Slide 1
... top produces a changing magnetic field at the bottom of a metal pan. The changing magnetic field gives rise to a current in the bottom of the pan. Because the pan has resistance, the current heats the pan. If the coil in the stove has low resistance it doesn’t get hot but the pan does. An insulator ...
... top produces a changing magnetic field at the bottom of a metal pan. The changing magnetic field gives rise to a current in the bottom of the pan. Because the pan has resistance, the current heats the pan. If the coil in the stove has low resistance it doesn’t get hot but the pan does. An insulator ...
PHYS632_L12_ch_32_Ma..
... In Figure 32-39, the capacitor with circular plates of radius R = 16.0 cm is connected to a source of emf script e = script em sin ωt, where script em = 220 V and ω = 120 rad/s. The maximum value of the displacement current is id = 7.60 µA. Neglect fringing of the electric field at the edges of the ...
... In Figure 32-39, the capacitor with circular plates of radius R = 16.0 cm is connected to a source of emf script e = script em sin ωt, where script em = 220 V and ω = 120 rad/s. The maximum value of the displacement current is id = 7.60 µA. Neglect fringing of the electric field at the edges of the ...
Magnetic field
... This magnetic field forms circles around a straight wire carrying the current. Point your thumb in the direction of the current (which is toward the negative terminal) If you curl your fingers around the wire, the way your fingers curve is in the direction of the magnetic field. ...
... This magnetic field forms circles around a straight wire carrying the current. Point your thumb in the direction of the current (which is toward the negative terminal) If you curl your fingers around the wire, the way your fingers curve is in the direction of the magnetic field. ...
Magnetotactic Bacteria
... lines point slightly down (into the center of the Earth) http://visual.merriamwebster.com/earth/geography/cartography/hemispheres ...
... lines point slightly down (into the center of the Earth) http://visual.merriamwebster.com/earth/geography/cartography/hemispheres ...
Magnetism and Electric Currents
... it produces a strong magnetic field inside of the coil • This is referred to as an electromagnet because the magnetic field only exists when current flows through the wire ...
... it produces a strong magnetic field inside of the coil • This is referred to as an electromagnet because the magnetic field only exists when current flows through the wire ...
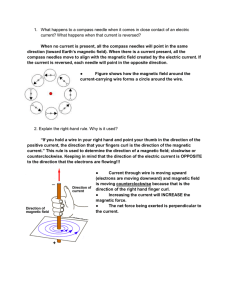
When no current is present, all the compass
... loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. Thus creating a stronger magnetic field, similar to a bar magnet. ● More loops and a stronger current will create a stronger magnetic field. ...
... loop of wire adds to the strength of the magnetic field of any neighboring loops. Thus creating a stronger magnetic field, similar to a bar magnet. ● More loops and a stronger current will create a stronger magnetic field. ...
Discussion 11
... energy from one circuit to another through magnetic coupling. A changing current in the first coil (the primary ) creates a changing magnetic field; in turn, this magnetic field induces a changing voltage in the second coil (the secondary). ...
... energy from one circuit to another through magnetic coupling. A changing current in the first coil (the primary ) creates a changing magnetic field; in turn, this magnetic field induces a changing voltage in the second coil (the secondary). ...
Notes: Magnetism
... Force of attraction or repulsion between various substances, especially those made of iron, nickel and cobalt; it is due to the motion of electric charges" Magnetic Field What is it? ...
... Force of attraction or repulsion between various substances, especially those made of iron, nickel and cobalt; it is due to the motion of electric charges" Magnetic Field What is it? ...
Physics 121 Lab: Finding the horizontal component of the magnetic
... 220 Ohm resistor in the circuit is intended to prevent the current from getting too large and burning out the fuse of the multi-meter. Try running a current through the circuit to see that the compass needle does indeed deflect. Now do things more carefully. Turn on the power supply and set the curr ...
... 220 Ohm resistor in the circuit is intended to prevent the current from getting too large and burning out the fuse of the multi-meter. Try running a current through the circuit to see that the compass needle does indeed deflect. Now do things more carefully. Turn on the power supply and set the curr ...
How could a Rotating Body such as the Sun become a Magnet?
... motions, time must be maintained distinct from space, and the effect of convection must continue to be thrown on to the material observing system in the form of slight modification of its structure. ...
... motions, time must be maintained distinct from space, and the effect of convection must continue to be thrown on to the material observing system in the form of slight modification of its structure. ...
Slide 1
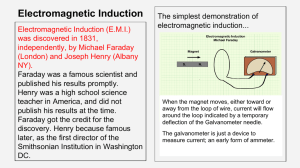
... Induced emf and Faraday’s Law Magnetic Induction We have found that an electric current can give rise to a magnetic field… I wonder if a magnetic field can somehow give rise to an electric current… ...
... Induced emf and Faraday’s Law Magnetic Induction We have found that an electric current can give rise to a magnetic field… I wonder if a magnetic field can somehow give rise to an electric current… ...
r - PolyU EIE
... Static Magnetic Fields (2 Weeks) 5.2 Fundamental postulates of magnetostatics in free space 5.4 Biot-Savart Law and Applications 5.10 Inductances and Inductors ...
... Static Magnetic Fields (2 Weeks) 5.2 Fundamental postulates of magnetostatics in free space 5.4 Biot-Savart Law and Applications 5.10 Inductances and Inductors ...
turbulence - "A" Laboratory, Department of Physics/Astrophysics
... Therefore the higher Vrms, the higher the Jeans mass. However locally the turbulence may trigger the collapse because of converging flow that gather material with a weak velocity dispersion. ...
... Therefore the higher Vrms, the higher the Jeans mass. However locally the turbulence may trigger the collapse because of converging flow that gather material with a weak velocity dispersion. ...
Magnetohydrodynamics

Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) (magneto fluid dynamics or hydromagnetics) is the study of the magnetic properties of electrically conducting fluids. Examples of such magneto-fluids include plasmas, liquid metals, and salt water or electrolytes. The word magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) is derived from magneto- meaning magnetic field, hydro- meaning water, and -dynamics meaning movement. The field of MHD was initiated by Hannes Alfvén, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1970.The fundamental concept behind MHD is that magnetic fields can induce currents in a moving conductive fluid, which in turn polarizes the fluid and reciprocally changes the magnetic field itself. The set of equations that describe MHD are a combination of the Navier-Stokes equations of fluid dynamics and Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. These differential equations must be solved simultaneously, either analytically or numerically.