Magnetic Fields & Magnetic Field Strength
... • We have seen that magnets can exert a force on objects without touching them. For this reason we speak of a magnetic field around a magnet, in the same way that we speak of an electric field around a charged object. ...
... • We have seen that magnets can exert a force on objects without touching them. For this reason we speak of a magnetic field around a magnet, in the same way that we speak of an electric field around a charged object. ...
di/dt - s3.amazonaws.com
... uniform magnetic field. A magnetic field with a magnitude of 1.5 T is directed along the positive z-direction, which is upward. a) If the loop is removed from the field region in a time interval of 2.010-3 s, find the average emf that will be induced in the wire loop during the extraction process. ...
... uniform magnetic field. A magnetic field with a magnitude of 1.5 T is directed along the positive z-direction, which is upward. a) If the loop is removed from the field region in a time interval of 2.010-3 s, find the average emf that will be induced in the wire loop during the extraction process. ...
1 - tamta
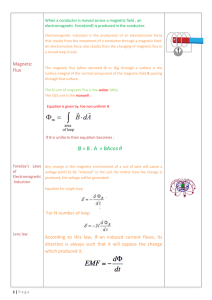
... To find the total amount of flux passing through area A, we need to multiply the magnetic flux density B by the number of square meters in area A. This can be expressed mathematically as flux = flux density × area, or ...
... To find the total amount of flux passing through area A, we need to multiply the magnetic flux density B by the number of square meters in area A. This can be expressed mathematically as flux = flux density × area, or ...
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction
... – The motion of a magnet can induce current in practical ways. If a credit card has a magnet strip on its back, “swiping” the card can generate tiny currents that send information to cash registers. – A coil of wire and magnets set into motion around each other will generate currents in the wire. A ...
... – The motion of a magnet can induce current in practical ways. If a credit card has a magnet strip on its back, “swiping” the card can generate tiny currents that send information to cash registers. – A coil of wire and magnets set into motion around each other will generate currents in the wire. A ...
PHY2054_f11-10
... The secondary circuit acts as if a source of emf were connected to it for a short time ...
... The secondary circuit acts as if a source of emf were connected to it for a short time ...
Faraday paradox

This article describes the Faraday paradox in electromagnetism. There are many Faraday paradoxs in electrochemistry: see Faraday paradox (electrochemistry).The Faraday paradox (or Faraday's paradox) is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes:1. Faraday's law predicts that there will be zero EMF but there is a non-zero EMF.2. Faraday's law predicts that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is a zero EMF.Faraday deduced this law in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox.