01 - Edublogs
... _____ 8. What happens to the magnetic field if more loops per meter are added to a solenoid? a. The magnetic field becomes weaker. b. The magnetic field becomes stronger. c. The magnetic field turns on and off. d. There is no change in the magnetic field. _____ 9. A solenoid wrapped around a soft ir ...
... _____ 8. What happens to the magnetic field if more loops per meter are added to a solenoid? a. The magnetic field becomes weaker. b. The magnetic field becomes stronger. c. The magnetic field turns on and off. d. There is no change in the magnetic field. _____ 9. A solenoid wrapped around a soft ir ...
Le magnétisme et l`électromagnétisme
... i) To increase the intensity of the magnetic field of a live wire, it can be rolled ________________________ into a coil of regularly shaped loops to form a magnetic field solenoid ________________________ . This formation will have a ________________________ that resembles that of a bar magnet. How ...
... i) To increase the intensity of the magnetic field of a live wire, it can be rolled ________________________ into a coil of regularly shaped loops to form a magnetic field solenoid ________________________ . This formation will have a ________________________ that resembles that of a bar magnet. How ...
magnetic dipole
... was brought to Europe in the Middle Ages from the Chinese who had been using the compass for over 1500 years ...
... was brought to Europe in the Middle Ages from the Chinese who had been using the compass for over 1500 years ...
MAGNETIC ATTRACTION
... • Depend on the structure of the atoms making up the object. • A spinning electron (negatively charged) creates a magnetic field. • A bar magnet has what is called a magnetic domain. It has a strong representation and therefore a stronger attraction. • Materials that have a very strong attraction to ...
... • Depend on the structure of the atoms making up the object. • A spinning electron (negatively charged) creates a magnetic field. • A bar magnet has what is called a magnetic domain. It has a strong representation and therefore a stronger attraction. • Materials that have a very strong attraction to ...
Honors Physics Unit 8 Review Guide Magnetism Test Format 15
... Forces in Magnetic Fields F = qvB – Lorentz force on a moving charged particle F = BIL – force on a wire Direction given by right-hand rule #2 (gun position with fingers) Thumb = force Index = velocity/current Middle = magnetic field Negative charges go the other way Force is perpend ...
... Forces in Magnetic Fields F = qvB – Lorentz force on a moving charged particle F = BIL – force on a wire Direction given by right-hand rule #2 (gun position with fingers) Thumb = force Index = velocity/current Middle = magnetic field Negative charges go the other way Force is perpend ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE
... solenoid depends on the number of loops of wire and the amount of current in the wire. • An electromagnet is a strong magnet created when an iron core is inserted into the center of a current-carrying solenoid. ...
... solenoid depends on the number of loops of wire and the amount of current in the wire. • An electromagnet is a strong magnet created when an iron core is inserted into the center of a current-carrying solenoid. ...
Notes24
... generated in a superconductor will persist indefinitely. Magnetic fields created by these currents will also persist indefinitely. ...
... generated in a superconductor will persist indefinitely. Magnetic fields created by these currents will also persist indefinitely. ...
Electricity and Magnetism - GTT-MOE-WMS
... Types of Magnets Magnets in Nature Magnetite is a mineral that is naturally magnetic. Human-Made Magnets Some materials can be magnetized when placed near a strong magnetic field. Soft magnetic materials (Iron) Hard magnetic materials (Cobalt, Nickel) Electromagnets Magnets can be made by passing a ...
... Types of Magnets Magnets in Nature Magnetite is a mineral that is naturally magnetic. Human-Made Magnets Some materials can be magnetized when placed near a strong magnetic field. Soft magnetic materials (Iron) Hard magnetic materials (Cobalt, Nickel) Electromagnets Magnets can be made by passing a ...
High Speed, High Resolution Multi-Probe Magnetic Field Mapping
... The SENIS Magnetic Field Mapper can map dc and ac magnetic fields associated with permanent magnets and electromagnets. The base Field Probe is a unique three-component (Bx, By, Bz) Integrated Circuit (IC) with a sensing volume of less than 0.15 x 0.15 x 0.01mm, enabling very high position resolutio ...
... The SENIS Magnetic Field Mapper can map dc and ac magnetic fields associated with permanent magnets and electromagnets. The base Field Probe is a unique three-component (Bx, By, Bz) Integrated Circuit (IC) with a sensing volume of less than 0.15 x 0.15 x 0.01mm, enabling very high position resolutio ...
L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]
... Magnetic fields exert forces on the electrons moving in a wire (current) ...
... Magnetic fields exert forces on the electrons moving in a wire (current) ...
EM worksheet
... Both magnets and electromagnets have their attractive features. Electromagnets can be made stronger by adding coils or turns of wire or by adding more electricity. Permanent magnets can actually lose some of their magnetism overtime as a result of being dropped repeatedly. Similar to regular magnets ...
... Both magnets and electromagnets have their attractive features. Electromagnets can be made stronger by adding coils or turns of wire or by adding more electricity. Permanent magnets can actually lose some of their magnetism overtime as a result of being dropped repeatedly. Similar to regular magnets ...
SPH3U - K-Moncrief
... If you cut a magnet in two pieces, each piece will have a north and south pole. You can keep cutting to make smaller and smaller magnets – but each one will be weaker in strength. ...
... If you cut a magnet in two pieces, each piece will have a north and south pole. You can keep cutting to make smaller and smaller magnets – but each one will be weaker in strength. ...
Magnetism
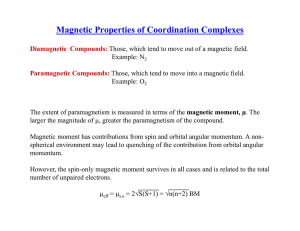
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.


















![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008057814_1-60bd3a273eeadb9e6de7a28a98376c5d-300x300.png)