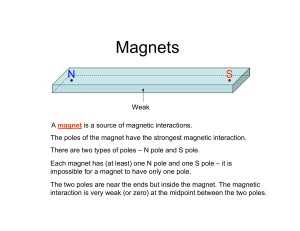
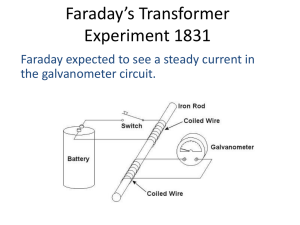
The Magnetic Field
... • Superconductors are formed when certain materials are cooled to low temperatures. ...
... • Superconductors are formed when certain materials are cooled to low temperatures. ...
forces - UMN Physics home
... prediction? Why or why not? Repeat this procedure for the south pole. Should there be any difference? In what direction did the beam deflect? If you placed the bar magnet perpendicular to the screen of the CRT, should you see a deflection? Try this experiment with both poles of the magnet. Record yo ...
... prediction? Why or why not? Repeat this procedure for the south pole. Should there be any difference? In what direction did the beam deflect? If you placed the bar magnet perpendicular to the screen of the CRT, should you see a deflection? Try this experiment with both poles of the magnet. Record yo ...
File - Electric Circuit Analysis
... where R is the reluctance, l is the length of the magnetic path, and A is the cross-sectional area. The t in the units At/Wb is the number of turns of the applied winding (At = Ampere turns) . ...
... where R is the reluctance, l is the length of the magnetic path, and A is the cross-sectional area. The t in the units At/Wb is the number of turns of the applied winding (At = Ampere turns) . ...
THE EFFECT OF ELECTRIC FIELD ON
... (σ,εr,µr), all of which are frequency-dependent [3]. Since biological material, in electromagnetic sense, consists of several different types of tissue with different electromagnetic features, it is necessary to model it according to the part-by-part principle. The block human model is suitable not ...
... (σ,εr,µr), all of which are frequency-dependent [3]. Since biological material, in electromagnetic sense, consists of several different types of tissue with different electromagnetic features, it is necessary to model it according to the part-by-part principle. The block human model is suitable not ...
here - RAD 2012
... -Very high value of electric field strength is found at one measurement point around transformer station in Vrbas, under the high voltage power transmission lines, where the transmission lines are connected to the transformer station -This value, which is mainly caused by transmission lines, reache ...
... -Very high value of electric field strength is found at one measurement point around transformer station in Vrbas, under the high voltage power transmission lines, where the transmission lines are connected to the transformer station -This value, which is mainly caused by transmission lines, reache ...
PHYSICS 202/202P: AN INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICITY
... ä Radiation: light, x-rays, radio-waves,... ä Magnetism: electric motors, MRI,... ä Chemistry: chemical bonds, reactions,... ...
... ä Radiation: light, x-rays, radio-waves,... ä Magnetism: electric motors, MRI,... ä Chemistry: chemical bonds, reactions,... ...
How does the MRI scanner work? Your body is composed of small
... Your body is composed of small particles called atoms. Most of the body is composed of Hydrogen atoms that under normal circumstances spin around at random. However, when you are placed within a strong magnetic field, the hydrogen atoms line up and spin in the same direction as the magnetic field. W ...
... Your body is composed of small particles called atoms. Most of the body is composed of Hydrogen atoms that under normal circumstances spin around at random. However, when you are placed within a strong magnetic field, the hydrogen atoms line up and spin in the same direction as the magnetic field. W ...
Document
... The U.S. Navy has long proposed the construction of extremely low-frequency (ELF) communications systems; such waves could penetrate the oceans to reach distant submarines. Calculate the length of a quarter-wavelength antenna for a transmitter generating ELF waves of frequency 75 Hz. How practical ...
... The U.S. Navy has long proposed the construction of extremely low-frequency (ELF) communications systems; such waves could penetrate the oceans to reach distant submarines. Calculate the length of a quarter-wavelength antenna for a transmitter generating ELF waves of frequency 75 Hz. How practical ...
Electromagnet
... Discuss, in detail, the concept of electricity, electrical circuits, and magnetism. Describe specific examples of electricity and magnetism and their uses. Discuss the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Discuss the concept of an electromagnet and how it is formed. Cite your te ...
... Discuss, in detail, the concept of electricity, electrical circuits, and magnetism. Describe specific examples of electricity and magnetism and their uses. Discuss the relationship between electricity and magnetism. Discuss the concept of an electromagnet and how it is formed. Cite your te ...
Section 17.3 - CPO Science
... 2. One or more fixed magnets around the rotor. 3. A commutator that switches the direction of current to keep the rotor spinning. ...
... 2. One or more fixed magnets around the rotor. 3. A commutator that switches the direction of current to keep the rotor spinning. ...
1. Two electromagnetic waves travel through empty space
... Experiment II: With the magnetic field held constant, the loop is moved to the right. The loop remains in the plane of the page and never exits the magnetic field. Experiment III: With the magnetic field held constant, the loop is shrunk to one half its initial radius, always remaining within the pl ...
... Experiment II: With the magnetic field held constant, the loop is moved to the right. The loop remains in the plane of the page and never exits the magnetic field. Experiment III: With the magnetic field held constant, the loop is shrunk to one half its initial radius, always remaining within the pl ...