CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... produces 2 closely related catecholamine hormones, which function in the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system: ...
... produces 2 closely related catecholamine hormones, which function in the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system: ...
Chapter 19 - endocrine - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
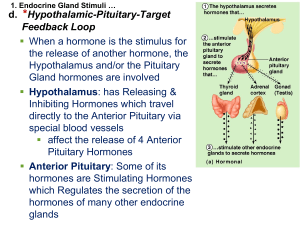
... regulatory hormones to control activity of the adenohypophysis (anterior lobe of the pituitary gland). Regulatory hormones reach their targets via the hypophyseal ...
... regulatory hormones to control activity of the adenohypophysis (anterior lobe of the pituitary gland). Regulatory hormones reach their targets via the hypophyseal ...
The Endocrine System
... – endocrine glands are ductless, their secretions (hormones) are released directly into the bloodstream and travel to target organs. – Note that this is in contrast to digestive glands (exocrine), which have ducts for releasing the digestive enzymes. Endocrine/Parathyroid hormone animation MHHE ...
... – endocrine glands are ductless, their secretions (hormones) are released directly into the bloodstream and travel to target organs. – Note that this is in contrast to digestive glands (exocrine), which have ducts for releasing the digestive enzymes. Endocrine/Parathyroid hormone animation MHHE ...
Biology 416K Summer 2002
... Define hormone, target cell, ligand, receptor, endocrine, paracrine and autocrine. State the basic characteristics of hormones. For each hormone in Figs 7-2 and 7-13, state the following: - full name (spelling counts) - name and location of secreting organ - chemical class and basic chemical s ...
... Define hormone, target cell, ligand, receptor, endocrine, paracrine and autocrine. State the basic characteristics of hormones. For each hormone in Figs 7-2 and 7-13, state the following: - full name (spelling counts) - name and location of secreting organ - chemical class and basic chemical s ...
Endocrine Ch 16-Fall 2016-StudentRevised
... sugar levels Rising blood glucose levels return blood sugar to homeostatic set point; stimulus for glucagon release diminishes Liver breaks down glycogen stores and releases glucose to the blood ...
... sugar levels Rising blood glucose levels return blood sugar to homeostatic set point; stimulus for glucagon release diminishes Liver breaks down glycogen stores and releases glucose to the blood ...
Endocrine Note Cards
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
Hormones Gone Wild KEY
... The endocrine system releases hormones to maintain homeostasis and uses feedback to regulate the levels of these chemical signals. Hormones help balance the amount of water in our body, the amount of calcium in our blood and bones, and the amount of growth in cells and tissues. In your study of diab ...
... The endocrine system releases hormones to maintain homeostasis and uses feedback to regulate the levels of these chemical signals. Hormones help balance the amount of water in our body, the amount of calcium in our blood and bones, and the amount of growth in cells and tissues. In your study of diab ...
Hormonal Control
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary does not synthesize hormones, but it does store and release ADH. The main function of ADH is to decrease urinary output and maintain water levels. In the absence of ADH, normal urine output of 1-2 L would increase to 25 L per day. ADH is also released if there is ...
... The posterior lobe of the pituitary does not synthesize hormones, but it does store and release ADH. The main function of ADH is to decrease urinary output and maintain water levels. In the absence of ADH, normal urine output of 1-2 L would increase to 25 L per day. ADH is also released if there is ...
Ch 17 Powerpoint
... II in the lung, which causes aldosterone secretion which ↑blood volume & ↑in blood pressure. »A second target for angiotensin II is arteriole walls – they constrict which further increases blood pressure. ...
... II in the lung, which causes aldosterone secretion which ↑blood volume & ↑in blood pressure. »A second target for angiotensin II is arteriole walls – they constrict which further increases blood pressure. ...
Pituitary Hormones and Their Control by the Hypothalamus
... The molecular weight of somatomedins C is about 7500, and it’s concentration in the plasma closely follow the rate of growth hormone secretion. E. g. the pygmies of Africa have a congenital in ability to synthesize significant amounts of somatomedins C. therefore even their plasma concentration of g ...
... The molecular weight of somatomedins C is about 7500, and it’s concentration in the plasma closely follow the rate of growth hormone secretion. E. g. the pygmies of Africa have a congenital in ability to synthesize significant amounts of somatomedins C. therefore even their plasma concentration of g ...
Chapter 13 Endocrine
... ii. Populations of cells that provide the endocrine function of the pancreas are called ______ iii. Name the three distinct types of hormone-producing cells in the pancreas. Indicate the hormone secreted by each cell type. ...
... ii. Populations of cells that provide the endocrine function of the pancreas are called ______ iii. Name the three distinct types of hormone-producing cells in the pancreas. Indicate the hormone secreted by each cell type. ...
File
... • Each hormone has a corrective effect, eliminating the stimulus, which then leads to a reduction in hormone secretion. • This process is called a negative feedback homeostatic control system to keep hormones at normal levels. (if levels increased it would be called positive feedback) ...
... • Each hormone has a corrective effect, eliminating the stimulus, which then leads to a reduction in hormone secretion. • This process is called a negative feedback homeostatic control system to keep hormones at normal levels. (if levels increased it would be called positive feedback) ...
Endocrine System Disorders
... Endocrine system - together with the nervous system, acts as the body´s communication network ...
... Endocrine system - together with the nervous system, acts as the body´s communication network ...
thyroid hormone
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
Slide 1
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
The Endocrine System
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
Endocrine System
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
Unit One – Concept Two - Calgary Christian School
... Prolactin (PRL) – targets mammary glands, stimulates milk production (inhibited by an inhibitory hormone produced in the hypothalamus - dopamine ) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) – targets ovaries and testes, stimulates follicle development in female ovaries and stimulates the development of sper ...
... Prolactin (PRL) – targets mammary glands, stimulates milk production (inhibited by an inhibitory hormone produced in the hypothalamus - dopamine ) Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) – targets ovaries and testes, stimulates follicle development in female ovaries and stimulates the development of sper ...
thyroid releasing hormone
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
... thyroid hormone Blue is from hypothalamus Black is from pituitary ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) produce corticosteroids: aldosterone and turns on TSH cortisol CRH (corticotropin releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on ACTH estrog ...
thyroid releasing hormone
... hormone Blue is from hypothalamus ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce Black is from pituitary corticosteroids: aldosterone and cortisol TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on TSH estrogen production; stimulates sperm CRH (corticotropin releasing ...
... hormone Blue is from hypothalamus ACTH stimulates the adrenal cortex to produce Black is from pituitary corticosteroids: aldosterone and cortisol TRH (thyroid releasing hormone) FSH stimulates follicle growth and ovarian turns on TSH estrogen production; stimulates sperm CRH (corticotropin releasing ...
Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of
... Secrete into a duct and to the outside of a body surface sweat, tear, saliva Secrete (hormone) into the blood Hormone circulates in blood and acts at target organs where hormone receptor is expressed insulin ...
... Secrete into a duct and to the outside of a body surface sweat, tear, saliva Secrete (hormone) into the blood Hormone circulates in blood and acts at target organs where hormone receptor is expressed insulin ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Releasing Factors (hormones) stimulate secretion by Anterior Pituitary Inhibiting Factors (hormones) are antagonistic to Releasing Nervous tissue carries hormones to ...
... Releasing Factors (hormones) stimulate secretion by Anterior Pituitary Inhibiting Factors (hormones) are antagonistic to Releasing Nervous tissue carries hormones to ...
Endocrine System
... the pancreas does not produce enough of the hormone insulin or the body does not effectively use the insulin it does produce. Because insulin is instrumental in helping the body convert sugars and starches into necessary energy, there can be serious consequences if diabetes is left undiagnosed and/o ...
... the pancreas does not produce enough of the hormone insulin or the body does not effectively use the insulin it does produce. Because insulin is instrumental in helping the body convert sugars and starches into necessary energy, there can be serious consequences if diabetes is left undiagnosed and/o ...