What Is Electricity?
... magnetism? In the Delta Science Content Reader Electricity and Magnetism, students first explore atoms and electric charge. Students compare static electricity and current electricity, as well as series circuits and parallel circuits. Then they explore the relationship between electricity and magnet ...
... magnetism? In the Delta Science Content Reader Electricity and Magnetism, students first explore atoms and electric charge. Students compare static electricity and current electricity, as well as series circuits and parallel circuits. Then they explore the relationship between electricity and magnet ...
electric flux - MSU Denver Sites
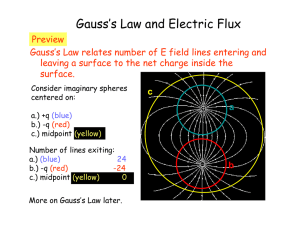
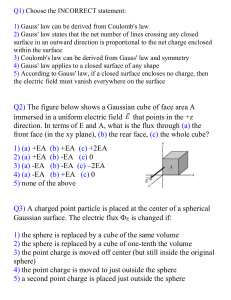
... Example 22.2 Electric flux through a cube An imaginary cube of side L is in a region of uniform electric field E. Find the electric flux through each surface of the cube when (a) it is oriented with two of its faces perpendicular ...
... Example 22.2 Electric flux through a cube An imaginary cube of side L is in a region of uniform electric field E. Find the electric flux through each surface of the cube when (a) it is oriented with two of its faces perpendicular ...
kq A q B
... This is an activity pulled from a lecture covering electric charges from PHYS1010 at CU Boulder exploring the nature of charges and forces. The applets used as part of the activity are the Electric Field Hockey, Charges and Fields, Balloons and Static Electricity, and John Travoltage. Five concept q ...
... This is an activity pulled from a lecture covering electric charges from PHYS1010 at CU Boulder exploring the nature of charges and forces. The applets used as part of the activity are the Electric Field Hockey, Charges and Fields, Balloons and Static Electricity, and John Travoltage. Five concept q ...
Physics-part2 - National University
... Design of Experiment: Principles of experimental design and analysis of variance, Meaning of experiments and randomization, Replication and local control, Basic designs: CRD, RBD and LSD, Analysis of these designs, Estimation of parameters, Missing plot estimation and analysis, Factorial experiment, ...
... Design of Experiment: Principles of experimental design and analysis of variance, Meaning of experiments and randomization, Replication and local control, Basic designs: CRD, RBD and LSD, Analysis of these designs, Estimation of parameters, Missing plot estimation and analysis, Factorial experiment, ...
Bound charges and currents
... To set the stage, we first outline the common way of introducing bound charges and currents at the advanced level (see, e.g., Sec. 4.2 of Ref. 3). The discussion of fields in matter typically begins by noting that when dielectrics are placed in an external electric field they become polarized; that ...
... To set the stage, we first outline the common way of introducing bound charges and currents at the advanced level (see, e.g., Sec. 4.2 of Ref. 3). The discussion of fields in matter typically begins by noting that when dielectrics are placed in an external electric field they become polarized; that ...
Electromagnetism - Delta Education
... points south. Unlike magnetic poles attract each other, and like poles repel.) As appropriate, tell students that the latter is called the Law of Magnetic Attraction. Ask, How can you “see” a magnetic field if it is invisible? (You can see its effect. Iron filings line up along the field lines and g ...
... points south. Unlike magnetic poles attract each other, and like poles repel.) As appropriate, tell students that the latter is called the Law of Magnetic Attraction. Ask, How can you “see” a magnetic field if it is invisible? (You can see its effect. Iron filings line up along the field lines and g ...
Q1. Two identical conducting spheres A and B carry equal charge Q
... Figure 1 shows a dipole rotating under the effect of an electric field pointing along the negative x-axis. Which one of the following statements is TRUE Figure 1 ...
... Figure 1 shows a dipole rotating under the effect of an electric field pointing along the negative x-axis. Which one of the following statements is TRUE Figure 1 ...
P3 Revision - the Redhill Academy
... coil back in. Diaphragm vibrates so much sound waves are produced Watch a video ...
... coil back in. Diaphragm vibrates so much sound waves are produced Watch a video ...
Handout 4 - electric energy and potential
... Definition: A field is conservative if the work done in moving between any two points is independent of the path taken. E is conservative because ∆V is independent of the path. Proof: Consider the field due to a point charge Q. If we can prove it for this we can argue from the principle of superposi ...
... Definition: A field is conservative if the work done in moving between any two points is independent of the path taken. E is conservative because ∆V is independent of the path. Proof: Consider the field due to a point charge Q. If we can prove it for this we can argue from the principle of superposi ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.