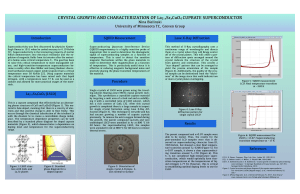
Magnetic Neutron Scattering and Spin
... 3 The neutron spin operator does not appear the the cross section for coherent nuclear scattering. The neutron spin state is therefore unaffected by nuclear scattering. By contrast, magnetic neutron scattering can be (but does not have to be) associated with a spin-flip of the neutron. ...
... 3 The neutron spin operator does not appear the the cross section for coherent nuclear scattering. The neutron spin state is therefore unaffected by nuclear scattering. By contrast, magnetic neutron scattering can be (but does not have to be) associated with a spin-flip of the neutron. ...
Lecture32
... Announcements Change of plans for today: Demos on light and selected review for today ...
... Announcements Change of plans for today: Demos on light and selected review for today ...
Chapter 7 The compass
... the direction relative to the geographic north. The magnetic compass is the most familiar compass type. It functions as a pointer to magnetic north, the local magnetic meridian, because the magnetized needle at its heart aligns itself with the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field. The ...
... the direction relative to the geographic north. The magnetic compass is the most familiar compass type. It functions as a pointer to magnetic north, the local magnetic meridian, because the magnetized needle at its heart aligns itself with the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field. The ...
Virtual ChemLab: General Chemistry Laboratories, Student Lab
... 3. Turn on the Phosphor Screen. (Click on the green/red button.) What do you observe? The phosphor screen detects charged particles (such as electrons) and it glows momentarily at the positions where the particles impact the screen. 4. Drag the lab window down and left and the phosphor screen window ...
... 3. Turn on the Phosphor Screen. (Click on the green/red button.) What do you observe? The phosphor screen detects charged particles (such as electrons) and it glows momentarily at the positions where the particles impact the screen. 4. Drag the lab window down and left and the phosphor screen window ...
1 Magnetism 2 Magnetic Field and Magnetic Force
... is magnetized. relative permeability : denoted Km ; the additional magnetic field in a paramagnetic material than would be measured in a vacuum; for a given material, Km depends on temperature. permeability of a material : µ = Km µ0 diamagnetic: materials that have no net atomic current loops, but i ...
... is magnetized. relative permeability : denoted Km ; the additional magnetic field in a paramagnetic material than would be measured in a vacuum; for a given material, Km depends on temperature. permeability of a material : µ = Km µ0 diamagnetic: materials that have no net atomic current loops, but i ...
B - Fort Bend ISD
... The Chinese used them for navigating ships in the 12th century. We know they contained iron ore which is called magnetite. ...
... The Chinese used them for navigating ships in the 12th century. We know they contained iron ore which is called magnetite. ...
Investigation of plagioclase crystals from the ~2
... effects which would appear in paleointensity records [1, 2]. Hence more extensive knowledge of changes in paleointensity would lend great insight into the thermal evolution of the Earth. Paleointensity is studied by measuring remanent magnetization in rocks containing ferromagnetic minerals, which a ...
... effects which would appear in paleointensity records [1, 2]. Hence more extensive knowledge of changes in paleointensity would lend great insight into the thermal evolution of the Earth. Paleointensity is studied by measuring remanent magnetization in rocks containing ferromagnetic minerals, which a ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.