Ch. 21: Gauss`s Law - University of Colorado Boulder
... shown. Both surfaces surround the same net charge, so the flux through each is the same. But only the left-hand situation has enough symmetry to allow the use of Gauss’s law to calculate the field. The electric fields differ in the two situations, even though the fluxes are the same ...
... shown. Both surfaces surround the same net charge, so the flux through each is the same. But only the left-hand situation has enough symmetry to allow the use of Gauss’s law to calculate the field. The electric fields differ in the two situations, even though the fluxes are the same ...
The Fields of a Short, Linear Dipole Antenna If There Were No
... The first term of eqs. (47) and (50) could be called the retarded Coulomb field, and the first term of eqs. (48) and (51) could be called the retarded Biot-Savart field. Both of these terms vary as the inverse square of the distance between the source and observer, and so they are important in the near ...
... The first term of eqs. (47) and (50) could be called the retarded Coulomb field, and the first term of eqs. (48) and (51) could be called the retarded Biot-Savart field. Both of these terms vary as the inverse square of the distance between the source and observer, and so they are important in the near ...
AXIEM™ White Paper
... This type of simulation also gets the transmission line properties per unit length. The FEM meshes the cross section in triangles and solves for the electric field on each of the meshes. The advantage of this technique is that can account for the loss and internal inductance in the transmission line ...
... This type of simulation also gets the transmission line properties per unit length. The FEM meshes the cross section in triangles and solves for the electric field on each of the meshes. The advantage of this technique is that can account for the loss and internal inductance in the transmission line ...
Particle-in-cell simulations of fast magnetic field penetration into
... It is important to note that the magnetic field will penetrate only in regions of plasma where the Hall speed is positive. When V H<0, Eq. ~7! predicts evanescent waves that do not propagate. Furthermore, if the plasma is initially magnetized then expulsion of the magnetic field is expected in regio ...
... It is important to note that the magnetic field will penetrate only in regions of plasma where the Hall speed is positive. When V H<0, Eq. ~7! predicts evanescent waves that do not propagate. Furthermore, if the plasma is initially magnetized then expulsion of the magnetic field is expected in regio ...
Maxwell`s Original Equations
... force) that acts on an element moving with velocity v in a magnetic field. The solenoidal alignment of the tiny vortices causes a differential centrifugal pressure to act on either side of the element when it is moving at right angles to the rotation axes of the vortices, and this causes a deflectio ...
... force) that acts on an element moving with velocity v in a magnetic field. The solenoidal alignment of the tiny vortices causes a differential centrifugal pressure to act on either side of the element when it is moving at right angles to the rotation axes of the vortices, and this causes a deflectio ...
to PDF - The Applied Computational Electromagnetics
... In practice, very often there is a need for getting homogeneous electric fields, with required features and of high precision. Those fields are used widely in technique: they are applied in electrical machines for high field generation, NMR spectroscopy, MHD technique, nuclear and plasma physics, so ...
... In practice, very often there is a need for getting homogeneous electric fields, with required features and of high precision. Those fields are used widely in technique: they are applied in electrical machines for high field generation, NMR spectroscopy, MHD technique, nuclear and plasma physics, so ...
2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Science SMART Teacher`s
... Science SMART Teacher’s Guide Grade 4 Chapter 6 Lesson Plans ...
... Science SMART Teacher’s Guide Grade 4 Chapter 6 Lesson Plans ...
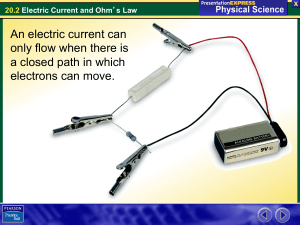
The electric field
... the . treatment, you discover a hollow metal cylinder in your basement, large enough to climb inside. In which of the following cases will you not be shocked? (a) You climb inside the cylinder, making contact with the inner surface. and your charged brother touches the outer metal surface, (b) Your ...
... the . treatment, you discover a hollow metal cylinder in your basement, large enough to climb inside. In which of the following cases will you not be shocked? (a) You climb inside the cylinder, making contact with the inner surface. and your charged brother touches the outer metal surface, (b) Your ...
Study Modules XII Physics - Kendriya Vidyalaya Bilaspur
... force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields. Cyclotron. Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field. Force between two parallel currentcarrying conductors-definition of ampere. Torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic field; moving coil galv ...
... force on a moving charge in uniform magnetic and electric fields. Cyclotron. Force on a current-carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field. Force between two parallel currentcarrying conductors-definition of ampere. Torque experienced by a current loop in uniform magnetic field; moving coil galv ...