Electricity & Magnetism
... Magnetism is produced by two motions of electrons… their spin and their orbiting motion about the nucleus The space around a moving electric charge is “altered”… the alteration is called a magnetic field ...
... Magnetism is produced by two motions of electrons… their spin and their orbiting motion about the nucleus The space around a moving electric charge is “altered”… the alteration is called a magnetic field ...
Magnetic Induction
... • If you move a conductor in a magnetic field, the “free” electrons experience a Force of F=qv x B, they tend to move, that’s a current! • Voltage induced in a conductor moving through a magnetic field • Current induced in a conducting loop ...
... • If you move a conductor in a magnetic field, the “free” electrons experience a Force of F=qv x B, they tend to move, that’s a current! • Voltage induced in a conductor moving through a magnetic field • Current induced in a conducting loop ...
Continental Drift Continental Drift Continental Drift
... will be horizontal – Anywhere in-between, the orientation will be at some angle ...
... will be horizontal – Anywhere in-between, the orientation will be at some angle ...
Document
... 1996, Kudoh et al. 1998). It is also assumed that there exists a corona outside the disk with uniformly high temperature. The corona is in hydrostatic equilibrium without rotation. The initial magnetic field is assumed to be uniform and parallel to the rotation axis of the disk; (Br, Bφ, Bz) = (0, 0 ...
... 1996, Kudoh et al. 1998). It is also assumed that there exists a corona outside the disk with uniformly high temperature. The corona is in hydrostatic equilibrium without rotation. The initial magnetic field is assumed to be uniform and parallel to the rotation axis of the disk; (Br, Bφ, Bz) = (0, 0 ...
SPH 3U(G) TEST
... Which statement about the magnetic north pole of Earth is true? a. Its location never changes. b. It corresponds to the N-pole of a bar magnet. c. It is at the same location as the geographic north pole of Earth. d. It corresponds to the S-pole of a bar magnet. e. both A and D ...
... Which statement about the magnetic north pole of Earth is true? a. Its location never changes. b. It corresponds to the N-pole of a bar magnet. c. It is at the same location as the geographic north pole of Earth. d. It corresponds to the S-pole of a bar magnet. e. both A and D ...
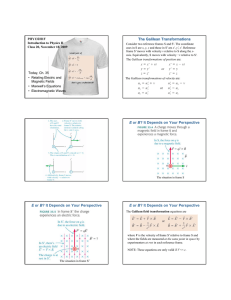
The Galilean Transformations E or B?
... Maxwell, using his equations of the electromagnetic field, was the first to understand that light is an oscillation of the electromagnetic field. Maxwell was able to predict that • Electromagnetic waves can exist at any frequency, not just at the frequencies of visible light. This prediction was the ...
... Maxwell, using his equations of the electromagnetic field, was the first to understand that light is an oscillation of the electromagnetic field. Maxwell was able to predict that • Electromagnetic waves can exist at any frequency, not just at the frequencies of visible light. This prediction was the ...
methodological aspects of gas phase studies of an electric
... There is currently undoubtedly that the ionization of the atom and the strong external magnetic fields cansignificantly affect the likelihood of nuclear decay, and even change the very conditions of stability of nuclei. For the weak nuclear processes (±-decay and K-capture) the effect studied in co ...
... There is currently undoubtedly that the ionization of the atom and the strong external magnetic fields cansignificantly affect the likelihood of nuclear decay, and even change the very conditions of stability of nuclei. For the weak nuclear processes (±-decay and K-capture) the effect studied in co ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.