Electricity
... another object, leaving that object with a positive charge. Induction occurs as a result of the interaction of the electric fields around two objects that are not in contact. ...
... another object, leaving that object with a positive charge. Induction occurs as a result of the interaction of the electric fields around two objects that are not in contact. ...
SA1 REVISION WORKSHEET 2
... point directly above it? 9. Draw the patterns of magnetic field lines through and around a current carrying solenoid. What does the magnetic field pattern inside the solenoid indicate? (A)How can this principle be utilized to make an electromagnet? (B) State two ways by which strength of this electr ...
... point directly above it? 9. Draw the patterns of magnetic field lines through and around a current carrying solenoid. What does the magnetic field pattern inside the solenoid indicate? (A)How can this principle be utilized to make an electromagnet? (B) State two ways by which strength of this electr ...
Q- (a) A positive ion of mass m and charge q, initially at rest is
... The potential is the energy stored per unit charge hence the difference in the electrostatic potential energy of charge q1 when the potential is change by V is given by qV Thus the loss in electrostatic potential energy when the charge is accelerated through a potential difference V is qV. As there ...
... The potential is the energy stored per unit charge hence the difference in the electrostatic potential energy of charge q1 when the potential is change by V is given by qV Thus the loss in electrostatic potential energy when the charge is accelerated through a potential difference V is qV. As there ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... Permission is granted for the purchaser to print copies for non-commercial educational purposes only. Visit us at www.NewPathLearning.com. ...
... Permission is granted for the purchaser to print copies for non-commercial educational purposes only. Visit us at www.NewPathLearning.com. ...
Grade-Level Domain MAP
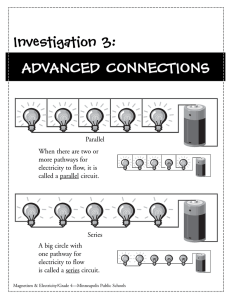
... Short circuit: sudden surge of amperage due to the reduction of resistance in a circuit; protection from short circuits is achieved by fuses and circuit breakers ...
... Short circuit: sudden surge of amperage due to the reduction of resistance in a circuit; protection from short circuits is achieved by fuses and circuit breakers ...
electrictiy note packet Unit 6
... gravity = determined by the distance (height) from Earth (Newton's law) ...
... gravity = determined by the distance (height) from Earth (Newton's law) ...
introduction
... Electricity, all the phenomena that result from the interaction of electrical charges. Electric and magnetic effects are caused by the relative positions and movements of charged particles of matter. When a charge is stationary (static), it produces electrostatic forces on charged objects, and when ...
... Electricity, all the phenomena that result from the interaction of electrical charges. Electric and magnetic effects are caused by the relative positions and movements of charged particles of matter. When a charge is stationary (static), it produces electrostatic forces on charged objects, and when ...
Discovering Electricity
... new science that he named ‘electrodynamics’, which is called electromagnetism today. In 1820 he discovered that a magnetic attraction or repulsion existed between two wires carrying current, depending on the direction of the flow. He developed a mathematical theory about the relationship between ele ...
... new science that he named ‘electrodynamics’, which is called electromagnetism today. In 1820 he discovered that a magnetic attraction or repulsion existed between two wires carrying current, depending on the direction of the flow. He developed a mathematical theory about the relationship between ele ...
Electricity

Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and flow of electric charge. Electricity gives a wide variety of well-known effects, such as lightning, static electricity, electromagnetic induction and electric current. In addition, electricity permits the creation and reception of electromagnetic radiation such as radio waves.In electricity, charges produce electromagnetic fields which act on other charges. Electricity occurs due to several types of physics: electric charge: a property of some subatomic particles, which determines their electromagnetic interactions. Electrically charged matter is influenced by, and produces, electromagnetic fields. electric field (see electrostatics): an especially simple type of electromagnetic field produced by an electric charge even when it is not moving (i.e., there is no electric current). The electric field produces a force on other charges in its vicinity. electric potential: the capacity of an electric field to do work on an electric charge, typically measured in volts. electric current: a movement or flow of electrically charged particles, typically measured in amperes. electromagnets: Moving charges produce a magnetic field. Electric currents generate magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields generate electric currents.In electrical engineering, electricity is used for: electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment; electronics which deals with electrical circuits that involve active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies.Electrical phenomena have been studied since antiquity, though progress in theoretical understanding remained slow until the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Even then, practical applications for electricity were few, and it would not be until the late nineteenth century that engineers were able to put it to industrial and residential use. The rapid expansion in electrical technology at this time transformed industry and society. Electricity's extraordinary versatility means it can be put to an almost limitless set of applications which include transport, heating, lighting, communications, and computation. Electrical power is now the backbone of modern industrial society.