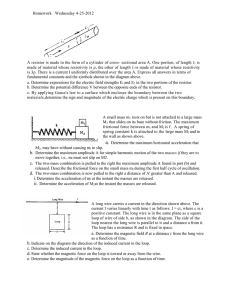
Homework Wednesday 4-25-2012 A resistor is made in the form of a
... a. A long straight wire carries current I into the plane of the page as shown above. Using Ampere's law, develop an expression for the magnetic field intensity at a point M that is a distance R from the center of the wire. On the diagram above indicate your path of integration and indicate the direc ...
... a. A long straight wire carries current I into the plane of the page as shown above. Using Ampere's law, develop an expression for the magnetic field intensity at a point M that is a distance R from the center of the wire. On the diagram above indicate your path of integration and indicate the direc ...
The field concepts of Faraday and Maxwell
... we find the same definition offield as a region of space surrounding electrified or magnetized bodies, On §44 he wrote, [9, VoL 1, p. 471: "lhe ch:tric field is the portion of space in the neighbourhood of electrified bodies, considered with reference to electric phenomena.~ A similar definition is ...
... we find the same definition offield as a region of space surrounding electrified or magnetized bodies, On §44 he wrote, [9, VoL 1, p. 471: "lhe ch:tric field is the portion of space in the neighbourhood of electrified bodies, considered with reference to electric phenomena.~ A similar definition is ...
Electromagnetism
... field around it, an external magnetic field around the wire can cause the wire to move. This is because of the attraction or repulsion of the two magnetic fields (the one around the wire and the external one). ...
... field around it, an external magnetic field around the wire can cause the wire to move. This is because of the attraction or repulsion of the two magnetic fields (the one around the wire and the external one). ...
lecture 29 motional emf
... component of the Earth’s magnetic field is Bv = 5.0 × 10-6 T, and its horizontal component is Bh = 1.4 × 10-6 T, what is the induced emf between the wing ...
... component of the Earth’s magnetic field is Bv = 5.0 × 10-6 T, and its horizontal component is Bh = 1.4 × 10-6 T, what is the induced emf between the wing ...
ELECTROMAGNETISM
... At this stage, you understand roughly as much about the classification of interactions as physicists understood around the year 1800. There appear to be three fundamentally different types of interactions: gravitational, electrical, and magnetic. Many types of interactions that appear superficially ...
... At this stage, you understand roughly as much about the classification of interactions as physicists understood around the year 1800. There appear to be three fundamentally different types of interactions: gravitational, electrical, and magnetic. Many types of interactions that appear superficially ...
Digital Design
... by Albert Einstein, Annalen der Physik 17 (1905), p. 891. “It is well known that if we attempt to apply Maxwell's electro-dynamics, as conceived at the present time, to moving bodies, we are led to asymmetry which does not agree with observed phenomena. Let us think of the mutual action between a ma ...
... by Albert Einstein, Annalen der Physik 17 (1905), p. 891. “It is well known that if we attempt to apply Maxwell's electro-dynamics, as conceived at the present time, to moving bodies, we are led to asymmetry which does not agree with observed phenomena. Let us think of the mutual action between a ma ...
Slide 1
... – A solenoid (a length of copper wire wound into a long coil) is connected to a battery in series. – A iron bar is then placed inside the solenoid – The polarities depend no the direction of the flow of the current A magnet created in this way is ________ A) Strong ...
... – A solenoid (a length of copper wire wound into a long coil) is connected to a battery in series. – A iron bar is then placed inside the solenoid – The polarities depend no the direction of the flow of the current A magnet created in this way is ________ A) Strong ...
Magnet Lab - Warren County Schools
... A magnet is a solid object, usually a rock or piece of metal, that can push or pull objects made of iron. Go on a magnet hunt around your house to find out what types of objects are magnetic. Look around and make of a list of objects you see that you think will be attracted to a magnet and another l ...
... A magnet is a solid object, usually a rock or piece of metal, that can push or pull objects made of iron. Go on a magnet hunt around your house to find out what types of objects are magnetic. Look around and make of a list of objects you see that you think will be attracted to a magnet and another l ...
ppt
... agrees so exactly with the velocity of light calculated from the optical experiments, that we can scarcely avoid the inference that light consists in the transverse undulation of same medium which is the cause of electric and magnetic ...
... agrees so exactly with the velocity of light calculated from the optical experiments, that we can scarcely avoid the inference that light consists in the transverse undulation of same medium which is the cause of electric and magnetic ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.