worksheet - Fullerland
... centers are 0.40 m apart. April rubs the eggs to shine them up, and in doing so places a charge on each egg. The egg on the left acquires a charge of 6.0 X 10-6 C while the egg on the right is charged with 4.0 X 10 -6 C. What is the electric field at a point 0.15 m to the right of the egg on the lef ...
... centers are 0.40 m apart. April rubs the eggs to shine them up, and in doing so places a charge on each egg. The egg on the left acquires a charge of 6.0 X 10-6 C while the egg on the right is charged with 4.0 X 10 -6 C. What is the electric field at a point 0.15 m to the right of the egg on the lef ...
Section 17.2
... 17.2 Electomagnets Electromagnets are magnets that are created when there is electric current flowing in a wire. ...
... 17.2 Electomagnets Electromagnets are magnets that are created when there is electric current flowing in a wire. ...
The Physical Entity of Vector Potential in Electromagnetism
... long solenoid is circled in its central plane by a conducting loop (Figure 1). When a sinusoidal current is supplied to the solenoid, there is a corresponding voltage induced in the loop, despite the fact that no sensible magnetic field exists in the vicinity of the loop. So the question is posed: “ ...
... long solenoid is circled in its central plane by a conducting loop (Figure 1). When a sinusoidal current is supplied to the solenoid, there is a corresponding voltage induced in the loop, despite the fact that no sensible magnetic field exists in the vicinity of the loop. So the question is posed: “ ...
Slide 1
... The electromagnetic radiation from an explosion (especially a nuclear explosion) or an intensely fluctuating magnetic field caused by Compton-recoil electrons and photoelectrons from photons scattered in the materials of the electronic or explosive device or in a surrounding medium. The resulting ...
... The electromagnetic radiation from an explosion (especially a nuclear explosion) or an intensely fluctuating magnetic field caused by Compton-recoil electrons and photoelectrons from photons scattered in the materials of the electronic or explosive device or in a surrounding medium. The resulting ...
File
... Collect a 20 coin and cut out a piece of paper the size of a 20 cent coin. (a) Drop the paper and 20 cent coin from the same height at the same time. Write an inference to explain what happened in terms of any forces acting. Because the paper is lighter (has smaller weight force) it took longer (air ...
... Collect a 20 coin and cut out a piece of paper the size of a 20 cent coin. (a) Drop the paper and 20 cent coin from the same height at the same time. Write an inference to explain what happened in terms of any forces acting. Because the paper is lighter (has smaller weight force) it took longer (air ...
Phys132 Lecture 5 - University of Connecticut
... Law should be equal to zero -- since no magnetic current. • Therefore(?), maybe there is a problem with Ampere’s Law. • In fact, Maxwell proposes a modification of Ampere’s Law by adding another term (the “displacement” current) to the right hand side of the equation! ie ...
... Law should be equal to zero -- since no magnetic current. • Therefore(?), maybe there is a problem with Ampere’s Law. • In fact, Maxwell proposes a modification of Ampere’s Law by adding another term (the “displacement” current) to the right hand side of the equation! ie ...
AP Physics
... 1. Do problems Exercise B page 589 and problem 2, 3, 8, 9 page 610-1. Answers at the end of the packet. 2. A 20-turn wire coil in the shape of a rectangle, 0.25 m by 0.15 m, has a resistance of 5.0 Ω. In position 1 shown below, the loop is in a uniform magnetic field B of 0.20 T. The field is direct ...
... 1. Do problems Exercise B page 589 and problem 2, 3, 8, 9 page 610-1. Answers at the end of the packet. 2. A 20-turn wire coil in the shape of a rectangle, 0.25 m by 0.15 m, has a resistance of 5.0 Ω. In position 1 shown below, the loop is in a uniform magnetic field B of 0.20 T. The field is direct ...
Adobe Acrobat file ()
... The U.S. Navy has long proposed the construction of extremely low-frequency (ELF) communications systems; such waves could penetrate the oceans to reach distant submarines. Calculate the length of a quarter-wavelength antenna for a transmitter generating ELF waves of frequency 75 Hz. How practical ...
... The U.S. Navy has long proposed the construction of extremely low-frequency (ELF) communications systems; such waves could penetrate the oceans to reach distant submarines. Calculate the length of a quarter-wavelength antenna for a transmitter generating ELF waves of frequency 75 Hz. How practical ...
chapter20
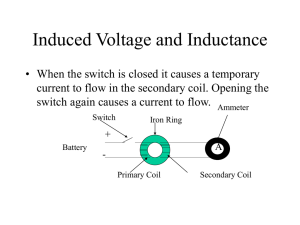
... • When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current (a). • When the magnet is held stationary, there is no current (b). • When the magnet moves away from the loop, the ammeter shows a current in the opposite direction (c ). • If the loop is moved instead of the m ...
... • When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current (a). • When the magnet is held stationary, there is no current (b). • When the magnet moves away from the loop, the ammeter shows a current in the opposite direction (c ). • If the loop is moved instead of the m ...
phys1444-spring12
... (c) Determine the magnetic field induced between the plates. Assume E is uniform between the plates at any instant and is zero at all points beyond the edges of the plates. The magnetic field lines generated by changing electric field is perpendicular to E and is circular due to symmetry d E Whose ...
... (c) Determine the magnetic field induced between the plates. Assume E is uniform between the plates at any instant and is zero at all points beyond the edges of the plates. The magnetic field lines generated by changing electric field is perpendicular to E and is circular due to symmetry d E Whose ...
Electromagnetism: The Motor Lab Student Version Key Concepts
... for the movement of many devices including cars and computers. In fact, small motors and magnets are important parts of many kinds of medical equipment. Can you think of any other devices that use motors? Electricity is the effect of the interactions between objects containing electric currents, o ...
... for the movement of many devices including cars and computers. In fact, small motors and magnets are important parts of many kinds of medical equipment. Can you think of any other devices that use motors? Electricity is the effect of the interactions between objects containing electric currents, o ...
10th CBSE {SA - 1} Revision Pack Booklet - 4
... (c) How are they an improvement on simple devices? Why are solar cell panels costly? Solution: (a) Solar concentrators are the devices which concentrate solar heat in a small area to raise its temperature to high degrees. This heat can be used to cook food, heat water and generate electricity. (b) S ...
... (c) How are they an improvement on simple devices? Why are solar cell panels costly? Solution: (a) Solar concentrators are the devices which concentrate solar heat in a small area to raise its temperature to high degrees. This heat can be used to cook food, heat water and generate electricity. (b) S ...
Chapter 15: Magnetism
... are two ways to increase the current in a simple electromagnet: 1. Add more turns of wire around the nail. ...
... are two ways to increase the current in a simple electromagnet: 1. Add more turns of wire around the nail. ...