f. Physics notes 2 (DOC).
... We have seen that electric fields are superposable. That is, the electric field generated by a set of charges distributed in space is simply the vector sum of the electric fields generated by each charge taken separately. Well, if electric fields are superposable, it follows from Eq. (90) that elect ...
... We have seen that electric fields are superposable. That is, the electric field generated by a set of charges distributed in space is simply the vector sum of the electric fields generated by each charge taken separately. Well, if electric fields are superposable, it follows from Eq. (90) that elect ...
15 Electricity and Magnetism
... A summary is a short version of a large amount of text. When you write a summary, you use words to explain the main idea and details of a concept in simpler terms. Writing summaries can help you understand complex concepts and communicate them to someone who is not familiar with them. When you read ...
... A summary is a short version of a large amount of text. When you write a summary, you use words to explain the main idea and details of a concept in simpler terms. Writing summaries can help you understand complex concepts and communicate them to someone who is not familiar with them. When you read ...
lecture14
... thus the new B field points to the right. An induced counterclockwise current produces just such a B field. ...
... thus the new B field points to the right. An induced counterclockwise current produces just such a B field. ...
Lightning Room education kit: Classroom activities
... someone else after walking on carpet. These incidents involve static electricity. Static electricity occurs when electric charge builds up in one place. When you rub two different materials together, you can move negative charges (electrons) from one material to the other. This is often referred to ...
... someone else after walking on carpet. These incidents involve static electricity. Static electricity occurs when electric charge builds up in one place. When you rub two different materials together, you can move negative charges (electrons) from one material to the other. This is often referred to ...
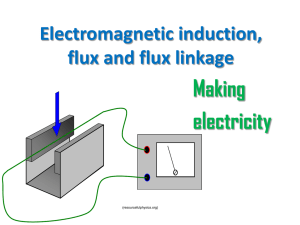
Electromagnetic induction, flux and flux linkage
... How is the ‘electricity’ made? The same is true for other electrons in the rod, so the end P Q L will become negatively v P Flux charged, density (B) leaving Q with a positive charge. As a result, an electric field E builds up until the force on electrons in the rod due to this electric field (= Ee ...
... How is the ‘electricity’ made? The same is true for other electrons in the rod, so the end P Q L will become negatively v P Flux charged, density (B) leaving Q with a positive charge. As a result, an electric field E builds up until the force on electrons in the rod due to this electric field (= Ee ...
ppt document
... Gauss’ Law for velocity If we integrate over a complete closed surface, then we have dV/dt (created or destroyed) = v dA . However, we know mass (and water) can’t be created or destroyed, so v dA = 0. Electric field is a vector just like velocity is a vector. The sources of electric field are c ...
... Gauss’ Law for velocity If we integrate over a complete closed surface, then we have dV/dt (created or destroyed) = v dA . However, we know mass (and water) can’t be created or destroyed, so v dA = 0. Electric field is a vector just like velocity is a vector. The sources of electric field are c ...
Chapter 8 Relativistic Electromagnetism
... Chapter 8 Relativistic Electromagnetism In which it is shown that electricity and magnetism can no more be separated than space and time. ...
... Chapter 8 Relativistic Electromagnetism In which it is shown that electricity and magnetism can no more be separated than space and time. ...
© DISNEY 2012
... part of a closed-loop circuit, meaning the electrons must move along a path. Every circuit must also have a conductor – a material, like most metals, that freely gives up electrons, allowing electricity to flow. Materials that hold their electrons tightly, such as rubber, cotton or glass are called ...
... part of a closed-loop circuit, meaning the electrons must move along a path. Every circuit must also have a conductor – a material, like most metals, that freely gives up electrons, allowing electricity to flow. Materials that hold their electrons tightly, such as rubber, cotton or glass are called ...
Gravitation, Electrostatics, and the Electron-Positron
... elementary particles being altered. This fact is also important in relation to the net charge on a wire in an electric circuit. That net charge can alter without changing the number of particles in the system. Hence, charge is something that is introduced into an electric circuit from the exterior p ...
... elementary particles being altered. This fact is also important in relation to the net charge on a wire in an electric circuit. That net charge can alter without changing the number of particles in the system. Hence, charge is something that is introduced into an electric circuit from the exterior p ...
Electric Art From Electromagnetism to Electrodynamics
... shortness sake, we shall call the uniting conductor, or the uniting wire. To the effect which takes place in this conductor and in the surrounding space, we shall give the name of the conflict of electricity.” Instead of adopting a more conventional view of a current as a stream of electric particle ...
... shortness sake, we shall call the uniting conductor, or the uniting wire. To the effect which takes place in this conductor and in the surrounding space, we shall give the name of the conflict of electricity.” Instead of adopting a more conventional view of a current as a stream of electric particle ...
ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM
... electrons move from one atom to another in a wire, they produce an electric current. So electrons are not lost but rather are exchanged among atoms. Q: Does electricity flow through the hollow inside of a wire? ...
... electrons move from one atom to another in a wire, they produce an electric current. So electrons are not lost but rather are exchanged among atoms. Q: Does electricity flow through the hollow inside of a wire? ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.