PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... 30.4.4. A coil of wire that forms a complete loop is moving with a constant speed v toward a very long, current carrying wire, only a portion of which is shown. What affect, if any, does the current carrying wire have on the coil of wire? a) Since the magnetic field increases as the coil approaches ...
... 30.4.4. A coil of wire that forms a complete loop is moving with a constant speed v toward a very long, current carrying wire, only a portion of which is shown. What affect, if any, does the current carrying wire have on the coil of wire? a) Since the magnetic field increases as the coil approaches ...
A point charge is moving with speed 2 ´ 107 m/s along the x axis. At t
... The Biot–Savart law is similar to Coulomb's law in that both A. are inverse square laws. B. include the permeability of free space. C. deal with excess charges. D. are not electrical in nature. E. are described by all of these. ...
... The Biot–Savart law is similar to Coulomb's law in that both A. are inverse square laws. B. include the permeability of free space. C. deal with excess charges. D. are not electrical in nature. E. are described by all of these. ...
Tectonics and Paleomagnetism
... it because rocks contain magnetic records of the past. MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF ROCKS—Most people do not realize that a large number of the rocks in the world have tiny magnets in them. These can be small iron particles within larger rocks. Lava, flowing out from volcanoes, cools into rocks containing ...
... it because rocks contain magnetic records of the past. MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF ROCKS—Most people do not realize that a large number of the rocks in the world have tiny magnets in them. These can be small iron particles within larger rocks. Lava, flowing out from volcanoes, cools into rocks containing ...
Mott phases and phase transitions in graphene
... But which order is catalyzed? The Hamiltonian is : so that, ...
... But which order is catalyzed? The Hamiltonian is : so that, ...
ABSTRACT - buergerwelle.de
... uncertainty in relation to exposure to EMFs was also addressed by Sir Harry Gibbs in a wide ranging inquiry into community needs and high voltage transmission line development in Australia. In his March, 1991 Report (2) he said: “It has not been established that electric fields or magnetic fields of ...
... uncertainty in relation to exposure to EMFs was also addressed by Sir Harry Gibbs in a wide ranging inquiry into community needs and high voltage transmission line development in Australia. In his March, 1991 Report (2) he said: “It has not been established that electric fields or magnetic fields of ...
selescu 347
... equation of motion can not disappear, because it is originating in the time-dependent term (H j)/cρ in the right-hand side of this equation, this fact being the essentials of the electromagnetic field (H may even have a time variable direction). Taking into account that on any “i” stream and vorte ...
... equation of motion can not disappear, because it is originating in the time-dependent term (H j)/cρ in the right-hand side of this equation, this fact being the essentials of the electromagnetic field (H may even have a time variable direction). Taking into account that on any “i” stream and vorte ...
Method sheet lines magnetism
... prevented earlier experimenters from seeing the effect. (Note that the available equipment –voltaic piles, typically – would only produce a small current, so the effect would in any case have been very weak.) Experiment: Set a compass pointing north-south; place a wire above it, lying east-west. Con ...
... prevented earlier experimenters from seeing the effect. (Note that the available equipment –voltaic piles, typically – would only produce a small current, so the effect would in any case have been very weak.) Experiment: Set a compass pointing north-south; place a wire above it, lying east-west. Con ...
The Role of Ions in Body Chemistry Negative Ion Report: The CBS
... H+ and OH- are electrified and behave in magnetic fields in exactly the same way that electrons circulate in wires - except that in having more mass, they move more slowly and H+ ions move in the opposite direction to OH- ions. The way ions tend to behave in magnetic fields, one way or the other, de ...
... H+ and OH- are electrified and behave in magnetic fields in exactly the same way that electrons circulate in wires - except that in having more mass, they move more slowly and H+ ions move in the opposite direction to OH- ions. The way ions tend to behave in magnetic fields, one way or the other, de ...
Magnetic properties of superconductors
... We cannot define M as for normal conductors according to when on any cross section. ...
... We cannot define M as for normal conductors according to when on any cross section. ...
Magnetohydrodynamic Effects in Gamma
... Roming et al. 2006) may be attributed to highly magnetized ejecta (if optical flashes are related the emission from RS) • The magnetic acceleration mechanism suggests that s and g are not independent parameters at the deceleration radius. • For high-s flow, ejecta would experience magnetic accelerat ...
... Roming et al. 2006) may be attributed to highly magnetized ejecta (if optical flashes are related the emission from RS) • The magnetic acceleration mechanism suggests that s and g are not independent parameters at the deceleration radius. • For high-s flow, ejecta would experience magnetic accelerat ...
MAGNETIC FORCE ON A CURRENT
... To show that the magnetic force on a wire is proportional to the current in the wire and to use that force to calculate the magnetic field strength. APPARATUS: Large electromagnet with DC power supply Two ammeters U-shaped wire suspended from balance DC power supply for wire Gaussmeter with transver ...
... To show that the magnetic force on a wire is proportional to the current in the wire and to use that force to calculate the magnetic field strength. APPARATUS: Large electromagnet with DC power supply Two ammeters U-shaped wire suspended from balance DC power supply for wire Gaussmeter with transver ...
Electromagnetic Waves in Media with Ferromagnetic Losses
... magnetic fields is nor how it is created but just treat it as an invisible direction in space with which a compass needle aligns itself. All materials consist of very small elements called atoms. For some materials these atoms posses a so called magnetic moment that may be viewed as a tiny compass n ...
... magnetic fields is nor how it is created but just treat it as an invisible direction in space with which a compass needle aligns itself. All materials consist of very small elements called atoms. For some materials these atoms posses a so called magnetic moment that may be viewed as a tiny compass n ...
Functional and Structural MRI of the Human Auditory System
... (deoxy)hemoglobin recruited by firing neurons • Structure AND function in single scan – High spatial resolution with modest temporal resolution ...
... (deoxy)hemoglobin recruited by firing neurons • Structure AND function in single scan – High spatial resolution with modest temporal resolution ...
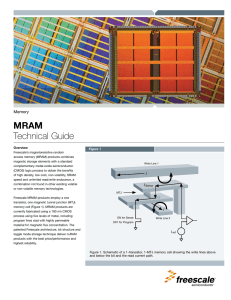
MRAM Technical Guide
... Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) require a posted warning for areas around instruments that exceed 5 Gauss. As is evident, the specification for MRAM products exceeds these values by a wide margin. There are two main sources of magnetic fields— current-carrying wires and permanen ...
... Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) require a posted warning for areas around instruments that exceed 5 Gauss. As is evident, the specification for MRAM products exceeds these values by a wide margin. There are two main sources of magnetic fields— current-carrying wires and permanen ...
LAB COURSE: 253B/255B FALL 2014
... using appropriate forms from an athletic or academic advisor); and (v) a properly documented medical reason. Note: A slip stating that the student visited the Student Health Center does not fulfill this requirement. Documentation that you were hospitalized or an official doctor’s note is required. ...
... using appropriate forms from an athletic or academic advisor); and (v) a properly documented medical reason. Note: A slip stating that the student visited the Student Health Center does not fulfill this requirement. Documentation that you were hospitalized or an official doctor’s note is required. ...
Evolution of Rising Magnetic Cavities and UHECR acceleration
... We seek solutions that take into account the plasma pressure and have no surface currents ...
... We seek solutions that take into account the plasma pressure and have no surface currents ...
Magnetic plasmon resonance - The University of Texas at Austin
... of the wire are now fully accounted for. Electric field E can be always presented in terms of the vector potential A and electric potential as E = − + ikA. In the standard Lorentz gage the electric potential equals to 共r1兲 = 兰exp共ikr12兲q共r2兲 / r12 dr2 and the vector potential A共r1兲 = c−1 兰 ex ...
... of the wire are now fully accounted for. Electric field E can be always presented in terms of the vector potential A and electric potential as E = − + ikA. In the standard Lorentz gage the electric potential equals to 共r1兲 = 兰exp共ikr12兲q共r2兲 / r12 dr2 and the vector potential A共r1兲 = c−1 兰 ex ...
Copyright 2009 Pearson
... magnetic field can be established in a given material. It is measured in units of the weber per ampere-turn meter. • The permeability of a vacuum (m0) is 4p x 10-7 weber per ampere-turn meter, which is used as a reference. • Relative Permeability (mr) is the ratio of the absolute permeability to the ...
... magnetic field can be established in a given material. It is measured in units of the weber per ampere-turn meter. • The permeability of a vacuum (m0) is 4p x 10-7 weber per ampere-turn meter, which is used as a reference. • Relative Permeability (mr) is the ratio of the absolute permeability to the ...
Lecture 8: Mirror / tokamak
... flow pattern (ions as well as electrons) is closed in the poloidal plane In every small volume the ions leaving the volume are replaced by the ions entering No charge separation Note, this is of course a cartoon picture. ...
... flow pattern (ions as well as electrons) is closed in the poloidal plane In every small volume the ions leaving the volume are replaced by the ions entering No charge separation Note, this is of course a cartoon picture. ...
Magnet

A magnet (from Greek μαγνήτις λίθος magnḗtis líthos, ""Magnesian stone"") is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets.A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include iron, nickel, cobalt, some alloys of rare earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond weakly to a magnetic field, by one of several other types of magnetism.Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically ""soft"" materials like annealed iron, which can be magnetized but do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically ""hard"" materials, which do. Permanent magnets are made from ""hard"" ferromagnetic materials such as alnico and ferrite that are subjected to special processing in a powerful magnetic field during manufacture, to align their internal microcrystalline structure, making them very hard to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a certain magnetic field must be applied, and this threshold depends on coercivity of the respective material. ""Hard"" materials have high coercivity, whereas ""soft"" materials have low coercivity.An electromagnet is made from a coil of wire that acts as a magnet when an electric current passes through it but stops being a magnet when the current stops. Often, the coil is wrapped around a core of ""soft"" ferromagnetic material such as steel, which greatly enhances the magnetic field produced by the coil.The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment or, alternatively, the total magnetic flux it produces. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization.