Student Objective Students will be able to…
... 10. What is the one important difference between electric charges and magnetic poles? __________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 10. What is the one important difference between electric charges and magnetic poles? __________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ...
Document
... magnetic field of strength 0.50 T. a) Sketch the situation. b) Choose a direction for the current and indicate the direction of the force on the wire for your choice. c) If the magnitude of the force is 10 N, find the current in the wire. ...
... magnetic field of strength 0.50 T. a) Sketch the situation. b) Choose a direction for the current and indicate the direction of the force on the wire for your choice. c) If the magnitude of the force is 10 N, find the current in the wire. ...
Magnetic Fields
... Why do you think this pattern occurs? The iron filings line up according to the forces within the magnetic field. GTE-11 ...
... Why do you think this pattern occurs? The iron filings line up according to the forces within the magnetic field. GTE-11 ...
Modeling the Magnetic Pickup of an Electric Guitar
... The Magnetic Pickup Permanent magnet induces magnetism in wire When wire oscillates, the flux through the coil ...
... The Magnetic Pickup Permanent magnet induces magnetism in wire When wire oscillates, the flux through the coil ...
Electromagnetics (Math - 262)
... capacitor. Effect of a dielectric. Molecular model of induced charges. Polarization and displacement. ...
... capacitor. Effect of a dielectric. Molecular model of induced charges. Polarization and displacement. ...
Ch. 17 Sec. 2
... Ocean Rocks Scientists collected samples of the deep-sea sediments 1st: Ages of rocks vary from place to place ...
... Ocean Rocks Scientists collected samples of the deep-sea sediments 1st: Ages of rocks vary from place to place ...
Electricity Ch. 18 Sect. 2
... • solenoid: a coil of wire with an electric current in it – In a solenoid, the magnetic field of each loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. • The strength of a solenoid can be increased. – More loops or more current can create a stronger magnetic field. • ...
... • solenoid: a coil of wire with an electric current in it – In a solenoid, the magnetic field of each loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. • The strength of a solenoid can be increased. – More loops or more current can create a stronger magnetic field. • ...
magnetic - Timber Ridge Elementary
... Earth acts like a giant magnet and is surrounded by a magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to point either North or South. ...
... Earth acts like a giant magnet and is surrounded by a magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to point either North or South. ...
Electricity from Magnetism
... that electricity became practical for use in technology. His efforts created the “ancestor” of the electric motor and generators. • Discovered electromagnetic induction (1831) ….which was a turning point in physics ...
... that electricity became practical for use in technology. His efforts created the “ancestor” of the electric motor and generators. • Discovered electromagnetic induction (1831) ….which was a turning point in physics ...
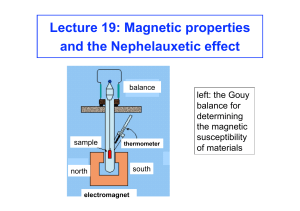
Lecture 19: Magnetic properties and the Nephelauxetic effect
... The value of λ is negligible for very light atoms, but increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ is an order of magnitude larger than for the first-row anal ...
... The value of λ is negligible for very light atoms, but increases with increasing atomic weight, so that for heavier d-block elements, and for f-block elements, the orbital contribution is considerable. For 2nd and 3rd row dblock elements, λ is an order of magnitude larger than for the first-row anal ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.