Physics 112 Magnetic Phase Transitions, and Free Energies in a
... T → Tc− , so this is a continuous (often called second order ) transition. Which state, you might ask, is selected, the one with positive m or the one with negative m? In the absence of any small perturbation to bias the spins up or down, such as a magnetic field, the system will select one of these ...
... T → Tc− , so this is a continuous (often called second order ) transition. Which state, you might ask, is selected, the one with positive m or the one with negative m? In the absence of any small perturbation to bias the spins up or down, such as a magnetic field, the system will select one of these ...
Why won`t my compass work the other side of the equator
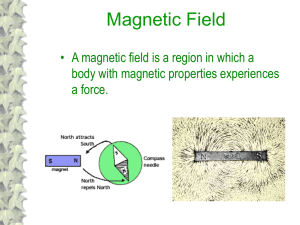
... The 3D magnetic field of the Earth is best modelled using the ‘Magnetic Earth: modelling the magnetic field of the Earth’ Earthlearningidea. This uses a clay or Plasticine™ ball with a bar magnet hidden inside; a Magnaprobe™ is used to plot the magnetic field of the magnet hidden inside the ball. Wh ...
... The 3D magnetic field of the Earth is best modelled using the ‘Magnetic Earth: modelling the magnetic field of the Earth’ Earthlearningidea. This uses a clay or Plasticine™ ball with a bar magnet hidden inside; a Magnaprobe™ is used to plot the magnetic field of the magnet hidden inside the ball. Wh ...
History of Magnetism - School of Applied Non
... Atoms consist of Protons, Neutrons, and electrons. A stable or balanced atom will have the same number of (+) protons and (-) electrons. The neutrons are there to keep the positive charges from repelling each other, keeping the nucleus (centre) of the atom together and stable. To date we have no kno ...
... Atoms consist of Protons, Neutrons, and electrons. A stable or balanced atom will have the same number of (+) protons and (-) electrons. The neutrons are there to keep the positive charges from repelling each other, keeping the nucleus (centre) of the atom together and stable. To date we have no kno ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.