Interactions_C2-Making magnets
... toatanow least battery 20or • connected Magnetswire this way times become a source around aofelectromagnet. electricity. a magnetic are called such an iron • object electromagnets. The iron nailas loses its nail. magnetism once it is • disconnected, Connect the ends andof will the not wireable be to ...
... toatanow least battery 20or • connected Magnetswire this way times become a source around aofelectromagnet. electricity. a magnetic are called such an iron • object electromagnets. The iron nailas loses its nail. magnetism once it is • disconnected, Connect the ends andof will the not wireable be to ...
Electric Forces and Fields
... Charge moves freely within conductors The excess charges will repel each other to reach a stable equilibrium The charges collect at the surface of the object, and spread out. Charges move so that the field lines are always perpendicular to the surface of the conductor ...
... Charge moves freely within conductors The excess charges will repel each other to reach a stable equilibrium The charges collect at the surface of the object, and spread out. Charges move so that the field lines are always perpendicular to the surface of the conductor ...
Ενότητα 9: Electric Meters
... principally are the ohm, volt, ampere, coulomb, henry, farad, watt, and joule. Given that all forms of matter exhibit one or more electrical characteristics, electrical measurements may be taken from an essentially unlimited number of sources. ...
... principally are the ohm, volt, ampere, coulomb, henry, farad, watt, and joule. Given that all forms of matter exhibit one or more electrical characteristics, electrical measurements may be taken from an essentially unlimited number of sources. ...
PHYS 241-1
... Chapter 30 Induction and Inductance Review and Summary is on p. 816. Know the definition of magnetic flux, Equation 30-1. Know Faraday's law of induction, Equations 30-4 and 30-5. Be able to state Lenz's law: An induced current has a direction such that the magnetic field due to the current opposes ...
... Chapter 30 Induction and Inductance Review and Summary is on p. 816. Know the definition of magnetic flux, Equation 30-1. Know Faraday's law of induction, Equations 30-4 and 30-5. Be able to state Lenz's law: An induced current has a direction such that the magnetic field due to the current opposes ...
PHYS 4202/6202 (as of Jan. 03/2015) Electricity and Magnetism II
... Consistency of Maxwell’s equations; differential consequences* Law of Conservation of Energy in the presence of the electromagnetic field Poynting’s Vector Examples: Electromagnetic energy flow in various situations (cont.) PART 3: ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION (from slowly moving sources) ...
... Consistency of Maxwell’s equations; differential consequences* Law of Conservation of Energy in the presence of the electromagnetic field Poynting’s Vector Examples: Electromagnetic energy flow in various situations (cont.) PART 3: ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION (from slowly moving sources) ...
if on the Internet, Press on your browser to
... system has been proven with working devices. Monopoles have not been actually observed as yet. But Berry's phase for the photon (monopole effects) has recently been tested successfully in Physical Review Letters. As you know, back in 1986 Tomita & Chiao have produced the Berry's phase effect with RF ...
... system has been proven with working devices. Monopoles have not been actually observed as yet. But Berry's phase for the photon (monopole effects) has recently been tested successfully in Physical Review Letters. As you know, back in 1986 Tomita & Chiao have produced the Berry's phase effect with RF ...
Vol. 19, No 4, Nov 2016
... In 1833 Heinrich Lenz introduced the first electrodynamic law emanating from the principle of conservation of energy. According to Lenz’s Law if an increasing (or decreasing) magnetic flux induces an electromotive force (EMF), the resulting current will oppose a further increase (or decrease) in mag ...
... In 1833 Heinrich Lenz introduced the first electrodynamic law emanating from the principle of conservation of energy. According to Lenz’s Law if an increasing (or decreasing) magnetic flux induces an electromotive force (EMF), the resulting current will oppose a further increase (or decrease) in mag ...
The Atom`s Family
... electric charges have on one another Magnetic field: a way to picture the effects that magnetic poles have on other magnets Dipole: the combined field of two charges of opposite signs or a pair of magnetic poles ...
... electric charges have on one another Magnetic field: a way to picture the effects that magnetic poles have on other magnets Dipole: the combined field of two charges of opposite signs or a pair of magnetic poles ...
win1Tues
... force F (Q1, #1, 2) 22-4: Field due to a point charge (Q2, 5, #4, 11, ) 22-8: Point charge can be accelerated by an electric field (Q8, #38, 39, 49) Compare to gravity: #75, 85 (42) ...
... force F (Q1, #1, 2) 22-4: Field due to a point charge (Q2, 5, #4, 11, ) 22-8: Point charge can be accelerated by an electric field (Q8, #38, 39, 49) Compare to gravity: #75, 85 (42) ...
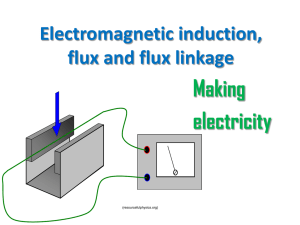
Electromagnetic induction, flux and flux linkage
... rod, so the end P Q L will become negatively v P Flux charged, density (B) leaving Q with a positive charge. As a result, an electric field E builds up until the force on electrons in the rod due to this electric field (= Ee) balances the force due to the magnetic field. ...
... rod, so the end P Q L will become negatively v P Flux charged, density (B) leaving Q with a positive charge. As a result, an electric field E builds up until the force on electrons in the rod due to this electric field (= Ee) balances the force due to the magnetic field. ...