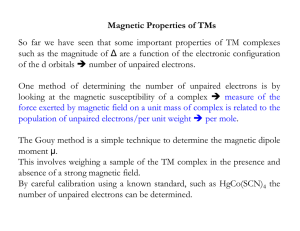
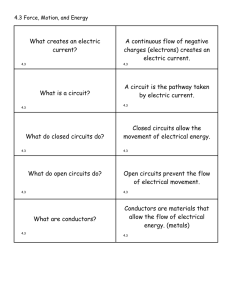
Magnetism - TeacherWeb
... Units of Magnetic Field B Tesla (SI Unit) Gauss (cgs unit) 1 Tesla = 104 Gauss Earth magnetic field about 0.5 gauss ...
... Units of Magnetic Field B Tesla (SI Unit) Gauss (cgs unit) 1 Tesla = 104 Gauss Earth magnetic field about 0.5 gauss ...
Magnetic field - Southgate Schools
... by chance in 1820. As he prepared for one of his classes, he noticed that when he turned on the electric current in a wire, a compass needle that was on another experiment changed its position. When the electric current was turned off, the compass needle returned to its original position. ...
... by chance in 1820. As he prepared for one of his classes, he noticed that when he turned on the electric current in a wire, a compass needle that was on another experiment changed its position. When the electric current was turned off, the compass needle returned to its original position. ...
1a.Magnetism
... Magnetism was discovered as early as the 6th century, BC First artificial magnet was discovered in China around 1 AD by stroking certain materials with iron The first technological application of magnetism is believed to be the compass There are many similarities between magnetism and electricity ...
... Magnetism was discovered as early as the 6th century, BC First artificial magnet was discovered in China around 1 AD by stroking certain materials with iron The first technological application of magnetism is believed to be the compass There are many similarities between magnetism and electricity ...
Magnetic separation
... • The rate of sample introduction is controlled by the angle of the feed outlet shoot and the strength of feed vibration • The speed at which material moved down the ramp is controlled by the strength of the chute ...
... • The rate of sample introduction is controlled by the angle of the feed outlet shoot and the strength of feed vibration • The speed at which material moved down the ramp is controlled by the strength of the chute ...
Slide 1
... To figure out the force on a positive charge, use the right hand (or opposite from negative charges) This is how Jay can smash particles together http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bEvLK 11jdJ8 The resultant of the velocity and the force can produce circular motion ...
... To figure out the force on a positive charge, use the right hand (or opposite from negative charges) This is how Jay can smash particles together http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bEvLK 11jdJ8 The resultant of the velocity and the force can produce circular motion ...
4.1.4 Summary to: Magnetic Materials - Definitions and General Relations
... contributions from the electrons, and their orbits (including bonding orbitals etc.), it is either: Zero - we then have a diamagnetic material. Magnetic field induces dipoles, somewhat analogous to elctronic polarization in dielectrics. Always very weak effect (except for superconductors) Unimportan ...
... contributions from the electrons, and their orbits (including bonding orbitals etc.), it is either: Zero - we then have a diamagnetic material. Magnetic field induces dipoles, somewhat analogous to elctronic polarization in dielectrics. Always very weak effect (except for superconductors) Unimportan ...
4.1.4 Summary to: Magnetic Materials - Definitions and General Relations
... contributions from the electrons, and their orbits (including bonding orbitals etc.), it is either: Zero - we then have a diamagnetic material. Magnetic field induces dipoles, somewhat analogous to elctronic polarization in dielectrics. Always very weak effect (except for superconductors) Unimportan ...
... contributions from the electrons, and their orbits (including bonding orbitals etc.), it is either: Zero - we then have a diamagnetic material. Magnetic field induces dipoles, somewhat analogous to elctronic polarization in dielectrics. Always very weak effect (except for superconductors) Unimportan ...
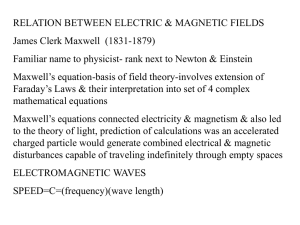
Electromagnetic fields
... Maxwell’s equations connected electricity & magnetism & also led to the theory of light, prediction of calculations was an accelerated charged particle would generate combined electrical & magnetic disturbances capable of traveling indefinitely through empty spaces ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES SPEED=C=(fre ...
... Maxwell’s equations connected electricity & magnetism & also led to the theory of light, prediction of calculations was an accelerated charged particle would generate combined electrical & magnetic disturbances capable of traveling indefinitely through empty spaces ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES SPEED=C=(fre ...
Magnets - OptionsHighSchool
... What are magnetic pole reversals, and what evidence is there that the Earth's magnetic field has undergone pole ...
... What are magnetic pole reversals, and what evidence is there that the Earth's magnetic field has undergone pole ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.