Summary Units (SI): Length: m = meter Time: s = second Mass: kg
... Moving charge q along electric field E does work: W = F.d = qE.d Electrostatic forces are conservative -> work stored in electrostatic potential energy Upot. Electrostatic potential energy Upot of a charged object divided by its charge q equals potential V [measured in Volt = V]. A charge q changes ...
... Moving charge q along electric field E does work: W = F.d = qE.d Electrostatic forces are conservative -> work stored in electrostatic potential energy Upot. Electrostatic potential energy Upot of a charged object divided by its charge q equals potential V [measured in Volt = V]. A charge q changes ...
How electromagnetism works
... Insulated wire Note that the wire must be an insulated wire. A bare wire would cause an electrical short and the current would then run through the nail or metal core. In some electromagnets, like in an electric motor, the wire will look like bare copper, but it is insulated with a thin coating of a ...
... Insulated wire Note that the wire must be an insulated wire. A bare wire would cause an electrical short and the current would then run through the nail or metal core. In some electromagnets, like in an electric motor, the wire will look like bare copper, but it is insulated with a thin coating of a ...
PowerPoint Ch 32
... In moving across an inductor of inductance L along (or against) the presumed direction of the current I, the potential change is ΔV = –L dI/dt (or +L dI/dt, respectively). Magnetic materials will change selfinductance by changing magnetic flux ...
... In moving across an inductor of inductance L along (or against) the presumed direction of the current I, the potential change is ΔV = –L dI/dt (or +L dI/dt, respectively). Magnetic materials will change selfinductance by changing magnetic flux ...
Lesson 1: 4th Grade Science: "A Hairy Picture": Magnets Big Idea
... of cases, or extreme circumstances. Electrons, however, are much more flowing. They can move from atom to atom and sometimes even leave the atom all together (ionization.) Electrons surround atoms in pairs. If one electron spins upward, the other spins downward. It's impossible for both of the elect ...
... of cases, or extreme circumstances. Electrons, however, are much more flowing. They can move from atom to atom and sometimes even leave the atom all together (ionization.) Electrons surround atoms in pairs. If one electron spins upward, the other spins downward. It's impossible for both of the elect ...
Magnetism can produce current.
... car also contains many devices that use electrical energy. Some of them are familiar—the headlights, turn signals, radio, power windows, and door locks. Others may be less familiar, such as the spark plugs that ignite the gasoline, the fuel and oil pumps that move fluids in the engine, and the air c ...
... car also contains many devices that use electrical energy. Some of them are familiar—the headlights, turn signals, radio, power windows, and door locks. Others may be less familiar, such as the spark plugs that ignite the gasoline, the fuel and oil pumps that move fluids in the engine, and the air c ...
magnetic field induced by overhead power transmission lines in
... µr: permeability relative (µ r = 1) µ0: permeability of the free space (µ0 =4 π 10-7 H/m) so ...
... µr: permeability relative (µ r = 1) µ0: permeability of the free space (µ0 =4 π 10-7 H/m) so ...
BASANT`S SCIENCE ACADEMY A compass needle is a small bar
... List the properties of magnetic lines of force. The properties of magnetic lines of force are as follows. (a) Magnetic field lines emerge from the north pole. (b) They merge at the south pole. (c) The direction of field lines inside the magnet is from the south pole to the north pole. (d) Magnetic l ...
... List the properties of magnetic lines of force. The properties of magnetic lines of force are as follows. (a) Magnetic field lines emerge from the north pole. (b) They merge at the south pole. (c) The direction of field lines inside the magnet is from the south pole to the north pole. (d) Magnetic l ...
chapter34
... Ampere’s Law applies to the wire part. The current flows into the upper plate of the capacitor, flows out from the lower plate, creating charge accumulation in the capacitor and build up the electric field. Constructing a Gaussian surface which has two parts: S1 and S2. ...
... Ampere’s Law applies to the wire part. The current flows into the upper plate of the capacitor, flows out from the lower plate, creating charge accumulation in the capacitor and build up the electric field. Constructing a Gaussian surface which has two parts: S1 and S2. ...
Course Unit Title General Physics II Course Unit Code PHY 102
... • To be able to use his/her knowledge in the fields of other sciences and/or engineering. • Understanding how physics approach and solve problems in electricity and magnetism. Learning Outcomes At the end of the course the student should be able to Assessment ...
... • To be able to use his/her knowledge in the fields of other sciences and/or engineering. • Understanding how physics approach and solve problems in electricity and magnetism. Learning Outcomes At the end of the course the student should be able to Assessment ...
Lesson 11. Topic “ Magnetism” Grammar material: The Present
... well-known English physicist (1540-1603). He carried out various important experiments on electricity and magnetism and wrote a book where he put together all that was known about magnetism. He proved that the earth itself was a great magnet. Reference must be made here to Galileo, the famous Italia ...
... well-known English physicist (1540-1603). He carried out various important experiments on electricity and magnetism and wrote a book where he put together all that was known about magnetism. He proved that the earth itself was a great magnet. Reference must be made here to Galileo, the famous Italia ...
What state and other requrements
... Superconductors can also be made into supercapacitors which can potentially hold as much energy as a battery, but be charged in seconds. The applications of superconductors are nearly limitless, but most of them have to be operated at very cold temperatures which presents problems. There are two typ ...
... Superconductors can also be made into supercapacitors which can potentially hold as much energy as a battery, but be charged in seconds. The applications of superconductors are nearly limitless, but most of them have to be operated at very cold temperatures which presents problems. There are two typ ...
CHAPTER 27 SOURCES OF MAGNETIC FIELD • Magnetic field due
... Question 27.10: A coaxial cable is connected so that the instantaneous current to a load flows through the inner central conductor and returns through the outer copper braid, as shown. If you could “see” magnetic field lines, what would they look like outside the cable if the instantaneous current i ...
... Question 27.10: A coaxial cable is connected so that the instantaneous current to a load flows through the inner central conductor and returns through the outer copper braid, as shown. If you could “see” magnetic field lines, what would they look like outside the cable if the instantaneous current i ...
Chapter 4: Magnetostatics
... – Whereas the tangential component of E is continuous across the boundary, the tangential component of H may not be continuous (unless Js=0). ...
... – Whereas the tangential component of E is continuous across the boundary, the tangential component of H may not be continuous (unless Js=0). ...
File
... wire (………………………..) wound round a piece of iron. The electromagnet creates a magnetic field when electricity passes through the coil. ...
... wire (………………………..) wound round a piece of iron. The electromagnet creates a magnetic field when electricity passes through the coil. ...
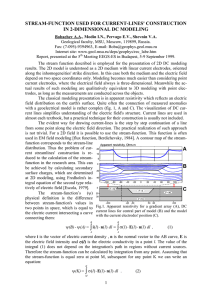
current fuction usage for current lines construction in 2d models
... Thus the surface charge density reveals a distribution of streamlines (fig.2). The upper left corner of the object is less expressed in the apparent resistivity than the upper right. Both corners will be expressed clearer in the case of a conductive object. The best way to visualize surface charge d ...
... Thus the surface charge density reveals a distribution of streamlines (fig.2). The upper left corner of the object is less expressed in the apparent resistivity than the upper right. Both corners will be expressed clearer in the case of a conductive object. The best way to visualize surface charge d ...
MAGNETISM
... 12.- Magnets with a weak force can reverse their polarity thruogh the action of a strong magnetic field. ...
... 12.- Magnets with a weak force can reverse their polarity thruogh the action of a strong magnetic field. ...
... •The electric field delivers the energy to the water molecules in the food. •The oscillating electric field makes the water molecules oscillate with the frequency of the wave (2.4 × 109 Hz) •Transfer of energy is very efficient, only for water (resonance) •In the process, bonds break between neighbo ...