MAGNETIC FORCE ON A CURRENT
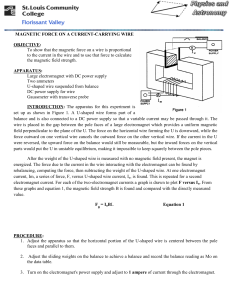
... Large electromagnet with DC power supply Two ammeters U-shaped wire suspended from balance DC power supply for wire Gaussmeter with transverse probe INTRODUCTION: The apparatus for this experiment is set up as shown in Figure 1. A U-shaped wire forms part of a balance and is also connected to a DC p ...
... Large electromagnet with DC power supply Two ammeters U-shaped wire suspended from balance DC power supply for wire Gaussmeter with transverse probe INTRODUCTION: The apparatus for this experiment is set up as shown in Figure 1. A U-shaped wire forms part of a balance and is also connected to a DC p ...
PowerPoint Ch 32
... 32-3 Energy in Magnetic Fields The energy in a solenoid depends on the current, and therefore on the magnetic field created by the current: ...
... 32-3 Energy in Magnetic Fields The energy in a solenoid depends on the current, and therefore on the magnetic field created by the current: ...
5 - apel slice
... In a simple circuit, known as a series circuit, electric charge can flow only in one path. When the power source is turned on, the charged particles in the wire start flowing in one direction around a single loop. Any bulb along this path receives the same amount of electrical energy. If all the bul ...
... In a simple circuit, known as a series circuit, electric charge can flow only in one path. When the power source is turned on, the charged particles in the wire start flowing in one direction around a single loop. Any bulb along this path receives the same amount of electrical energy. If all the bul ...
Chapter 14: Magnets and Electromagnetism 1. Electrons flow
... Chapter 14: Magnets and Electromagnetism 1. Electrons flow around a circular wire loop in a horizontal plane, in a direction that is clockwise when viewed from above. This causes a magnetic field. Inside the loop, the direction of this field is A. up. B. down. C. toward the center of the loop. D. ra ...
... Chapter 14: Magnets and Electromagnetism 1. Electrons flow around a circular wire loop in a horizontal plane, in a direction that is clockwise when viewed from above. This causes a magnetic field. Inside the loop, the direction of this field is A. up. B. down. C. toward the center of the loop. D. ra ...
Electromagnetism
... Review the idea of electric circuits and batteries in terms of the flow if electrons through wires. Speculate on whether it might be possible to “see” the movement of electrons without using a light bulb or something similar. Bring out the large coil of wire and hook it up to the battery and switch. ...
... Review the idea of electric circuits and batteries in terms of the flow if electrons through wires. Speculate on whether it might be possible to “see” the movement of electrons without using a light bulb or something similar. Bring out the large coil of wire and hook it up to the battery and switch. ...
The electric force in an electric field
... A capacitor consists of two metal plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. ...
... A capacitor consists of two metal plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. ...
17.1 Electric Potential and Potential Difference
... near the positive plate will be acted upon by the electric force which will move it towards the negative plate. The work done on the positive charge is f x d, and this work results in the particle gaining kinetic energy (f x d). Thus it must lose potential energy equal to -(f x d). The electric fiel ...
... near the positive plate will be acted upon by the electric force which will move it towards the negative plate. The work done on the positive charge is f x d, and this work results in the particle gaining kinetic energy (f x d). Thus it must lose potential energy equal to -(f x d). The electric fiel ...
Phys 122-TT - UMD Physics
... throughout. Also, do review the essentials of vector algebra [see Notes from PHYS 121]. If you need help, please get it as soon as possible. As described below, I am always available. Never hesitate to let me know if you are experiencing difficulties. Online Text We have come to the present situatio ...
... throughout. Also, do review the essentials of vector algebra [see Notes from PHYS 121]. If you need help, please get it as soon as possible. As described below, I am always available. Never hesitate to let me know if you are experiencing difficulties. Online Text We have come to the present situatio ...
Chapter 20 Electric Potential and Electric Potential Energy
... (a) If two spheres of different radii have the same electric potential at their surfaces, the sphere with the smaller radius of curvature has the greater charge density and the greater electric field. (b) An arbitrarily shaped conductor can be approximated by spheres with the same potential at the s ...
... (a) If two spheres of different radii have the same electric potential at their surfaces, the sphere with the smaller radius of curvature has the greater charge density and the greater electric field. (b) An arbitrarily shaped conductor can be approximated by spheres with the same potential at the s ...
Unit 9: Energy, electricity and magnetism
... These objects become positively or negatively electrically charged. ● Opposite charges (positive and negative) attract each other. ● Same charges (positive and positive / negative and negative) repel each other. ...
... These objects become positively or negatively electrically charged. ● Opposite charges (positive and negative) attract each other. ● Same charges (positive and positive / negative and negative) repel each other. ...
File - GALVANOMETER
... first described by Hans Oersted in 1820. The phenomenon was studied both for its own sake and as a means of measuring electrical current. The earliest galvanometer was reported by Johann Schweigger at the University of Halle on 16 September 1820. André-Marie Ampère also contributed to its developmen ...
... first described by Hans Oersted in 1820. The phenomenon was studied both for its own sake and as a means of measuring electrical current. The earliest galvanometer was reported by Johann Schweigger at the University of Halle on 16 September 1820. André-Marie Ampère also contributed to its developmen ...
Electric current
An electric current is a flow of electric charge. In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire. It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in a plasma.The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.Electric currents cause Joule heating, which creates light in incandescent light bulbs. They also create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, inductors and generators.The particles that carry the charge in an electric current are called charge carriers. In metals, one or more electrons from each atom are loosely bound to the atom, and can move freely about within the metal. These conduction electrons are the charge carriers in metal conductors.























