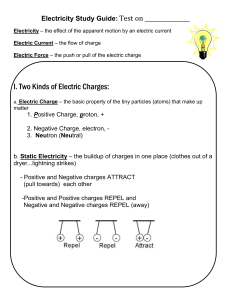
Electric Charge
... b. Electromagnet – a temporary magnet made by wrapping a coil carrying a current around an iron core. Created by wrapping a wire around an iron core (nail) and connecting both ends of the wire to a battery The electric current flows through the coiled wire and charges the ...
... b. Electromagnet – a temporary magnet made by wrapping a coil carrying a current around an iron core. Created by wrapping a wire around an iron core (nail) and connecting both ends of the wire to a battery The electric current flows through the coiled wire and charges the ...
WELCOME TO PHYSICS 1103
... •How do electric motors work? •What causes a changing magnetic field in a motor? •How do electric generators work? ...
... •How do electric motors work? •What causes a changing magnetic field in a motor? •How do electric generators work? ...
ch 1-Complex representation of EM waves
... ε can be determined via measurements on a parallel plate capacitor filled with a given material using the equation C=εA/d ...
... ε can be determined via measurements on a parallel plate capacitor filled with a given material using the equation C=εA/d ...
Electricity and Magnetism
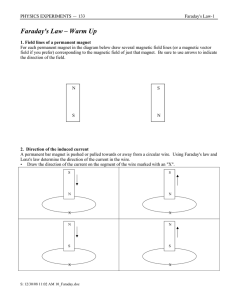
... depends on the direction that the current is flowing through the wire. A simple rule, called the right hand rule, makes it easy to find the direction of the magnetic field if the direction of the current is known. The right hand rule is illustrated in Figure 1.3. When the thumb of the right hand is ...
... depends on the direction that the current is flowing through the wire. A simple rule, called the right hand rule, makes it easy to find the direction of the magnetic field if the direction of the current is known. The right hand rule is illustrated in Figure 1.3. When the thumb of the right hand is ...
Particle motion (powerpoint)
... The force accelerates the particle leading to a higher velocity The higher velocity however means a larger Larmor radius The circular orbit no longer closes on itself A drift results. ...
... The force accelerates the particle leading to a higher velocity The higher velocity however means a larger Larmor radius The circular orbit no longer closes on itself A drift results. ...
B - LSU Physics
... 30.4.4. A coil of wire that forms a complete loop is moving with a constant speed v toward a very long, current carrying wire, only a portion of which is shown. What affect, if any, does the current carrying wire have on the coil of wire? a) Since the magnetic field increases as the coil approaches ...
... 30.4.4. A coil of wire that forms a complete loop is moving with a constant speed v toward a very long, current carrying wire, only a portion of which is shown. What affect, if any, does the current carrying wire have on the coil of wire? a) Since the magnetic field increases as the coil approaches ...
1B11 Foundations of Astronomy Star names and magnitudes
... •These “separate” plasma cells are partitioned by thin current sheets, which support the change in magnetic fields across the boundary. Recall: ...
... •These “separate” plasma cells are partitioned by thin current sheets, which support the change in magnetic fields across the boundary. Recall: ...
1 Electric field of a discrete charge distribution (4 points) 2 Electric
... Calculate the electric fields for the following charge distributions. a) The field (both components, Ex and Ey ) in the center of a half ring with radius R (see Fig.2) and uniformly distributed charge Q. (2 points) b) The field E(r) of a spherically symmetric charge distribution with total charge Q, ...
... Calculate the electric fields for the following charge distributions. a) The field (both components, Ex and Ey ) in the center of a half ring with radius R (see Fig.2) and uniformly distributed charge Q. (2 points) b) The field E(r) of a spherically symmetric charge distribution with total charge Q, ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.