Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... atom within a small pebble were the size of the pebble itself, the pebble would be larger than Mount Everest. ...
... atom within a small pebble were the size of the pebble itself, the pebble would be larger than Mount Everest. ...
A is for atom
... form of light. The frequency (colour) of the radiation is directly related to the ……………………….. between the energy levels. Since each element has its own ……………………series of ...
... form of light. The frequency (colour) of the radiation is directly related to the ……………………….. between the energy levels. Since each element has its own ……………………series of ...
class xi chemistry holiday homework
... threshold energy or work function. No photoelectric effect is shown if incident frequency is less than v0 even if intensity of a radiation is increased. However, number of photoelectrons ejected is proportional to the intensity of incident radiation. ...
... threshold energy or work function. No photoelectric effect is shown if incident frequency is less than v0 even if intensity of a radiation is increased. However, number of photoelectrons ejected is proportional to the intensity of incident radiation. ...
Atomic Structure Study Guide
... Gold Foil Experiment: Marsden aimed a narrow beam of alpha particles at the gold. The screen around the gold was made of a material that produced a flash of light when struck by a fast-moving alpha particle. By observing the flash, Marsden could figure out the path of an alpha particle after it pass ...
... Gold Foil Experiment: Marsden aimed a narrow beam of alpha particles at the gold. The screen around the gold was made of a material that produced a flash of light when struck by a fast-moving alpha particle. By observing the flash, Marsden could figure out the path of an alpha particle after it pass ...
Periodic Table Oakland Schools Chemistry Resource Unit Andrew D. Hulbert
... properties of the missing elements in his table, leaving blanks to be filled in later. Mendeleev did not have knowledge of atomic numbers or electron configuration. Families were arranged according to increasing atomic mass and their observed properties. Forty years after Mendeleev published his per ...
... properties of the missing elements in his table, leaving blanks to be filled in later. Mendeleev did not have knowledge of atomic numbers or electron configuration. Families were arranged according to increasing atomic mass and their observed properties. Forty years after Mendeleev published his per ...
Untitled
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
Section 6.1 Development of the Modern Periodic Table
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
... electrons indicates the period on the periodic table in which it is found. • The number of valence electrons for elements in groups 13-18 is ten less than their group number. ...
Chapter 2 ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... • Using two scientific laws discovered in the late 1700’s, Dalton built his atomic theory ...
... • Using two scientific laws discovered in the late 1700’s, Dalton built his atomic theory ...
2.1 Imaging and Moving Individual Atoms
... 2.1 Imaging and Moving Individual Atoms page 43 2.2 Early Ideas about the Building Blocks of Matter page 45 2.3 Modern Atomic Theory and the Laws That Led to It page 45 2.4 The Discovery of the Electron 49 2.5 The Structure of the Atom page 51 2.6 Subatomic Particles: Protons, Neutrons, and Electron ...
... 2.1 Imaging and Moving Individual Atoms page 43 2.2 Early Ideas about the Building Blocks of Matter page 45 2.3 Modern Atomic Theory and the Laws That Led to It page 45 2.4 The Discovery of the Electron 49 2.5 The Structure of the Atom page 51 2.6 Subatomic Particles: Protons, Neutrons, and Electron ...
Covalent bond - general description 1H: 1s : F • + • F : → : F : F
... Orbital overlap was an idea first proposed by Linus Pauling to explain the molecular bond angles observed through experimentation and is the basis for the concept of orbital hybridisation. s-orbitals are spherical and have no directionality in space while p-orbitals are oriented 90° to one another. ...
... Orbital overlap was an idea first proposed by Linus Pauling to explain the molecular bond angles observed through experimentation and is the basis for the concept of orbital hybridisation. s-orbitals are spherical and have no directionality in space while p-orbitals are oriented 90° to one another. ...
Science 9 - Ms. J Reed
... Fill the electron shells Potassium has 19 electrons (from atomic number) So, 2 electrons in the first shell, 8 in the second, 8 in the third and 1 in the fourth ...
... Fill the electron shells Potassium has 19 electrons (from atomic number) So, 2 electrons in the first shell, 8 in the second, 8 in the third and 1 in the fourth ...
The Mighty Electron - MVUSD Haiku Learning
... minus sign, its an ion! If there is no sign, its neutral. • P = neutral atom of phosphorous • O-2 = ion of oxygen w/a -2 charge • Li+ = ion of lithium w/a +1 charge ...
... minus sign, its an ion! If there is no sign, its neutral. • P = neutral atom of phosphorous • O-2 = ion of oxygen w/a -2 charge • Li+ = ion of lithium w/a +1 charge ...
atoms - Tenafly High School
... Atoms can be further divided into their sub-atomic particles (electrons, protons, & neutrons) ...
... Atoms can be further divided into their sub-atomic particles (electrons, protons, & neutrons) ...
TE 802 Group Unit Plan - Stephen Stauffer MATC Portfolio
... nucleus are the important parts of the atom, the protons, and neutrons. Protons have a mass of 1.67262158 E-27 kg, and a positive charge therefore they repel each other very strongly so it is necessary for a very strong force to be present to keep the nucleus intact. Neutrons have a mass of 1.674927 ...
... nucleus are the important parts of the atom, the protons, and neutrons. Protons have a mass of 1.67262158 E-27 kg, and a positive charge therefore they repel each other very strongly so it is necessary for a very strong force to be present to keep the nucleus intact. Neutrons have a mass of 1.674927 ...
Section 6.1: Covalent Bonding Basics
... attracted to each other to form ionic compounds. When covalent compounds form, neutral atoms share electrons to produce stable compounds. Atoms that are covalently bonded are called molecules. Ionic compounds are not referred to as molecules. The simplest example of sharing electrons is found in dia ...
... attracted to each other to form ionic compounds. When covalent compounds form, neutral atoms share electrons to produce stable compounds. Atoms that are covalently bonded are called molecules. Ionic compounds are not referred to as molecules. The simplest example of sharing electrons is found in dia ...
Section 3.1
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged but never created, destroyed, or changed. ...
... 3. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. 4. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds. 5. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged but never created, destroyed, or changed. ...
Catalyst – September, 7(1+1) 2009 - stroh
... Key Point #5: Electronegativity DECREASES as you go DOWN the periodic table and INCREASES as you go LEFT TO RIGHT across the periodic table. ...
... Key Point #5: Electronegativity DECREASES as you go DOWN the periodic table and INCREASES as you go LEFT TO RIGHT across the periodic table. ...
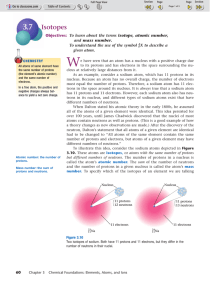
Isotopes
... all of the atoms of a given element were identical. This idea persisted for over 100 years, until James Chadwick discovered that the nuclei of most atoms contain neutrons as well as protons. (This is a good example of how a theory changes as new observations are made.) After the discovery of the neu ...
... all of the atoms of a given element were identical. This idea persisted for over 100 years, until James Chadwick discovered that the nuclei of most atoms contain neutrons as well as protons. (This is a good example of how a theory changes as new observations are made.) After the discovery of the neu ...
25 NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY NOTES __ /__ pts
... 5. Which two have the same mass? (alpha, protons, electrons, beta) 6. Which two have the same charge? (protons, electrons, neutrons, beta) 7. Which two have no charge? (protons, electrons, neutrons, gamma) 8. Which two have no mass? (protons, electrons, neutrons, gamma) 9. Which has the biggest mass ...
... 5. Which two have the same mass? (alpha, protons, electrons, beta) 6. Which two have the same charge? (protons, electrons, neutrons, beta) 7. Which two have no charge? (protons, electrons, neutrons, gamma) 8. Which two have no mass? (protons, electrons, neutrons, gamma) 9. Which has the biggest mass ...
Lone pairs
... If you cannot immediately determine the right configuration, take a deep breath and try again. Think of these as puzzles, keep on working with the pieces until they fit together ...
... If you cannot immediately determine the right configuration, take a deep breath and try again. Think of these as puzzles, keep on working with the pieces until they fit together ...
Unit 2: Structure of Matter Content Outline: History of the Atomic
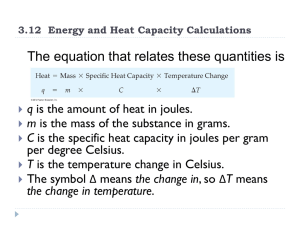
... III. Atomic Mass Units (AMU) A. Also Known as (A.K.A.) Mass Number B. This term refers to the total weight of an atom of that element. C. It is found by adding the number of protons and neutrons together. 1. Each proton OR each neutron has a mass of 1 AMU or 1 Dalton. 2. Electrons mass is insignifi ...
... III. Atomic Mass Units (AMU) A. Also Known as (A.K.A.) Mass Number B. This term refers to the total weight of an atom of that element. C. It is found by adding the number of protons and neutrons together. 1. Each proton OR each neutron has a mass of 1 AMU or 1 Dalton. 2. Electrons mass is insignifi ...
Chapter 18 - Powell County Schools
... Atomic mass, mass number, and isotopes Mass number In addition to the atomic number, every atomic nucleus can be described by its mass number. The mass number is equal to the total number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Recall that atoms of the same element have the same number o ...
... Atomic mass, mass number, and isotopes Mass number In addition to the atomic number, every atomic nucleus can be described by its mass number. The mass number is equal to the total number of protons plus neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Recall that atoms of the same element have the same number o ...
Atomic Theory
... These particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged subatomic particles. Protons cluster with uncharged subatomic particles called neutrons. Protons and neutrons form the central positively charged core, or nucleus, of an atom. Fast-moving, negatively charged electro ...
... These particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons are positively charged subatomic particles. Protons cluster with uncharged subatomic particles called neutrons. Protons and neutrons form the central positively charged core, or nucleus, of an atom. Fast-moving, negatively charged electro ...
14 Isotopes and Ions
... concentration of carbon-14, we can use this information to help solve questions about when the organism died. When an organism dies it has a specific ratio by mass of carbon-14 to carbon-12 incorporated in the cells of it's body. At the moment of death, no new carbon-14 containing molecules are meta ...
... concentration of carbon-14, we can use this information to help solve questions about when the organism died. When an organism dies it has a specific ratio by mass of carbon-14 to carbon-12 incorporated in the cells of it's body. At the moment of death, no new carbon-14 containing molecules are meta ...
3. classification of elements and periodicity in properties
... cerium to lutetium) are called Lanthanides or Lanthanones or Lanthanoids or rare earths. The 14 elements of seventh period (from thorium to lawrencium) are called Actinides or Actinones or Actinoids. The blocks in the Modern periodic table The Modern periodic table is divided into 4 blocks based on ...
... cerium to lutetium) are called Lanthanides or Lanthanones or Lanthanoids or rare earths. The 14 elements of seventh period (from thorium to lawrencium) are called Actinides or Actinones or Actinoids. The blocks in the Modern periodic table The Modern periodic table is divided into 4 blocks based on ...