Electromagnetic waves
... At any instant the fields are uniform over any plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation with speed c The entire pattern travels in the direction of propagation Electric and magnetic field are still transverse to the propagation direction at ...
... At any instant the fields are uniform over any plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation with speed c The entire pattern travels in the direction of propagation Electric and magnetic field are still transverse to the propagation direction at ...
Measurement of Electromagnetic Radiation Emitted during Rapid
... convolution of two cos2 θ distributions whose axes are at an angle of ζ with respect each other. The interaction of the static electric field with a dipolar molecule in solution results in fractional alignment of the molecules along the field direction. This fractional alignment can be calculated by ...
... convolution of two cos2 θ distributions whose axes are at an angle of ζ with respect each other. The interaction of the static electric field with a dipolar molecule in solution results in fractional alignment of the molecules along the field direction. This fractional alignment can be calculated by ...
Hyperfine Splitting and Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism of Ni at Multimegabar Pressure
... ferromagnetic up to this pressure, the highest pressure where magnetism in any material has been observed so far. Experimental observations are confirmed by theoretical ab initio DFT calculations, which reproduce the peculiar pressure dependence of the hyperfine field, and reveal that it is a clear ...
... ferromagnetic up to this pressure, the highest pressure where magnetism in any material has been observed so far. Experimental observations are confirmed by theoretical ab initio DFT calculations, which reproduce the peculiar pressure dependence of the hyperfine field, and reveal that it is a clear ...
Models of Simple Iron Cored Electromagnets
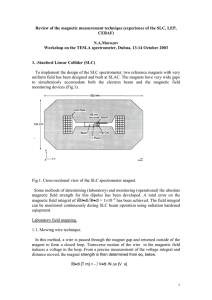
... initial value for the simulation results or a good guess for the non-linear solver [3]. Default XYZ components of the vector are 0 Wb/m and they are unchanged for this model, too. 3.1 Multi-turn Coil A Multi-Turn Coil represents the current carrying coil (Domain 2) and as the name suggests it consis ...
... initial value for the simulation results or a good guess for the non-linear solver [3]. Default XYZ components of the vector are 0 Wb/m and they are unchanged for this model, too. 3.1 Multi-turn Coil A Multi-Turn Coil represents the current carrying coil (Domain 2) and as the name suggests it consis ...
Compasstech
... 3. The vertical component of the earth's field is much stronger than the horizontal component (dip angle). 4. The dynamic conditions (accelerations) of the application prevent consistent measurement of the earth's horizontal magnetic field with the available compass technology. These problems must b ...
... 3. The vertical component of the earth's field is much stronger than the horizontal component (dip angle). 4. The dynamic conditions (accelerations) of the application prevent consistent measurement of the earth's horizontal magnetic field with the available compass technology. These problems must b ...
Force between magnets
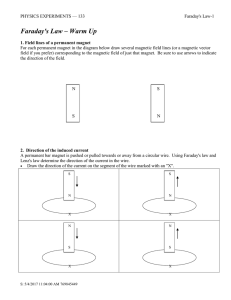
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.