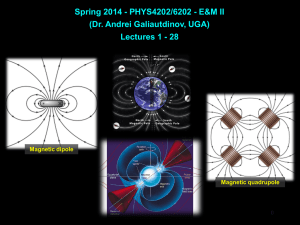
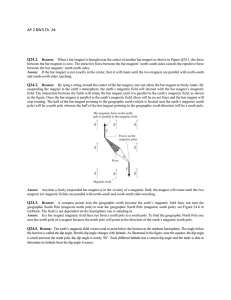
Document
... Ampere’s force law describes an “action at a distance” analogous to Coulomb’s law. In Coulomb’s law, it was useful to introduce the concept of an electric field to describe the interaction between the charges. In Ampere’s law, we can define an appropriate field that may be regarded as the means by w ...
... Ampere’s force law describes an “action at a distance” analogous to Coulomb’s law. In Coulomb’s law, it was useful to introduce the concept of an electric field to describe the interaction between the charges. In Ampere’s law, we can define an appropriate field that may be regarded as the means by w ...
ABSTRACT - buergerwelle.de
... further two in Australia (3 and 4) have recommended prudent avoidance but the term has not been, and by its nature, cannot be defined with precision. Prudent avoidance involves taking reasonable steps in any particular circumstance, and although a precise definition cannot be given, it is possible t ...
... further two in Australia (3 and 4) have recommended prudent avoidance but the term has not been, and by its nature, cannot be defined with precision. Prudent avoidance involves taking reasonable steps in any particular circumstance, and although a precise definition cannot be given, it is possible t ...
Section 22.2 - CPO Science
... adding a second battery. 2. Add more turns of wire around the nail. Why do these two techniques work? ...
... adding a second battery. 2. Add more turns of wire around the nail. Why do these two techniques work? ...
proposal and modalities for combined geoscientist examination for
... cover any one of these subjects together with a compulsory paper in General English and General studies. It is proposed that broadly the examination should be descriptive and be in two parts in the following pattern; the first part is compulsory and for 300 marks and the second part has an option of ...
... cover any one of these subjects together with a compulsory paper in General English and General studies. It is proposed that broadly the examination should be descriptive and be in two parts in the following pattern; the first part is compulsory and for 300 marks and the second part has an option of ...
Chapter 34.
... Ex- (Serway 34-19) In SI units, the electric field in an electromagnetic wave is described by Ey = 100 sin(1.00 x 107x -t). (a) Calculate the amplitude of the corresponding magnetic field. (b) Find the wavelength , (c) Find the frequency f. Also find an expression for the magnetic field. ...
... Ex- (Serway 34-19) In SI units, the electric field in an electromagnetic wave is described by Ey = 100 sin(1.00 x 107x -t). (a) Calculate the amplitude of the corresponding magnetic field. (b) Find the wavelength , (c) Find the frequency f. Also find an expression for the magnetic field. ...
Measurement of Residential Power Frequency
... magnetic fields are also highly variable not only at different locations but also over time at ...
... magnetic fields are also highly variable not only at different locations but also over time at ...
Unit 5 sun and star formation
... On the sun, coronal mass ejections occur when solar magnetic field lines snake around each other, forming the letter "S". Usually, they go past each other. But if they connect, it's like a short circuit. The mid-section breaks loose and drives out a coronal mass ejection. ...
... On the sun, coronal mass ejections occur when solar magnetic field lines snake around each other, forming the letter "S". Usually, they go past each other. But if they connect, it's like a short circuit. The mid-section breaks loose and drives out a coronal mass ejection. ...
Magnetic dipole moment of a moving electric dipole
... moving electric dipole is not divergenceless: by the continuity equation, ∇ · J = −∂ρb /∂t, and ∂ρb /∂t 6= 0 for the moving dipole’s charge density ρb (see Eq. (5)). But as a curl, the magnetization component Jm of the net current density J is divergenceless. It is only the magnetization current J R ...
... moving electric dipole is not divergenceless: by the continuity equation, ∇ · J = −∂ρb /∂t, and ∂ρb /∂t 6= 0 for the moving dipole’s charge density ρb (see Eq. (5)). But as a curl, the magnetization component Jm of the net current density J is divergenceless. It is only the magnetization current J R ...
Magnetochemistry

Magnetochemistry is concerned with the magnetic properties of chemical compounds. Magnetic properties arise from the spin and orbital angular momentum of the electrons contained in a compound. Compounds are diamagnetic when they contain no unpaired electrons. Molecular compounds that contain one or more unpaired electrons are paramagnetic. The magnitude of the paramagnetism is expressed as an effective magnetic moment, μeff. For first-row transition metals the magnitude of μeff is, to a first approximation, a simple function of the number of unpaired electrons, the spin-only formula. In general, spin-orbit coupling causes μeff to deviate from the spin-only formula. For the heavier transition metals, lanthanides and actinides, spin-orbit coupling cannot be ignored. Exchange interaction can occur in clusters and infinite lattices, resulting in ferromagnetism, antiferromagnetism or ferrimagnetism depending on the relative orientations of the individual spins.