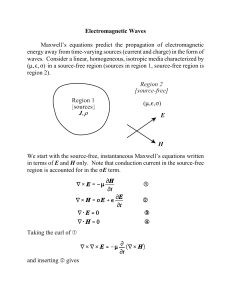
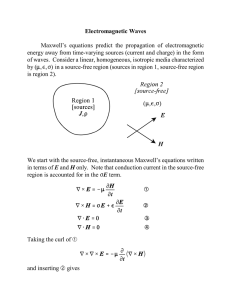
Solutions
... Where the lines are bunched together, the field is stronger; if the lines are diffuse the field is weaker (And the direction of the field is always tangent to the field lines). Now for A and B, the field lines are equally bunched up. The field lines are exactly the same for A and B (even though B is ...
... Where the lines are bunched together, the field is stronger; if the lines are diffuse the field is weaker (And the direction of the field is always tangent to the field lines). Now for A and B, the field lines are equally bunched up. The field lines are exactly the same for A and B (even though B is ...
video slide - Chabot College
... Magnitude and direction of an induced emf • Example 29.2 – 500 loop circular coil with radius 4.00 cm between poles of electromagnet. B field decreases at 0.200 T/second. What are magnitude and direction of induced EMF? Careful with flux ANGLE! ...
... Magnitude and direction of an induced emf • Example 29.2 – 500 loop circular coil with radius 4.00 cm between poles of electromagnet. B field decreases at 0.200 T/second. What are magnitude and direction of induced EMF? Careful with flux ANGLE! ...
The Two Kinds of Electric Charge
... velocity and H being vorticity. Maxwell explains this as being a result of differential centrifugal pressure from the tiny vortices, pressing unevenly on an object or an element of electric current. There can be no other possible explanation for a force which only acts when motion occurs, and which ...
... velocity and H being vorticity. Maxwell explains this as being a result of differential centrifugal pressure from the tiny vortices, pressing unevenly on an object or an element of electric current. There can be no other possible explanation for a force which only acts when motion occurs, and which ...
Physics 2020 Spring 2008
... 70) When the magnet is falling through either pipe, the magnetic field is static and unchanging relative to what? a) The magnet itself b) The pipes c) Neither the magnet itself or the pipes 71) Now suppose we, in our minds, divide the either pipe into a series of horizontal sections. These sections ...
... 70) When the magnet is falling through either pipe, the magnetic field is static and unchanging relative to what? a) The magnet itself b) The pipes c) Neither the magnet itself or the pipes 71) Now suppose we, in our minds, divide the either pipe into a series of horizontal sections. These sections ...
The Coriolis Force in Maxwell`s Equations
... form of the Coriolis force. The negative sign in equation [P] illustrates the reversal of cause and effect as compared to equation [K]. In equation [P], the magnetic flux density B has now come to refer to the fine-grain vorticity/angular momentum density. It is simply an issue of whether or not we ...
... form of the Coriolis force. The negative sign in equation [P] illustrates the reversal of cause and effect as compared to equation [K]. In equation [P], the magnetic flux density B has now come to refer to the fine-grain vorticity/angular momentum density. It is simply an issue of whether or not we ...
Electric charge
... dissimilar electric fields. Similarly, two similar electric fields (lines of force between them are in opposite directions), placed nearby but farther than certain distance, reduce distortion-density between them. Higher distortion-density on outer sides, while being transferred inwards, moves 3D ma ...
... dissimilar electric fields. Similarly, two similar electric fields (lines of force between them are in opposite directions), placed nearby but farther than certain distance, reduce distortion-density between them. Higher distortion-density on outer sides, while being transferred inwards, moves 3D ma ...
DISCOVERING AND ANALYZING MAGNETIC FIELDS
... of the battery; however, they provided a good approximation. With the nail inside, the solenoid became an iron core solenoid and the permeability constant changed to the permeability of iron given in Equation 3. The magnetic field strength for an iron core solenoid should increase approximately 2000 ...
... of the battery; however, they provided a good approximation. With the nail inside, the solenoid became an iron core solenoid and the permeability constant changed to the permeability of iron given in Equation 3. The magnetic field strength for an iron core solenoid should increase approximately 2000 ...
make an electromagnet (modified for adeed)
... [7] SA1.2 The student demonstrates an understanding of the processes of science by collaborating to design and conduct simple repeatable investigations, in order to record, analyze (i.e., range, mean, median, mode), interpret data, and present findings. [8] SA1.2 The student demonstrates an understa ...
... [7] SA1.2 The student demonstrates an understanding of the processes of science by collaborating to design and conduct simple repeatable investigations, in order to record, analyze (i.e., range, mean, median, mode), interpret data, and present findings. [8] SA1.2 The student demonstrates an understa ...
x0001 - My School Portfolio
... Oersted, discovered that there was a relationship between electricity and magnetism. Thanks to Oersted and a few others, by using electricity, we can now make huge magnets. We can also cause them to release their objects. Electricity and magnetism are closely related. The movement of electrons cause ...
... Oersted, discovered that there was a relationship between electricity and magnetism. Thanks to Oersted and a few others, by using electricity, we can now make huge magnets. We can also cause them to release their objects. Electricity and magnetism are closely related. The movement of electrons cause ...