The Endocrine System (Chapter 16)
... Describe the cellular structure of the thyroid gland and explain the steps involved in the synthesis and secretion of T3 and T4 from follicular cells. Explain what thyroxine is and which thyroid hormone is the active form circulating in the blood. Explain the physiological basis for the endocrine ab ...
... Describe the cellular structure of the thyroid gland and explain the steps involved in the synthesis and secretion of T3 and T4 from follicular cells. Explain what thyroxine is and which thyroid hormone is the active form circulating in the blood. Explain the physiological basis for the endocrine ab ...
L7 - Endocrine system - Moodle
... • Endocrine glands (ductless glands) – secretions (hormones) discharged into blood (or lymph) directly ...
... • Endocrine glands (ductless glands) – secretions (hormones) discharged into blood (or lymph) directly ...
Parathyroid glands produce parathyroid hormone, which
... PTH opposes the effect of thyrocalcitonin (or calcitonin), a hormone produced by the thyroid gland that regulates calcium levels. It does this by removing calcium from its storage sites in bones and releasing it into the bloodstream. It also signals the kidneys to reabsorb more of this mineral, tran ...
... PTH opposes the effect of thyrocalcitonin (or calcitonin), a hormone produced by the thyroid gland that regulates calcium levels. It does this by removing calcium from its storage sites in bones and releasing it into the bloodstream. It also signals the kidneys to reabsorb more of this mineral, tran ...
a11 Endocrine System
... The Endocrine System A more broad-based and long-lasting communication system than the nervous system Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes • Reproduction • Growth and development • Mobilization of body defenses • Maintenan ...
... The Endocrine System A more broad-based and long-lasting communication system than the nervous system Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes • Reproduction • Growth and development • Mobilization of body defenses • Maintenan ...
Lecture 1A PowerPoint
... (Body temperature lowers) increased body temp. (Heart rate slows) increase heart rate (Decreased blood sugar levels) increase BS levels (Increase in blood glucose levels) decrease BS levels (High blood pressure) lowers BP (Dehydration) increased hydration ...
... (Body temperature lowers) increased body temp. (Heart rate slows) increase heart rate (Decreased blood sugar levels) increase BS levels (Increase in blood glucose levels) decrease BS levels (High blood pressure) lowers BP (Dehydration) increased hydration ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 10
... amino acids, both of which can be used as an energy source. In the liver and in skeletal muscle, the glucose is stored as glycogen. In adipose tissue glucose is converted to fat. The amino acids can be used to synthesize proteins or glucose. ...
... amino acids, both of which can be used as an energy source. In the liver and in skeletal muscle, the glucose is stored as glycogen. In adipose tissue glucose is converted to fat. The amino acids can be used to synthesize proteins or glucose. ...
Endocrine Lecture Test Questions – Set 5
... a. anti-inflammatory actions b. maintenance of normal blood levels of calcium c. mobilization of stored fats d. promotion of gluconeogenesis e. immune suppression ...
... a. anti-inflammatory actions b. maintenance of normal blood levels of calcium c. mobilization of stored fats d. promotion of gluconeogenesis e. immune suppression ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 2 The Human Muscular
... a. Skeletal Muscle. Each skeletal muscle is an individual organ of the human body. Each is composed of several types of tissues, mainly striated muscle fibers, and fibrous connective tissue (FCT). Each is attached to and moves bones. Bones are parts of the skeleton serving as levers. The large porti ...
... a. Skeletal Muscle. Each skeletal muscle is an individual organ of the human body. Each is composed of several types of tissues, mainly striated muscle fibers, and fibrous connective tissue (FCT). Each is attached to and moves bones. Bones are parts of the skeleton serving as levers. The large porti ...
The Endocrine System: An Overview Endocrine - dr
... Amino acid-based hormones – protein based Steroids- lipid based derived from cholesterol ...
... Amino acid-based hormones – protein based Steroids- lipid based derived from cholesterol ...
SECOND HORMONE(s)
... 22. All of the following glands listed below are endocrine glands, except? Answer not given. . . You should be able to figure out from the choices given. 23. Characteristics of Exocrine Glands include all of the following, except? a. non-hormonal material secreted through ducts b. holocrine, merocri ...
... 22. All of the following glands listed below are endocrine glands, except? Answer not given. . . You should be able to figure out from the choices given. 23. Characteristics of Exocrine Glands include all of the following, except? a. non-hormonal material secreted through ducts b. holocrine, merocri ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System - Linn
... physiological system • Positive feedback—(uncommon) mechanisms that amplify physiological changes ...
... physiological system • Positive feedback—(uncommon) mechanisms that amplify physiological changes ...
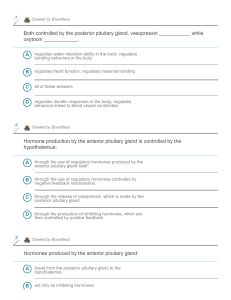
Both controlled by the posterior pituitary gland, vasopressin ______
... avoid insufficient amounts of calcium. ...
... avoid insufficient amounts of calcium. ...
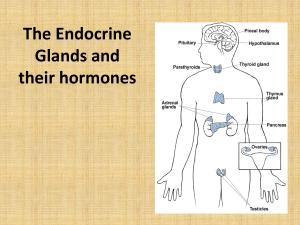
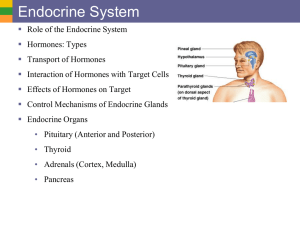
The Endocrine System
... these endocrine organs are distributed by the circulatory system to target tissues throughout the body. Each hormone affects a specific set of target tissues that may differ from that of other hormones. The selectivity is based on the presence or absence of hormone-specific receptors in the cell mem ...
... these endocrine organs are distributed by the circulatory system to target tissues throughout the body. Each hormone affects a specific set of target tissues that may differ from that of other hormones. The selectivity is based on the presence or absence of hormone-specific receptors in the cell mem ...
File - CAPE BIO UNIT I 2012
... • The endocrine tissue of the pancreas includes the islets of Langerhans. This area is responsible for the production and release of certain hormones into the bloodstream. The main three types of cells that produce hormones in the islets of Langerhans are: • Alpha cells - release the hormone glucag ...
... • The endocrine tissue of the pancreas includes the islets of Langerhans. This area is responsible for the production and release of certain hormones into the bloodstream. The main three types of cells that produce hormones in the islets of Langerhans are: • Alpha cells - release the hormone glucag ...
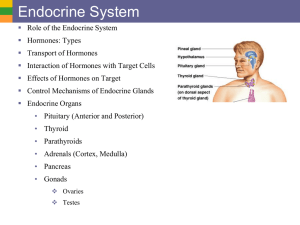
Endocrine System
... Endocrine glands - Secrete chemicals, hormones, directly into bloodstream. - Ductless glands Exocrine glands - Secrete substance through a duct i.e.Sweat, salivary, lacrimal and pancreas. Hormones = chemical substances that coordinate and direct target organ cells (only specific cells respond) ...
... Endocrine glands - Secrete chemicals, hormones, directly into bloodstream. - Ductless glands Exocrine glands - Secrete substance through a duct i.e.Sweat, salivary, lacrimal and pancreas. Hormones = chemical substances that coordinate and direct target organ cells (only specific cells respond) ...
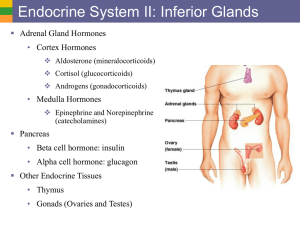
1c Endo Sys II - Inferior Glands
... Adipose tissue: leptin for appetite control Many other areas have scattered endocrine cells ...
... Adipose tissue: leptin for appetite control Many other areas have scattered endocrine cells ...
Sherwood 7
... autonomic, somatic, and endocrine responses that automatically accompany various emotional and behavioral states • Medulla within brain stem is region directly responsible for autonomic output • Some autonomic reflexes, such as urination, defecation, and erection, are integrated at spinal cord level ...
... autonomic, somatic, and endocrine responses that automatically accompany various emotional and behavioral states • Medulla within brain stem is region directly responsible for autonomic output • Some autonomic reflexes, such as urination, defecation, and erection, are integrated at spinal cord level ...
1 Endocrine System
... The Endocrine System A more broad-based and long-lasting communication system than the nervous system Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes • Reproduction • Growth and development • Mobilization of body defenses • Maintenan ...
... The Endocrine System A more broad-based and long-lasting communication system than the nervous system Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes • Reproduction • Growth and development • Mobilization of body defenses • Maintenan ...
Endocrine System: http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/ap1int.htm
... The thyroid is a small gland inside the neck, located in front of your breathing airway (trachea) and below your Adam's apple. The thyroid hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products wi ...
... The thyroid is a small gland inside the neck, located in front of your breathing airway (trachea) and below your Adam's apple. The thyroid hormones control your metabolism, which is the body's ability to break down food and store it as energy and the ability to break down food into waste products wi ...
File
... identify and give functions (including where blood is coming from and going to, as applicable) for each of the following: – left and right atria – left and right ventricles – coronary arteries and veins – anterior and posterior vena cava – aorta – pulmonary arteries and veins – pulmonary trunk – a ...
... identify and give functions (including where blood is coming from and going to, as applicable) for each of the following: – left and right atria – left and right ventricles – coronary arteries and veins – anterior and posterior vena cava – aorta – pulmonary arteries and veins – pulmonary trunk – a ...
The Adrenal Glands
... The glucocorticoids get their name from their effect of raising the level of blood sugar (glucose). One way they do this is by stimulating the liver to convert fat and protein into intermediate metabolites that are ultimately converted into glucose. The most abundant glucocorticoid is cortisol (also ...
... The glucocorticoids get their name from their effect of raising the level of blood sugar (glucose). One way they do this is by stimulating the liver to convert fat and protein into intermediate metabolites that are ultimately converted into glucose. The most abundant glucocorticoid is cortisol (also ...
End of Chapter 13 Questions
... Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is regulated in part by corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus in response to low levels of adrenal cortical hormones. Stress increases secretion of ACTH by stimulating CRH production. 20. List the major gonadotropins, and explain the general ...
... Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is regulated in part by corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus in response to low levels of adrenal cortical hormones. Stress increases secretion of ACTH by stimulating CRH production. 20. List the major gonadotropins, and explain the general ...
Biology 232
... increases solubility in blood plasma slows down breakdown and excretion provides hormone reserve in bloodstream free fraction (small percentage of unbound hormone) these are the only active form of hormones Mechanisms of Hormone Action – various target cells can respond differently to the same hormo ...
... increases solubility in blood plasma slows down breakdown and excretion provides hormone reserve in bloodstream free fraction (small percentage of unbound hormone) these are the only active form of hormones Mechanisms of Hormone Action – various target cells can respond differently to the same hormo ...
Thyroid Hormone
... • Has both exocrine and endocrine cells – Acinar cells (exocrine) produce enzyme-rich juice for digestion – Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) contain endocrine cells • Alpha () cells produce glucagon (hyperglycemic ...
... • Has both exocrine and endocrine cells – Acinar cells (exocrine) produce enzyme-rich juice for digestion – Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) contain endocrine cells • Alpha () cells produce glucagon (hyperglycemic ...
Cardiac physiology

Cardiac physiology or heart function is the study of healthy, unimpaired function of the heart: involving blood flow; myocardium structure; the electrical conduction system of the heart; the cardiac cycle and cardiac output and how these interact and depend on one another.