Lenz Law Digital Guide
... when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, positive and negative. Electric Current: A flow of electricity through a conductor. Electric Field: A region around a charged particle or object within which a force would be exerted on other charged particles or object ...
... when near other electrically charged matter. Electric charge comes in two types, positive and negative. Electric Current: A flow of electricity through a conductor. Electric Field: A region around a charged particle or object within which a force would be exerted on other charged particles or object ...
Fifth Grade Electricity and Magnetism
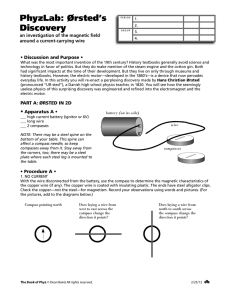
... a. Write instructions that others can follow in carrying out a scientific procedure. b. Make sketches to aid in explaining scientific procedures or ideas. c. Use numerical data in describing and comparing objects and events. d. Locate scientific information in reference books, back issues of newspap ...
... a. Write instructions that others can follow in carrying out a scientific procedure. b. Make sketches to aid in explaining scientific procedures or ideas. c. Use numerical data in describing and comparing objects and events. d. Locate scientific information in reference books, back issues of newspap ...
Solution Set 9 - 6911norfolk.com
... through vacuum. The transverse dimensions of the beam are less than 1 mm, and there are no positive charges in or near it. In the lab frame, what is approximately the electric field strength 1 cm away from the beam, and what is the average distance between the electrons, measured parallel to the beam ...
... through vacuum. The transverse dimensions of the beam are less than 1 mm, and there are no positive charges in or near it. In the lab frame, what is approximately the electric field strength 1 cm away from the beam, and what is the average distance between the electrons, measured parallel to the beam ...
Electromagnetism: The Motor Lab Student Version
... An electron is a negatively charged particle. The flow of these negatively charged is called an electric current. When the electrons flow in this current, they carry an electric charge, which causes electricity. This is the same electricity used to power many machines that you see everyday. Batterie ...
... An electron is a negatively charged particle. The flow of these negatively charged is called an electric current. When the electrons flow in this current, they carry an electric charge, which causes electricity. This is the same electricity used to power many machines that you see everyday. Batterie ...
Document
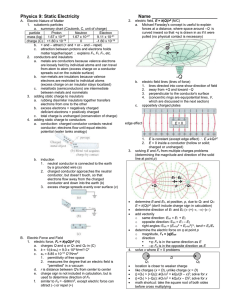
... a. metals are conductors because valence electrons are loosely held by individual atoms and can travel from atom to atom (excess charge on a conductor spreads out on the outside surface) b. non-metals are insulators because valence electrons are restricted to individual atoms (excess charge on an in ...
... a. metals are conductors because valence electrons are loosely held by individual atoms and can travel from atom to atom (excess charge on a conductor spreads out on the outside surface) b. non-metals are insulators because valence electrons are restricted to individual atoms (excess charge on an in ...
Electromagnet - Cascades Science Center Foundation
... Caution: The 6 volt battery is capable of sending lot of current into this electromagnet. Never touch the exposed electric contacts. The device may heat up if left on for too long. Continuous use will quickly drain the battery. Children should only use this device with adult supervision. ...
... Caution: The 6 volt battery is capable of sending lot of current into this electromagnet. Never touch the exposed electric contacts. The device may heat up if left on for too long. Continuous use will quickly drain the battery. Children should only use this device with adult supervision. ...
Chapter 24 Electric Potential
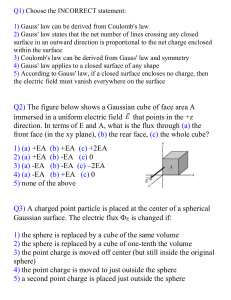
... Which of the following statements are CORRECT: (1) The electric flux through a Gaussian surface depends on the shape of the surface. (2) The electric flux through a closed surface depends on the net charge enclosed by the surface. (3) The electric field inside a uniformly charged solid conducting sp ...
... Which of the following statements are CORRECT: (1) The electric flux through a Gaussian surface depends on the shape of the surface. (2) The electric flux through a closed surface depends on the net charge enclosed by the surface. (3) The electric field inside a uniformly charged solid conducting sp ...
Powerpoint
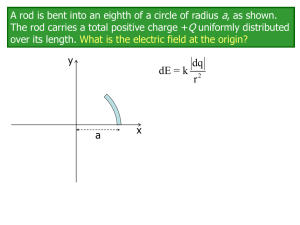
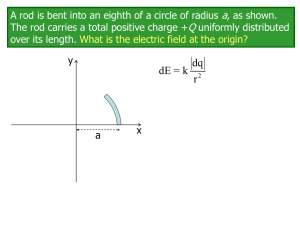
... A rod is bent into an eighth of a circle of radius a, as shown. The rod carries a total positive charge +Q uniformly distributed over its length. A negative point charge -q is placed at the origin. What is the electric force on the point charge? Express your answer in unit vector notation. You coul ...
... A rod is bent into an eighth of a circle of radius a, as shown. The rod carries a total positive charge +Q uniformly distributed over its length. A negative point charge -q is placed at the origin. What is the electric force on the point charge? Express your answer in unit vector notation. You coul ...
Xerographic Copiers
... charge is sprayed onto an insulating layer opposite charge flows onto the layer’s back the layer acts as a charged capacitor light selectively erases the separated charge the remaining charge attracts toner particles the toner particles are then bonded to paper ...
... charge is sprayed onto an insulating layer opposite charge flows onto the layer’s back the layer acts as a charged capacitor light selectively erases the separated charge the remaining charge attracts toner particles the toner particles are then bonded to paper ...
Exercises on Electrostatics Exercise 1.1 Suppose you have two
... The direction of the force is at an angle θ above the negative x-axis equal to tan(θ) = 2/1.5. So θ ≈ 53◦ above the negative x-axis. b) If the object at the origin were not present, what is the electric field at the origin due to the other two charges? ...
... The direction of the force is at an angle θ above the negative x-axis equal to tan(θ) = 2/1.5. So θ ≈ 53◦ above the negative x-axis. b) If the object at the origin were not present, what is the electric field at the origin due to the other two charges? ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.