Atomic Theory - Aurora City Schools
... called an isotope. • That’s why atomic mass is not a whole number, it averages all the isotopes • Write the mass number and atomic number to left of symbol ...
... called an isotope. • That’s why atomic mass is not a whole number, it averages all the isotopes • Write the mass number and atomic number to left of symbol ...
No Slide Title
... different from those of their component elements – In chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed but only exchanged between starting compounds to form new compounds ...
... different from those of their component elements – In chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed but only exchanged between starting compounds to form new compounds ...
Ch-6 - Stout Middle School
... repetition of chemical and physical properties of elements when arranged by increasing atomic number ...
... repetition of chemical and physical properties of elements when arranged by increasing atomic number ...
Atom Models - Democritus, Dalton, Thompson, Rutherford, Bohr
... • Elements are often symbolized with their mass ...
... • Elements are often symbolized with their mass ...
YEAR 9 REVISION LIST November Exam 2013
... In an atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. Atoms therefore have no overall electrical charge. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. The number of protons in an atom ...
... In an atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus. Atoms therefore have no overall electrical charge. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons. Atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. The number of protons in an atom ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure I. History of the Atom A. Democritus (400
... b. Atoms of different elements have different atomic numbers c. Electron number is always the same as the atomic number 1. Each positive charge is balanced by a negative charge for a neutral atom 2. Mass number: The sum of the protons and the neutrons in the nucleus of an atom a. Number of neutrons ...
... b. Atoms of different elements have different atomic numbers c. Electron number is always the same as the atomic number 1. Each positive charge is balanced by a negative charge for a neutral atom 2. Mass number: The sum of the protons and the neutrons in the nucleus of an atom a. Number of neutrons ...
The Periodic Table
... Chemistry – Dr. May Notes The Periodic Table Organization of the Elements Organizing by Properties Mendeleev (1834-1907) organized some elements according to the ratio of oxygen to the element when it oxidized. Periodic law states that properties of the elements repeat periodically when the elements ...
... Chemistry – Dr. May Notes The Periodic Table Organization of the Elements Organizing by Properties Mendeleev (1834-1907) organized some elements according to the ratio of oxygen to the element when it oxidized. Periodic law states that properties of the elements repeat periodically when the elements ...
Lesson 7
... -each electron in an orbit has a definite amount of energy -the farther the electron is from nucleus, the greater its energy -they release energy as light when they jump from higher to lower orbits -each orbit can hold a certain maximum number of electrons.(2, 8, 8) ...
... -each electron in an orbit has a definite amount of energy -the farther the electron is from nucleus, the greater its energy -they release energy as light when they jump from higher to lower orbits -each orbit can hold a certain maximum number of electrons.(2, 8, 8) ...
Isotope PPT - MrsPage.com
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
... Contain protons, neutrons, and electrons Protons & neutrons are found in the nucleus The nucleus contains most of the mass of an atom Electrons are distributed around the nucleus in energy levels/shells/orbitals (which make up the electron cloud) The outermost electrons in the shell farthest from th ...
General_Chemistry_Text_Assignments_-_HOLT
... The chemical reaction where elements react (bond together) to form a compound is called synthesis. Example: Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas react to synthesize water. 2H2 + O2 2H2O The elements in a compound can only be separated by a chemical reaction. This reaction breaks the bonds between the eleme ...
... The chemical reaction where elements react (bond together) to form a compound is called synthesis. Example: Hydrogen gas and oxygen gas react to synthesize water. 2H2 + O2 2H2O The elements in a compound can only be separated by a chemical reaction. This reaction breaks the bonds between the eleme ...
DALTON`S ATOMIC THEORY - 1808: Publication of Dalton`s "A New
... - Dalton's theory sets LIMITS on what can be done with chemistry. For example: Chemistry can't convert lead (an element) into gold (another element). Sorry, alchemists! You can't have a compound form in a chemical reaction that contains an element that was not in your starting materials. You can onl ...
... - Dalton's theory sets LIMITS on what can be done with chemistry. For example: Chemistry can't convert lead (an element) into gold (another element). Sorry, alchemists! You can't have a compound form in a chemical reaction that contains an element that was not in your starting materials. You can onl ...
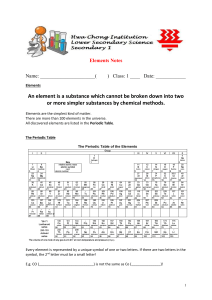
Name
... An element is a substance that contains only __________ kind of atom. All atoms of an element have the same number of __________________________, also their atomic number. At this time we know more than _________ elements, but only 90 of these occur in nature. Some familiar natural elements are : __ ...
... An element is a substance that contains only __________ kind of atom. All atoms of an element have the same number of __________________________, also their atomic number. At this time we know more than _________ elements, but only 90 of these occur in nature. Some familiar natural elements are : __ ...
CH 3 Atomic Structure Review-New
... 50. Two electrons must have __________ ______, if they occupy the same orbital. 51. Hund’s rule states that electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as ______ as possible. 52. In an electron configuration, a superscript ind ...
... 50. Two electrons must have __________ ______, if they occupy the same orbital. 51. Hund’s rule states that electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as ______ as possible. 52. In an electron configuration, a superscript ind ...
Unit 1: Introduction to Chemistry - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 50. Two electrons must have __________ ______, if they occupy the same orbital. 51. Hund’s rule states that electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as ______ as possible. 52. In an electron configuration, a superscript ind ...
... 50. Two electrons must have __________ ______, if they occupy the same orbital. 51. Hund’s rule states that electrons occupy orbitals of the same energy in a way that makes the number of electrons with the same spin direction as ______ as possible. 52. In an electron configuration, a superscript ind ...
john dalton!! - Hawk Chemistry
... • He was born September 6th, 1766 in Eaglesfield in Cumberland. • He died on July 27th, ...
... • He was born September 6th, 1766 in Eaglesfield in Cumberland. • He died on July 27th, ...
Chapter 6 Study Guide
... a. period 3, Group IIIA _____________________________________________ b. period 1, Group VIIIA ____________________________________________ c. period 4, Group IIA ______________________________________________ d. period 6, Group VA ______________________________________________ 7. How many Valence e ...
... a. period 3, Group IIIA _____________________________________________ b. period 1, Group VIIIA ____________________________________________ c. period 4, Group IIA ______________________________________________ d. period 6, Group VA ______________________________________________ 7. How many Valence e ...
Lecture 2: Atoms - U of L Class Index
... number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...
... number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have more than one naturally occurring isotope: ...
08_lecture_ppt - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 1. All matter = indivisible atoms 2. An element is made up of identical atoms. 3. Different elements have atoms with different masses. 4. Chemical compounds are made of atoms in specific integer ratios. 5. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
... 1. All matter = indivisible atoms 2. An element is made up of identical atoms. 3. Different elements have atoms with different masses. 4. Chemical compounds are made of atoms in specific integer ratios. 5. Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions. ...
Ch 6 Notes
... regular pattern, or a periodic pattern. Mendeleev placed the known elements in a table, where he arranged elements into columns with similar properties. ...
... regular pattern, or a periodic pattern. Mendeleev placed the known elements in a table, where he arranged elements into columns with similar properties. ...
The Chinese High School
... What is steel? It cannot be found in the periodic table – so it is not an element! On the same note, what is brass? Or bronze? What is 12K/18K/24K gold? What is the difference between the different types of gold? All these questions can be answered with one key word – do you know what it is? ...
... What is steel? It cannot be found in the periodic table – so it is not an element! On the same note, what is brass? Or bronze? What is 12K/18K/24K gold? What is the difference between the different types of gold? All these questions can be answered with one key word – do you know what it is? ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... b. Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. c. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. d. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds e. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, ...
... b. Atoms of a given element are identical in their physical and chemical properties. c. Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties. d. Atoms of different elements combine in simple, whole number ratios to form compounds e. In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, ...
Matter Test: Review
... 24. Circle the letters that identify quantities that are always equal to an element’s atomic number. a. Number of nuclei b. Number of protons c. Number of neutrons d. Number of electrons 25. All oxygen atoms have 8 protons. Circle the letter of the number of neutrons in an atom of oxygen-18. a. 8 ...
... 24. Circle the letters that identify quantities that are always equal to an element’s atomic number. a. Number of nuclei b. Number of protons c. Number of neutrons d. Number of electrons 25. All oxygen atoms have 8 protons. Circle the letter of the number of neutrons in an atom of oxygen-18. a. 8 ...
atoms
... Rutherford and the Nucleus: Gold Foil Experiment A few particles deflected strongly Some bounced back!! Neutrons (no charge): located in center of atom Protons (+): positively charged particles inside the ...
... Rutherford and the Nucleus: Gold Foil Experiment A few particles deflected strongly Some bounced back!! Neutrons (no charge): located in center of atom Protons (+): positively charged particles inside the ...