1. A bar magnet is broken in half. Each half is broken in half again
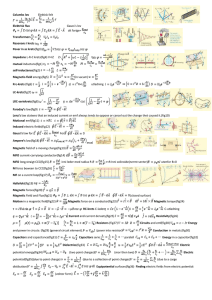
... 2. Maxwell's great contribution to electromagnetic theory was his hypothesis that: A) work is required to move a magnetic pole through a closed path surrounding a current B) a time-varying electric flux acts as a current for purposes of producing a magnetic field C) the speed of light could be deter ...
... 2. Maxwell's great contribution to electromagnetic theory was his hypothesis that: A) work is required to move a magnetic pole through a closed path surrounding a current B) a time-varying electric flux acts as a current for purposes of producing a magnetic field C) the speed of light could be deter ...
Notes–Maxwell`s Equations
... When to Use Normally used to determine the electric field due to some geometry of charge. If a “Gaussian Surface” is picked carefully such that the E-field has uniform intensity at all points, E comes out of the integral. Implies that if qencl = 0, the E-field must also be zero. Never, unless to pro ...
... When to Use Normally used to determine the electric field due to some geometry of charge. If a “Gaussian Surface” is picked carefully such that the E-field has uniform intensity at all points, E comes out of the integral. Implies that if qencl = 0, the E-field must also be zero. Never, unless to pro ...
DEVICE TOPIC THEORETICAL Lenz’s Law Demonstration
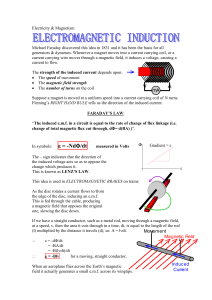
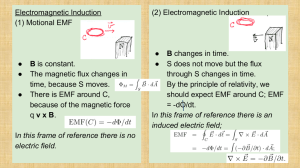
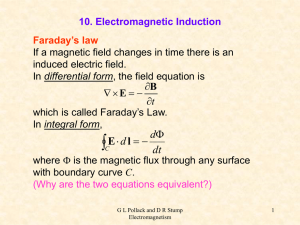
... Faraday’s Law of induction states that an electric current can be produced by a changing magnetic field. The direction of the induced emf and induced current is determined from Lenz’s Law which states that the polarity of the induced emf is such that it tends to produce a current that will create a ...
... Faraday’s Law of induction states that an electric current can be produced by a changing magnetic field. The direction of the induced emf and induced current is determined from Lenz’s Law which states that the polarity of the induced emf is such that it tends to produce a current that will create a ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.