F1004
... The Electricity and Magnetism course has as purpose that the students use the electrical and magnetic charge interactions in the functioning of simple devices, and the knowledge of electricity and magnetism to delve deeper in advanced topics such as electromagnetic fields. Course objective: By the e ...
... The Electricity and Magnetism course has as purpose that the students use the electrical and magnetic charge interactions in the functioning of simple devices, and the knowledge of electricity and magnetism to delve deeper in advanced topics such as electromagnetic fields. Course objective: By the e ...
Electricity and Magnetism - Blountstown Middle School
... places their hand on the ball and the machine is turned on, electrons are transferred to and collected on the person touching the silver ball. ...
... places their hand on the ball and the machine is turned on, electrons are transferred to and collected on the person touching the silver ball. ...
Electric Fields and Potential
... 1. Field lines must begin on positive charges or at infinity and must terminate on negative charges or at infinity. 2. The number of lines drawn leaving a positive charge or approaching a negative charge is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. 3. No two field lines from the same field can cr ...
... 1. Field lines must begin on positive charges or at infinity and must terminate on negative charges or at infinity. 2. The number of lines drawn leaving a positive charge or approaching a negative charge is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. 3. No two field lines from the same field can cr ...
Chapter 4
... RAD 350 Chapter 4 Electricity, Magnetism and Electromagnetism I. The primary purpose of an x-ray tube is to convert electric energy into electromagnetic energy or x-rays -energy conversion is around us everywhere -electricity created the heat in a hair dryer or toaster -chemical energy cranks the st ...
... RAD 350 Chapter 4 Electricity, Magnetism and Electromagnetism I. The primary purpose of an x-ray tube is to convert electric energy into electromagnetic energy or x-rays -energy conversion is around us everywhere -electricity created the heat in a hair dryer or toaster -chemical energy cranks the st ...
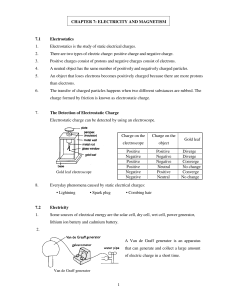
1 CHAPTER 7: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 7.1
... Electrostatics is the study of static electrical charges. ...
... Electrostatics is the study of static electrical charges. ...
Welcome Back Scientists!
... http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/legacy/faraday https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yA8gZM3fghc So magnetic fields can cause electrons to move in a wire And electrons moving in a wire is called… Electricity!!! – so the reverse process of a motor GENERATES electricity (what do you think w ...
... http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/legacy/faraday https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yA8gZM3fghc So magnetic fields can cause electrons to move in a wire And electrons moving in a wire is called… Electricity!!! – so the reverse process of a motor GENERATES electricity (what do you think w ...
Sample - Rose
... b) Determine the electric field at the center of the of the circle when the switch is closed. Assume that the resultant charges are uniformly distributed along the whole 180 degree segment. Do not substitute numbers in the equation in the beginning. ...
... b) Determine the electric field at the center of the of the circle when the switch is closed. Assume that the resultant charges are uniformly distributed along the whole 180 degree segment. Do not substitute numbers in the equation in the beginning. ...
Step 3: Electricity
... Electricity Science of Energy Station Six Teaches Students About The Relationship Between Magnetism and Electricity Shows Electricity Can Be Changed To Other Forms Of Energy Demonstrates How We Use Various Sources of Energy to Generate Electricity in A Power Plant ...
... Electricity Science of Energy Station Six Teaches Students About The Relationship Between Magnetism and Electricity Shows Electricity Can Be Changed To Other Forms Of Energy Demonstrates How We Use Various Sources of Energy to Generate Electricity in A Power Plant ...
Electricity

Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and electric current. In addition, electricity permits the creation and reception of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves.In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. electric field (see electrostatics): an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving (i.e., there is no electric current). The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts. electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes. electromagnets: Moving charges produce a magnetic field. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields generate electric currents.In electrical engineering, electricity is used for: electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment; electronics which deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies.Electrical phenomena have been studied since antiquity, though progress in theoretical understanding remained slow until the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Even then, practical applications for electricity were few, and it would not be until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put it to industrial and residential use. The rapid expansion in electrical technology at this time transformed industry and society. Electricity's extraordinary versatility means it can be put to an almost limitless set of applications which include transport, heating, lighting, communications, and computation. Electrical power is now the backbone of modern industrial society.