Lecture 23 Chapter 31 Induction and Inductance
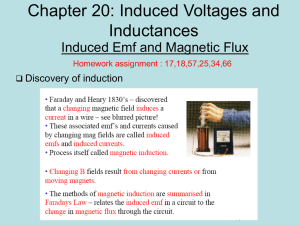
... • Faraday observed that an induced current (and an induced emf) can be generated in a loop of wire by: – Moving a permanent magnet in or out of the loop – Holding it close to a coil (solenoid) and changing the current in the coil – Keep the current in the coil constant but move the coil relative to ...
... • Faraday observed that an induced current (and an induced emf) can be generated in a loop of wire by: – Moving a permanent magnet in or out of the loop – Holding it close to a coil (solenoid) and changing the current in the coil – Keep the current in the coil constant but move the coil relative to ...
Lecture20
... the loop (B proportional to I). - Flux through the loop increases with I. - Emf induced to oppose the initial direction of the current flow. - Self-induction: changing the current through the loop inducing an opposing emf the loop. ...
... the loop (B proportional to I). - Flux through the loop increases with I. - Emf induced to oppose the initial direction of the current flow. - Self-induction: changing the current through the loop inducing an opposing emf the loop. ...
PHYS 196 Class Problem 1
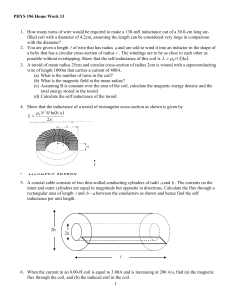
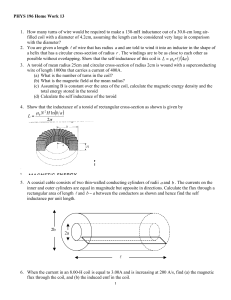
... 9. A coil that has self-inductance of 2.00-H and a resistance of 12.0-Ω is connected to an ideal 24.0-V battery. (a) What is the steady current? (b) How much energy is stored in the inductor when the steadystate current is established? 10. A 200-turn solenoid has a cross-sectional area equal to 4.0c ...
... 9. A coil that has self-inductance of 2.00-H and a resistance of 12.0-Ω is connected to an ideal 24.0-V battery. (a) What is the steady current? (b) How much energy is stored in the inductor when the steadystate current is established? 10. A 200-turn solenoid has a cross-sectional area equal to 4.0c ...
Estimation of Magnetic Torquing and Momentum
... It may be more reasonable to base our magnetic moment and momentum storage requirements off of a momentum dumping scheme that limits its dumping of momentum more than the previously analyzed minimum magnetic moment method. Such a strategy will require higher magnetic moment, but will probably not re ...
... It may be more reasonable to base our magnetic moment and momentum storage requirements off of a momentum dumping scheme that limits its dumping of momentum more than the previously analyzed minimum magnetic moment method. Such a strategy will require higher magnetic moment, but will probably not re ...
Sample Lesson - Press For Learning
... • An electric current flowing through a wire creates a magnetic field around it. • If the wire is wrapped around an iron core, the magnetic field produced by the flow of current makes the iron core act as a magnet. Next, pose the question: Does the iron core (the nail) have to be present in order fo ...
... • An electric current flowing through a wire creates a magnetic field around it. • If the wire is wrapped around an iron core, the magnetic field produced by the flow of current makes the iron core act as a magnet. Next, pose the question: Does the iron core (the nail) have to be present in order fo ...
Lab 5: Mag-Lev Controller
... and the common lead (black mini-grabber) to ground. Adjust the voltage at VCollector to 3 Volts using Pot#4 (10k). The adjustment is as follows: VCollector > 3 volts – This means there is not enough current flowing through the magnet and the transistor to produce a large enough magnetic field to s ...
... and the common lead (black mini-grabber) to ground. Adjust the voltage at VCollector to 3 Volts using Pot#4 (10k). The adjustment is as follows: VCollector > 3 volts – This means there is not enough current flowing through the magnet and the transistor to produce a large enough magnetic field to s ...
Magnetic Fields and Magnetic Field Lines
... 1. The direction of the magnetic eld is tangent to the eld line at any point in space. A small compass will point in the direction of the eld line. 2. The strength of the eld is proportional to the closeness of the lines. It is exactly proportional to the number of lines per unit area perpendicu ...
... 1. The direction of the magnetic eld is tangent to the eld line at any point in space. A small compass will point in the direction of the eld line. 2. The strength of the eld is proportional to the closeness of the lines. It is exactly proportional to the number of lines per unit area perpendicu ...
Document
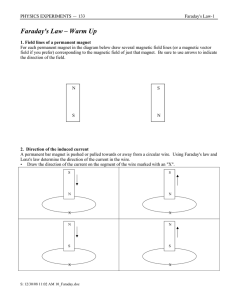
... The rectangular loop shown is pushed into the magnetic field which points inward. In what direction is the induced current? ...
... The rectangular loop shown is pushed into the magnetic field which points inward. In what direction is the induced current? ...
THE EFFECT OF MAGNETIC FIELD ON WATER HARDNESS
... treatment with an applied magnetic field has been known for many years and has been reported as being effective in numerous instances (Kobe et al [15]). Despite its ubiquity this science, there is relatively little scientific literature on magnetic water treatment. It is not clear how or even if, it ...
... treatment with an applied magnetic field has been known for many years and has been reported as being effective in numerous instances (Kobe et al [15]). Despite its ubiquity this science, there is relatively little scientific literature on magnetic water treatment. It is not clear how or even if, it ...
Force between magnets
Magnets exert forces and torques on each other due to the complex rules of electromagnetism. The forces of attraction field of magnets are due to microscopic currents of electrically charged electrons orbiting nuclei and the intrinsic magnetism of fundamental particles (such as electrons) that make up the material. Both of these are modeled quite well as tiny loops of current called magnetic dipoles that produce their own magnetic field and are affected by external magnetic fields. The most elementary force between magnets, therefore, is the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction. If all of the magnetic dipoles that make up two magnets are known then the net force on both magnets can be determined by summing up all these interactions between the dipoles of the first magnet and that of the second.It is always more convenient to model the force between two magnets as being due to forces between magnetic poles having magnetic charges 'smeared' over them. Such a model fails to account for many important properties of magnetism such as the relationship between angular momentum and magnetic dipoles. Further, magnetic charge does not exist. This model works quite well, though, in predicting the forces between simple magnets where good models of how the 'magnetic charge' is distributed is available.