
Lecture 10 - UConn Physics
... Electrically charged particles come under various sorts of forces. ...
... Electrically charged particles come under various sorts of forces. ...
1st question: How are magnetism and electricity related
... How the Telegraph works When you push down the key it gives the electrons a free path which activates the electromagnet which pulls the strip down. The strip makes a noise when it hits the nail. ...
... How the Telegraph works When you push down the key it gives the electrons a free path which activates the electromagnet which pulls the strip down. The strip makes a noise when it hits the nail. ...
Motors and Generators
... • F=BIlsin calculates the magnitude of the force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field, where F = the force on the conductor (N – newtons) B = the magnetic flux density of the external field (T – tesla) I = current in the conductor (A – amperes) l = the length of conductor in the fiel ...
... • F=BIlsin calculates the magnitude of the force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field, where F = the force on the conductor (N – newtons) B = the magnetic flux density of the external field (T – tesla) I = current in the conductor (A – amperes) l = the length of conductor in the fiel ...
Magnetic field
... either attract or repel each other. ► When 2 north poles or 2 south poles come close, you can feel a force preventing the magnets from touching. ► North poles always attract south poles. ► When 2 magnets come close, their magnetic fields combine. ...
... either attract or repel each other. ► When 2 north poles or 2 south poles come close, you can feel a force preventing the magnets from touching. ► North poles always attract south poles. ► When 2 magnets come close, their magnetic fields combine. ...
Experiment 3.3 Thomson Experiment Aim To use a computer
... In this step Magnetic field and electric field were both on and adjusted until the beam shows zero net deflection. ...
... In this step Magnetic field and electric field were both on and adjusted until the beam shows zero net deflection. ...
Problem Set 8
... Why? Question B If a negatively charged particle enters a region of uniform magnetic field which is perpendicular to the particle’s velocity, will the KE of the particle increase, decrease, or stay the same. Explain your answer. (Neglect gravity.) Question C How can you tell whether moving electrons ...
... Why? Question B If a negatively charged particle enters a region of uniform magnetic field which is perpendicular to the particle’s velocity, will the KE of the particle increase, decrease, or stay the same. Explain your answer. (Neglect gravity.) Question C How can you tell whether moving electrons ...
Combustion Equation
... – Adding more turns to the coil – Increasing the current flowing through the coil ...
... – Adding more turns to the coil – Increasing the current flowing through the coil ...
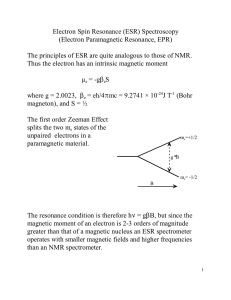
Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Spectroscopy (Electron
... g-values are determined by careful measurement of the frequency and magnetic field, or more commonly by using a reference of known g-value. A very common reference is the stable free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (C6H5)2NN(&){C6H2(NO2)3} for which g = 2.0036 In liquid samples the average (isotropic ...
... g-values are determined by careful measurement of the frequency and magnetic field, or more commonly by using a reference of known g-value. A very common reference is the stable free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (C6H5)2NN(&){C6H2(NO2)3} for which g = 2.0036 In liquid samples the average (isotropic ...
EMI (97-03)
... The U-shaped conductor lies perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B with magnitude B = 0.60 T, directed into the page. We lay a metal rod with length L = 0.10 m across the two arms of the conductor, forming a conducting loop, and move the rod to the right with constant speed v = 2.5 m/s. What is ...
... The U-shaped conductor lies perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B with magnitude B = 0.60 T, directed into the page. We lay a metal rod with length L = 0.10 m across the two arms of the conductor, forming a conducting loop, and move the rod to the right with constant speed v = 2.5 m/s. What is ...
Electromagnetic Induction - Lompoc Unified School District
... A conductive wire consisting of 3 loops and enclosing an area of .020 m2 is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of .030T. If the field goes to zero in .0045sec, what is the magnitude of the induced emf? ...
... A conductive wire consisting of 3 loops and enclosing an area of .020 m2 is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of .030T. If the field goes to zero in .0045sec, what is the magnitude of the induced emf? ...
International Community School, Abu Dhabi Physics – Project
... Circles of Magnetism A compass allows us to observe the direction of a magnetic field: compass needles are just little magnets that are free to rotate. Normally, compasses respond to Earth’s magnetic field, orienting themselves parallel to magnetic field lines. If we create a magnetic field that is ...
... Circles of Magnetism A compass allows us to observe the direction of a magnetic field: compass needles are just little magnets that are free to rotate. Normally, compasses respond to Earth’s magnetic field, orienting themselves parallel to magnetic field lines. If we create a magnetic field that is ...
Chapter 33. The Magnetic Field
... Current counterclockwise, north pole on bottom Current clockwise; north pole on bottom Current counterclockwise, north pole on top Current clockwise; north pole on top ...
... Current counterclockwise, north pole on bottom Current clockwise; north pole on bottom Current counterclockwise, north pole on top Current clockwise; north pole on top ...
m L
... (note this energy splitting is small ~10-5 eV in H). We can estimate the splitting using the Bohr model to estimate the internal magnetic field. For atomic electrons, the relative orbital motion of the nucleus creates a magnetic field (for l 0). The electron spin can have ms = ±1/2 relative to the ...
... (note this energy splitting is small ~10-5 eV in H). We can estimate the splitting using the Bohr model to estimate the internal magnetic field. For atomic electrons, the relative orbital motion of the nucleus creates a magnetic field (for l 0). The electron spin can have ms = ±1/2 relative to the ...
Magnetism
Magnetism is a class of physical phenomena that are mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Every material is influenced to some extent by a magnetic field. The most familiar effect is on permanent magnets, which have persistent magnetic moments caused by ferromagnetism. Most materials do not have permanent moments. Some are attracted to a magnetic field (paramagnetism); others are repulsed by a magnetic field (diamagnetism); others have a more complex relationship with an applied magnetic field (spin glass behavior and antiferromagnetism). Substances that are negligibly affected by magnetic fields are known as non-magnetic substances. These include copper, aluminium, gases, and plastic. Pure oxygen exhibits magnetic properties when cooled to a liquid state.The magnetic state (or magnetic phase) of a material depends on temperature and other variables such as pressure and the applied magnetic field. A material may exhibit more than one form of magnetism as these variables change.
















![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001677438_1-6f2ee9f2e116a6ee3a90ac77f126c6b0-300x300.png)





