the muscular system
... These are the male glands and are found in the groin, in the scrotum. The testes produce the hormone testosterone responsible for male sexual characteristics and for the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as the deepening of the voice and beard growth. ...
... These are the male glands and are found in the groin, in the scrotum. The testes produce the hormone testosterone responsible for male sexual characteristics and for the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as the deepening of the voice and beard growth. ...
Document
... • Name one hormone produced by each gland. • Give one function for each hormone. • Why is the pituitary often called the “master gland”? • Where would you find the Islets of Langerhans? ...
... • Name one hormone produced by each gland. • Give one function for each hormone. • Why is the pituitary often called the “master gland”? • Where would you find the Islets of Langerhans? ...
BIOLOGY 30 Review Assignment Part I
... In a normal male, the sequence of the structures numbered above through which sperm cells travel from the time when spermatogenesis occurs to the time when ejaculation occurs is _____, _____, _____, and _____. (Record all four digits of your answer in the numerical‐response section on the answer ...
... In a normal male, the sequence of the structures numbered above through which sperm cells travel from the time when spermatogenesis occurs to the time when ejaculation occurs is _____, _____, _____, and _____. (Record all four digits of your answer in the numerical‐response section on the answer ...
HumanEndocrineSystem
... seven hormones. One hormone, the human growth hormone (HGH), promotes body growth by accelerating protein synthesis. This hormone is also known as somatotropin. A deficiency of the hormone results in dwarfism; an oversecretion results in gigantism. Another hormone of the anterior pituitary is prolac ...
... seven hormones. One hormone, the human growth hormone (HGH), promotes body growth by accelerating protein synthesis. This hormone is also known as somatotropin. A deficiency of the hormone results in dwarfism; an oversecretion results in gigantism. Another hormone of the anterior pituitary is prolac ...
III Semester Botany MODULE 7 ENDOCRINOLOGY
... The thyroid gland is a large gland located in the neck, where it is attached to the trachea just below the larynx. The parathyroid glands are embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is composed of a large number of follicles, each a small spherical structure made of ...
... The thyroid gland is a large gland located in the neck, where it is attached to the trachea just below the larynx. The parathyroid glands are embedded in the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is composed of a large number of follicles, each a small spherical structure made of ...
chemical coordination and integration
... Pancreas is a composite gland (Figure 22.1) which acts as both exocrine and endocrine gland. The endocrine pancreas consists of ‘Islets of Langerhans’. There are about 1 to 2 million Islets of Langerhans in a normal human pancreas representing only 1 to 2 per cent of the pancreatic tissue. The two m ...
... Pancreas is a composite gland (Figure 22.1) which acts as both exocrine and endocrine gland. The endocrine pancreas consists of ‘Islets of Langerhans’. There are about 1 to 2 million Islets of Langerhans in a normal human pancreas representing only 1 to 2 per cent of the pancreatic tissue. The two m ...
Topic: The Endocrine System
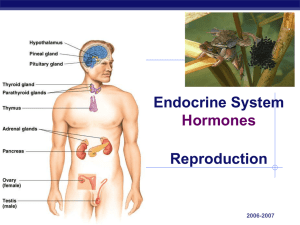
... What is the Hypothalamus? • Tiny gland located at the base of the brain • Major link between nervous and endocrine systems • Produces hormones that help turn all other endocrine glands on or off ...
... What is the Hypothalamus? • Tiny gland located at the base of the brain • Major link between nervous and endocrine systems • Produces hormones that help turn all other endocrine glands on or off ...
chemical signals in animals
... A)- Anterior pituitary hormones. 1) Growth hormone (GH): a protein. • Stimulates growth and metabolism. • Secretion is regulated by hypothalamic hormones. • Acts directly on boon tissues or acts via growth factors. • Gigantism: العملقةexcessive GH during development. • Acromegaly: excessive GH p ...
... A)- Anterior pituitary hormones. 1) Growth hormone (GH): a protein. • Stimulates growth and metabolism. • Secretion is regulated by hypothalamic hormones. • Acts directly on boon tissues or acts via growth factors. • Gigantism: العملقةexcessive GH during development. • Acromegaly: excessive GH p ...
MD0807 6-1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Review of the
... b. Effects of Thyroxin. When thyroxin reaches the cells of the body, it stimulates them to use more oxygen. This increases the metabolic rate (basal metabolism) of the body. Basal metabolism is defined as the amount of oxygen the body uses per unit of weight when the body is at rest. Thyroxin also ...
... b. Effects of Thyroxin. When thyroxin reaches the cells of the body, it stimulates them to use more oxygen. This increases the metabolic rate (basal metabolism) of the body. Basal metabolism is defined as the amount of oxygen the body uses per unit of weight when the body is at rest. Thyroxin also ...
Chapter 46 - Workforce3One
... reflex and uterine contractions in women during childbirth • Produced by neuron cell bodies located in hypothalamus----transported along axon tracts from hypothalamus------to posterior pituitary for storage-----Upon appropriate stimulation the neurohormones get released into blood ...
... reflex and uterine contractions in women during childbirth • Produced by neuron cell bodies located in hypothalamus----transported along axon tracts from hypothalamus------to posterior pituitary for storage-----Upon appropriate stimulation the neurohormones get released into blood ...
Hormones and Behavior 1
... -induces ACTH secretion Somatostatin-inhibits GH secretion Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) -induces GH secretion Prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH): Most likely dopamine -inhibits PRL secretion ...
... -induces ACTH secretion Somatostatin-inhibits GH secretion Growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) -induces GH secretion Prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH): Most likely dopamine -inhibits PRL secretion ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... 20 years old, 6ng/ml; 20 – 40 years old, 3ng/ml; 40 – 70 years old, 1.6ng/ml. The change of GH concentration within one day. ...
... 20 years old, 6ng/ml; 20 – 40 years old, 3ng/ml; 40 – 70 years old, 1.6ng/ml. The change of GH concentration within one day. ...
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... hair follicles in facial, pectoral, axillary, inguinal regions (hair growth) o genitalia (enlargement) o muscle and bone (growth and strengthening) o vocal cords in larynx (thicken resulting in deeper voice). ...
... hair follicles in facial, pectoral, axillary, inguinal regions (hair growth) o genitalia (enlargement) o muscle and bone (growth and strengthening) o vocal cords in larynx (thicken resulting in deeper voice). ...
The Endocrine System Chapter 47 1
... Develops from a pouch of epithelial tissue that pinches off the roof of the embryo’s mouth. – produces the hormones it secretes: growth hormone (GH) stimulates muscles and bones to grow adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) regulates glucose homeostasis thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulate ...
... Develops from a pouch of epithelial tissue that pinches off the roof of the embryo’s mouth. – produces the hormones it secretes: growth hormone (GH) stimulates muscles and bones to grow adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) regulates glucose homeostasis thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) stimulate ...
Endocrine Virtual Lab! AP Biology
... sustains the female reproductive tract. A woman who lacks ovaries (and therefore follicles) will not produce estrogen. However, the pituitary gland will secrete excess LH because the feedback inhibition no longer exists. Excess levels of estrogen cause early sexual development in the female as do hi ...
... sustains the female reproductive tract. A woman who lacks ovaries (and therefore follicles) will not produce estrogen. However, the pituitary gland will secrete excess LH because the feedback inhibition no longer exists. Excess levels of estrogen cause early sexual development in the female as do hi ...
Thyroid hormones
... Estradiol acts on ovarian follicles to promote granulosa cell differentiation, on uterus to stimulate its growth and maintain the cyclic change of uterine mucosa, on mammary gland to stimulate ductal growth, on bone to promote linear growth and closure of epiphyseal plates, on HPA to regulate secret ...
... Estradiol acts on ovarian follicles to promote granulosa cell differentiation, on uterus to stimulate its growth and maintain the cyclic change of uterine mucosa, on mammary gland to stimulate ductal growth, on bone to promote linear growth and closure of epiphyseal plates, on HPA to regulate secret ...
The Endocrine System
... fertilized egg Helps maintain pregnancy Prepares the breasts to produce milk ...
... fertilized egg Helps maintain pregnancy Prepares the breasts to produce milk ...
Chapter 13
... • Consists of a group of glands that produce hormones • Works with nervous system to control and coordinate all other body systems • Effects body systems by chemical stimuli ...
... • Consists of a group of glands that produce hormones • Works with nervous system to control and coordinate all other body systems • Effects body systems by chemical stimuli ...
Endocrine System
... • Release of hormones is controlled by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus • Hypothlamus produces two hormones that are transorted to neurosecretory cells of the posterior pituitary • The poterior pituitary is not strictly an endocrine gland, but does release hormones ...
... • Release of hormones is controlled by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus • Hypothlamus produces two hormones that are transorted to neurosecretory cells of the posterior pituitary • The poterior pituitary is not strictly an endocrine gland, but does release hormones ...
releasing hormones
... ◦ Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormone ◦ Secretion is regulated thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) from hypothalamus Low blood thyroid hormone levels cause TRH to be released TRH causes production of TSH High thyroid hormone levels inhibit TRH, which decreases TSH release ...
... ◦ Stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormone ◦ Secretion is regulated thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) from hypothalamus Low blood thyroid hormone levels cause TRH to be released TRH causes production of TSH High thyroid hormone levels inhibit TRH, which decreases TSH release ...
Endocrine functions of the pituitary and pineal glands 1/20
... Promotes Protein Synthesis, Stops growth plate DHEA (dehydroxyepandiosterone) is a precursor for testosterone synthesis – FSH release is inhibited because high levels of testosterone inhibit GnRH release from hypothalamus ...
... Promotes Protein Synthesis, Stops growth plate DHEA (dehydroxyepandiosterone) is a precursor for testosterone synthesis – FSH release is inhibited because high levels of testosterone inhibit GnRH release from hypothalamus ...
Document
... – The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine into the blood stream. • The effects of these hormones resemble those of the sympathetic division neurotransmitters of the same name, except that they last up to 10 times longer when they are secreted as hormones. ...
... – The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine into the blood stream. • The effects of these hormones resemble those of the sympathetic division neurotransmitters of the same name, except that they last up to 10 times longer when they are secreted as hormones. ...