the electric force of a current: weber and the surface charge of
... How often do you often read a book that has a large number of ‘aha!’ moments? This is a significant piece of scholarship that penetrates into a rather common misconception, no force on a stationary charge outside a current carrying wire, to elucidate its cause of error and to present the correct and ...
... How often do you often read a book that has a large number of ‘aha!’ moments? This is a significant piece of scholarship that penetrates into a rather common misconception, no force on a stationary charge outside a current carrying wire, to elucidate its cause of error and to present the correct and ...
Chapter 5
... Dynamic Electricity • Dynamic means “moving” • Dynamic electricity describes all of the phenomena related to electrical charges in motion. • Charges move when they are free to do so, namely when they are in contact with conductors ...
... Dynamic Electricity • Dynamic means “moving” • Dynamic electricity describes all of the phenomena related to electrical charges in motion. • Charges move when they are free to do so, namely when they are in contact with conductors ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant
... The rate at which energy is transferred from the source of motion is equal to the electrical power supplied to the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical ...
... The rate at which energy is transferred from the source of motion is equal to the electrical power supplied to the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical ...
Physics_A2_37_GeneratingElectricity
... The rate at which energy is transferred from the source of motion is equal to the electrical power supplied to the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical ...
... The rate at which energy is transferred from the source of motion is equal to the electrical power supplied to the components in the circuit : Electrical power = induced EMF x Current (voltage) Induced EMF is the energy supplied to each unit charge & current is the charge flow per second Electrical ...
Electricity Review Questions
... How can you increase the magnetic field in an electromagnet or solenoid? Add more coils of wire or increase current. ...
... How can you increase the magnetic field in an electromagnet or solenoid? Add more coils of wire or increase current. ...
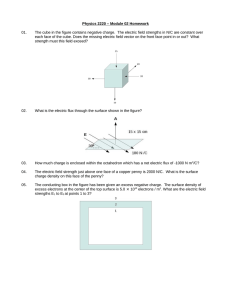
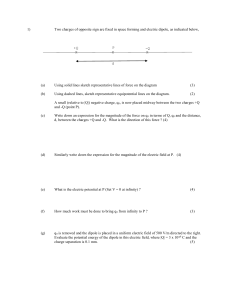
1) Two charges of opposite sign are fixed in space forming and
... A plastic rod is formed into a circle of radius R. It has a positive charge +Q uniformly distributed along one-third of its circumference and a negative charge of -4Q uniformly distributed along the rest of the circumference as shown. ...
... A plastic rod is formed into a circle of radius R. It has a positive charge +Q uniformly distributed along one-third of its circumference and a negative charge of -4Q uniformly distributed along the rest of the circumference as shown. ...
t299-1-03f
... . Use Gauss’ law to obtain expressions for the electric field in the three regions. In each case clearly define the Gaussian surface you are using and your assumptions about the electric field. (a) ...
... . Use Gauss’ law to obtain expressions for the electric field in the three regions. In each case clearly define the Gaussian surface you are using and your assumptions about the electric field. (a) ...
21-5M How are Electricity
... 5. DESCRIBE: What determines the direction of electric current in a wire when a magnet is moved around the wire? ...
... 5. DESCRIBE: What determines the direction of electric current in a wire when a magnet is moved around the wire? ...
Lecture 7 Extra
... current. With the magnetic permeability established, the electric permittivity takes the value given by the relationship ...
... current. With the magnetic permeability established, the electric permittivity takes the value given by the relationship ...
CHAPTER 3 QUIZ – ELECTROMAGNETISM
... An ELECTROMAGNET is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a GALVANOMETER. OERSTED found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a SOLENOID. ELECTROMAGNETISM is the relationship between ...
... An ELECTROMAGNET is a solenoid with iron in the middle of it. An instrument used to detect small currents is called a GALVANOMETER. OERSTED found that an electric current created a magnetic field. A long coil of wire with many loops is called a SOLENOID. ELECTROMAGNETISM is the relationship between ...
Electricity

Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and electric current. In addition, electricity permits the creation and reception of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves.In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. electric field (see electrostatics): an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving (i.e., there is no electric current). The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts. electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes. electromagnets: Moving charges produce a magnetic field. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields generate electric currents.In electrical engineering, electricity is used for: electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment; electronics which deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies.Electrical phenomena have been studied since antiquity, though progress in theoretical understanding remained slow until the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Even then, practical applications for electricity were few, and it would not be until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put it to industrial and residential use. The rapid expansion in electrical technology at this time transformed industry and society. Electricity's extraordinary versatility means it can be put to an almost limitless set of applications which include transport, heating, lighting, communications, and computation. Electrical power is now the backbone of modern industrial society.