gained (-) or lost (+) an electron
... When an atom gains an electron and becomes more (-) because there are more negative electrons present than positive protons. (Think: “An” means NOT or Negative for Ions) ...
... When an atom gains an electron and becomes more (-) because there are more negative electrons present than positive protons. (Think: “An” means NOT or Negative for Ions) ...
Matter: Building Blocks of the Universe Chapter 5 Classification of
... Elements at the left of a period tend to lose electrons easily when they combine with other elements o Elements at right of a period tend to gain electrons easily when they combine with other elements Amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom shows a periodic increase from left ...
... Elements at the left of a period tend to lose electrons easily when they combine with other elements o Elements at right of a period tend to gain electrons easily when they combine with other elements Amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom shows a periodic increase from left ...
Chapter 2 Test Review - Mercer Island School District
... Balancing demonstrates the Law of Conservation of Matter: Matter cannot be created or destroyed during a chemical reaction. Matter can only be rearranged. ...
... Balancing demonstrates the Law of Conservation of Matter: Matter cannot be created or destroyed during a chemical reaction. Matter can only be rearranged. ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
History of the Atom notes
... He believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible was not based on the scientific method – but just philosophy ...
... He believed that atoms were indivisible and indestructible was not based on the scientific method – but just philosophy ...
The Nature of Science Chapter 1
... – Atoms were hard, small particles – Believed different types of atoms existed for every type of matter and came in different shapes/sizes – Ideas were not accepted for nearly 2000 years! ...
... – Atoms were hard, small particles – Believed different types of atoms existed for every type of matter and came in different shapes/sizes – Ideas were not accepted for nearly 2000 years! ...
Atomic Theory
... around the nucleus in orbits. These orbits do not have set paths so they look like a cloud around the nucleus ...
... around the nucleus in orbits. These orbits do not have set paths so they look like a cloud around the nucleus ...
Periodic Table - MunterChemistry
... the atom’s electron affinity. • Halogens have high electron affinities because acquiring an electron will give them a full outer shell which increases the stability of the atom. • Half filled orbitals also give increased stability, so that the electron affinity of carbon is greater than the electron ...
... the atom’s electron affinity. • Halogens have high electron affinities because acquiring an electron will give them a full outer shell which increases the stability of the atom. • Half filled orbitals also give increased stability, so that the electron affinity of carbon is greater than the electron ...
Elements - Heartland
... Isotopes All atoms of one element have the same number of protons. But, they can have different numbers of neutrons, and hence, a different mass number. These different versions of atoms from one element are called isotopes. ...
... Isotopes All atoms of one element have the same number of protons. But, they can have different numbers of neutrons, and hence, a different mass number. These different versions of atoms from one element are called isotopes. ...
Name Period ______ Unit 4 Study Guide A common isotope of iron
... Describe what the chemical formula tells about an ionic or covalent compound. Draw a lewis dot diagram for Chlorine. When a Magnesium atom loses 2 electrons, it becomes a _________ ion. (Give the oxidation number.) Why do atoms form chemical bonds? How many valence electrons are in an atom of alumin ...
... Describe what the chemical formula tells about an ionic or covalent compound. Draw a lewis dot diagram for Chlorine. When a Magnesium atom loses 2 electrons, it becomes a _________ ion. (Give the oxidation number.) Why do atoms form chemical bonds? How many valence electrons are in an atom of alumin ...
JJ Thomson
... certain amounts or distances from nucleus; electron transitions from higher to lower levels result in discrete wavelengths of emitted light ...
... certain amounts or distances from nucleus; electron transitions from higher to lower levels result in discrete wavelengths of emitted light ...
CP3
... of an isotope in amu’s is simply the Mass number Most elements have several common isotopes Mass on periodic table must reflect this, that is why there are decimals Weighted average calculation (like grades) ...
... of an isotope in amu’s is simply the Mass number Most elements have several common isotopes Mass on periodic table must reflect this, that is why there are decimals Weighted average calculation (like grades) ...
Development of the Atomic Theory
... small, dense, positively charged center called the nucleus. ...
... small, dense, positively charged center called the nucleus. ...
Click here to the PPT
... The British physicist Ernest Rutherford, winner of the 1908 Nobel Prize in chemistry, pioneered the field of nuclear physics with his experimental research and his development of the nuclear theory of atomic ...
... The British physicist Ernest Rutherford, winner of the 1908 Nobel Prize in chemistry, pioneered the field of nuclear physics with his experimental research and his development of the nuclear theory of atomic ...
Chapter 4-1 & 4-2: The Periodic Table
... Halogens are non-metals Seven valence electrons making them highly reactive ...
... Halogens are non-metals Seven valence electrons making them highly reactive ...
Study Guide – Honors Chemistry: Exam One
... Sig figs – know how to calculate/determine Rules for significant zeros Rules for calculations o Addition and subtraction o Multiple and division ...
... Sig figs – know how to calculate/determine Rules for significant zeros Rules for calculations o Addition and subtraction o Multiple and division ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... periodic table Also known as Lanthanides because they follow the element lanthanum (La) on the table Scientists once thought these metals were available only in tiny amounts on the Earth ...
... periodic table Also known as Lanthanides because they follow the element lanthanum (La) on the table Scientists once thought these metals were available only in tiny amounts on the Earth ...
Atomic Theory
... masses, where ours today is arranged by increasing atomic numbers. Left spaces for elements which had not yet been discovered, but was able to predict what properties they would have by their location in his table. ...
... masses, where ours today is arranged by increasing atomic numbers. Left spaces for elements which had not yet been discovered, but was able to predict what properties they would have by their location in his table. ...
Periodic Trends Worksheet
... 11. a. Explain why it is harder to remove an inner shell electron than a valence electron from an atom. ...
... 11. a. Explain why it is harder to remove an inner shell electron than a valence electron from an atom. ...
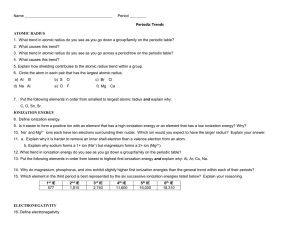
Periodic Trends Review Sheet
... 11. a. Explain why it is harder to remove an inner shell electron than a valence electron from an atom. b. Explain why sodium forms a 1+ ion (Na+) but magnesium forms a 2+ ion (Mg2+). 12. What trend in ionization energy do you see as you go down a group/family on the periodic table? 13. Put the foll ...
... 11. a. Explain why it is harder to remove an inner shell electron than a valence electron from an atom. b. Explain why sodium forms a 1+ ion (Na+) but magnesium forms a 2+ ion (Mg2+). 12. What trend in ionization energy do you see as you go down a group/family on the periodic table? 13. Put the foll ...
Chapters 4 and 5
... metal’s surface when light of a certain frequency shines on it. Frequency (color) of light, not brightness of light determines if electrons are emitted. Einstein (1905)- light has wave-like properties but is also a stream of tiny particles or bundles of energy called photons. Photon – a piece of EM ...
... metal’s surface when light of a certain frequency shines on it. Frequency (color) of light, not brightness of light determines if electrons are emitted. Einstein (1905)- light has wave-like properties but is also a stream of tiny particles or bundles of energy called photons. Photon – a piece of EM ...
8th-interlude-for-atoms - Epiphany Catholic School
... Are A & B different elements or isotopes? 2. C has an atomic number of 12 & mass number of 24. D has an atomic number of 13 & a mass number of 26. Are C & D different elements or isotopes? ...
... Are A & B different elements or isotopes? 2. C has an atomic number of 12 & mass number of 24. D has an atomic number of 13 & a mass number of 26. Are C & D different elements or isotopes? ...