Magnetism Study Guide and Review WS
... magnet in an arched pattern and show us that the effect of a magnet is strongest at its poles. In this picture, you can see the magnetic field because small pieces of iron have been placed under the magnet. The pieces align themselves along the lines of force and show us the magnet’s magnetic field. ...
... magnet in an arched pattern and show us that the effect of a magnet is strongest at its poles. In this picture, you can see the magnetic field because small pieces of iron have been placed under the magnet. The pieces align themselves along the lines of force and show us the magnet’s magnetic field. ...
B.Sc. PHYSICS GE Syllabus Under CHOICE BASED CREDIT
... uniformly charged spherical shell and solid sphere, plane charged sheet, charged conductor. Electric potential as line integral of electric field, potential due to a point charge, electric dipole, uniformly charged spherical shell and solid sphere. Calculation of electric field from potential. Capac ...
... uniformly charged spherical shell and solid sphere, plane charged sheet, charged conductor. Electric potential as line integral of electric field, potential due to a point charge, electric dipole, uniformly charged spherical shell and solid sphere. Calculation of electric field from potential. Capac ...
History of Magnetism - School of Applied Non
... repelling each other, keeping the nucleus (centre) of the atom together and stable. To date we have no knowledge of exactly where magnetism comes from, the most popular theory is summarized here: The protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, as seen in the drawing and the electron ...
... repelling each other, keeping the nucleus (centre) of the atom together and stable. To date we have no knowledge of exactly where magnetism comes from, the most popular theory is summarized here: The protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, as seen in the drawing and the electron ...
RIN #1 POWER FREQUENCY ELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC FIELDS
... continued to show that these fields can interact with biological systems. However the results to date have not provided conclusive evidence that these fields and their interactions cause adverse health effects, such as cancer. ...
... continued to show that these fields can interact with biological systems. However the results to date have not provided conclusive evidence that these fields and their interactions cause adverse health effects, such as cancer. ...
Electromagnetic Induction
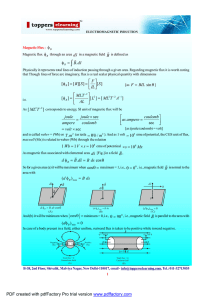
... (a) A curent from A to B is increasing in magnetude. What is the direction of induced current, if any in the loop shown in Fig. (b) If inslead of current it is an electron, what will happen ? Answer : (a) When current in the wire AB increases, the flux linked with the loop (which is out of the page) ...
... (a) A curent from A to B is increasing in magnetude. What is the direction of induced current, if any in the loop shown in Fig. (b) If inslead of current it is an electron, what will happen ? Answer : (a) When current in the wire AB increases, the flux linked with the loop (which is out of the page) ...
Magnet
... the wire to either side of the battery, the positive and the negative side. Then you put one wire going up one side of the battery and one going up on the other side. So the wires go up on either side of the battery like a circle. Then the light bulb has to be touching the copper parts on the end of ...
... the wire to either side of the battery, the positive and the negative side. Then you put one wire going up one side of the battery and one going up on the other side. So the wires go up on either side of the battery like a circle. Then the light bulb has to be touching the copper parts on the end of ...
TEP Earth`s magnetic field with Cobra4 Mobile
... “north/south” of the magnetic needle, the needle should be slightly turned away from its resting position several times. Possible friction resistance can be reduced by gently tapping the instrument. In order to determine the horizontal component hBE of the earth-magnetic field, the deflection angle ...
... “north/south” of the magnetic needle, the needle should be slightly turned away from its resting position several times. Possible friction resistance can be reduced by gently tapping the instrument. In order to determine the horizontal component hBE of the earth-magnetic field, the deflection angle ...
Effects of high static magnetic fields in magnetic resonance imaging
... Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an examination method without ionizing radiation to map structures or functions of tissues and organs using their different magnetic properties. A better signalto-noise ratio led to growing magnetic field strengths in today’s MR scanners resulting in a better reso ...
... Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is an examination method without ionizing radiation to map structures or functions of tissues and organs using their different magnetic properties. A better signalto-noise ratio led to growing magnetic field strengths in today’s MR scanners resulting in a better reso ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.