge ...
... Electromagnetic Induction, continued • The magnetic force acts on moving electric charges. – The force is at its maximum value when the charge moves perpendicularly to the field. – As the angle between the charge’s direction and the direction of the magnetic field decreases, the force on the charge ...
Electricity Ch. 18 Sect. 3
... Electromagnetic Induction, continued • The magnetic force acts on moving electric charges. – The force is at its maximum value when the charge moves perpendicularly to the field. – As the angle between the charge’s direction and the direction of the magnetic field decreases, the force on the charge ...
... Electromagnetic Induction, continued • The magnetic force acts on moving electric charges. – The force is at its maximum value when the charge moves perpendicularly to the field. – As the angle between the charge’s direction and the direction of the magnetic field decreases, the force on the charge ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.