File
... ______________ – Region of influence surrounding an object. (Think about baseball fields, battlefield, football field, etc.) A field model can be used to explain how 2 objects exerting (applying) forces on each other without touching. When a second object is placed in this region, the field exer ...
... ______________ – Region of influence surrounding an object. (Think about baseball fields, battlefield, football field, etc.) A field model can be used to explain how 2 objects exerting (applying) forces on each other without touching. When a second object is placed in this region, the field exer ...
1. A magnetic compass needle is placed in the plane... as shown in Figure. In which plane should a straight... X- Guess Questions solved SA-1: Magnetic effects of currents
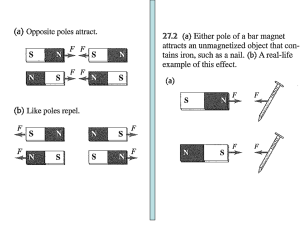
... field. This modifies the already existing earth’s magnetic field and a deflection results. Magnetic field has both direction and magnitude. Magnetic field lines emerge from N-pole and enter Spole. The magnetic field strength is represented diagrammatically by the degree of closeness of the field lin ...
... field. This modifies the already existing earth’s magnetic field and a deflection results. Magnetic field has both direction and magnitude. Magnetic field lines emerge from N-pole and enter Spole. The magnetic field strength is represented diagrammatically by the degree of closeness of the field lin ...
Maxwell`s Equations
... which is just c, the speed of light. Thus, for Maxwell’s equations to be correct in all reference frames we are led to Einstein’s theory of Special Relativity! The wavenumber k is actually a vector, as is the velocity v. They both point in the direction of the traveling wave. Notice that as time inc ...
... which is just c, the speed of light. Thus, for Maxwell’s equations to be correct in all reference frames we are led to Einstein’s theory of Special Relativity! The wavenumber k is actually a vector, as is the velocity v. They both point in the direction of the traveling wave. Notice that as time inc ...
Magnetism and its uses
... Each spinning electron causes a magnetic field to form around it. Most materials have electrons that exist in pairs that spin in opposite directions thus canceling out the magnetic field. The atoms in materials such as iron, cobalt and nickel have unpaired electrons, so the electrons' magnetic field ...
... Each spinning electron causes a magnetic field to form around it. Most materials have electrons that exist in pairs that spin in opposite directions thus canceling out the magnetic field. The atoms in materials such as iron, cobalt and nickel have unpaired electrons, so the electrons' magnetic field ...
EE-0903251-Electromagnetics I-Sep-2014-Fall
... Electric dipole, electric polarization, capacitors and boundary conditions. Poisson's and Laplace's equations. The method of images. Magnetic sources and fields: Line current, linear and surface current densities, Biot-Savart's law, Ampere's law, the curl and the Stock's theorem. Magnetic force, tor ...
... Electric dipole, electric polarization, capacitors and boundary conditions. Poisson's and Laplace's equations. The method of images. Magnetic sources and fields: Line current, linear and surface current densities, Biot-Savart's law, Ampere's law, the curl and the Stock's theorem. Magnetic force, tor ...
Magnetism
... 21.1 Magnets and Mag Fields How can a magnetic field affect a magnet that enters the field? ...
... 21.1 Magnets and Mag Fields How can a magnetic field affect a magnet that enters the field? ...
Motional emf
... The electric field is related to the potential difference across the wire as ∆V = EL, so that ∆V = EL = vBL so that as long as the rod moves through the magnetic filed, there is a potential difference across the rod. If the rod is part of a closed circuit loop so that the charges can flow around a l ...
... The electric field is related to the potential difference across the wire as ∆V = EL, so that ∆V = EL = vBL so that as long as the rod moves through the magnetic filed, there is a potential difference across the rod. If the rod is part of a closed circuit loop so that the charges can flow around a l ...
L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]
... • A compass needle is attracted to the earth’s north geographic pole • The earth’s magnetism is the magnetic north pole is due to currents flowing in inclined about 14° from the its molten core (not geographic north pole, or entirely understood!) by about 600 miles. ...
... • A compass needle is attracted to the earth’s north geographic pole • The earth’s magnetism is the magnetic north pole is due to currents flowing in inclined about 14° from the its molten core (not geographic north pole, or entirely understood!) by about 600 miles. ...
Layers of the Atmosphere
... Mesosphere 1. Meso = middle 2. 50 – 80 km above earth’s surface 3. As altitude increase, temperature decrease. 4. Meteorites burn up in the mesosphere – leaving a shooting star ...
... Mesosphere 1. Meso = middle 2. 50 – 80 km above earth’s surface 3. As altitude increase, temperature decrease. 4. Meteorites burn up in the mesosphere – leaving a shooting star ...
Electromagnetism
... secondary magnetic field (Self-induction). • The magnetic field resulting from an induced current is always opposite from the magnetic field that induced it (Lenz’s Law). • Oscillating electric and magnetic fields produce electromagnetic waves (e.g., light). ...
... secondary magnetic field (Self-induction). • The magnetic field resulting from an induced current is always opposite from the magnetic field that induced it (Lenz’s Law). • Oscillating electric and magnetic fields produce electromagnetic waves (e.g., light). ...
IOSR Journal of Mathematics (IOSR-JM)
... Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is concerned with the interaction of electrically conducting fluids and electromagnetic fields. When such fluid moves through a magnetic field, an electric field and consequently a current may be induced, and in turn the current interacts with the magnetic field to produce ...
... Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is concerned with the interaction of electrically conducting fluids and electromagnetic fields. When such fluid moves through a magnetic field, an electric field and consequently a current may be induced, and in turn the current interacts with the magnetic field to produce ...
Condensed_Magnetism in solids
... Langevin gave a satisfactory explanation of diamagnetism on the basis of electron theory the basic principle of which ia Lenz’s law in electromagnetic induction which states that when a magnetic flux linked with electric current due to revolving electrons is changed, an induced current is set up in ...
... Langevin gave a satisfactory explanation of diamagnetism on the basis of electron theory the basic principle of which ia Lenz’s law in electromagnetic induction which states that when a magnetic flux linked with electric current due to revolving electrons is changed, an induced current is set up in ...
Topic XIII – Waves and Sound - Science - Miami
... Describe how a current is affected by a magnetic field. Describe how magnetic fields are produced. Explain the relationship between moving charges and magnetic fields, as well as changing magnetic fields and electric fields Describe how a magnetic field exerts a force on a charged particle i ...
... Describe how a current is affected by a magnetic field. Describe how magnetic fields are produced. Explain the relationship between moving charges and magnetic fields, as well as changing magnetic fields and electric fields Describe how a magnetic field exerts a force on a charged particle i ...
Slide 1
... primary coil. • The output of the transformer is connected to the secondary coil. • The two coils have different numbers of turns to convert from one voltage to another. ...
... primary coil. • The output of the transformer is connected to the secondary coil. • The two coils have different numbers of turns to convert from one voltage to another. ...
Lecture 1 - web page for staff
... • Knowledge of fields in media and boundary conditions allows useful applications of material properties to microwave components • A uniform plane wave, both electric and magnetic fields lie in the transverse plane, the plane whose normal is the direction of propagation ...
... • Knowledge of fields in media and boundary conditions allows useful applications of material properties to microwave components • A uniform plane wave, both electric and magnetic fields lie in the transverse plane, the plane whose normal is the direction of propagation ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.











![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008057814_1-60bd3a273eeadb9e6de7a28a98376c5d-300x300.png)