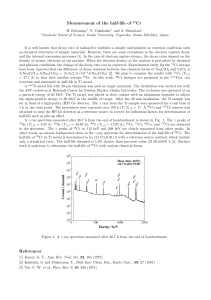
Measurement of the half-life of
... density of atomic electrons at the nucleus. When the electron density at the nucleus is perturbed by chemical and physical conditions, the change of the decay rate can be expected. Experimental study for the 51 Cr isotope have been reported that the difference of decay constant between two chemical f ...
... density of atomic electrons at the nucleus. When the electron density at the nucleus is perturbed by chemical and physical conditions, the change of the decay rate can be expected. Experimental study for the 51 Cr isotope have been reported that the difference of decay constant between two chemical f ...
Chapter 4 Atoms - Tangipahoa Parish School System
... • Isotope has same atomic number but different number of neutrons. • Isotopes have same atomic number but different mass numbers. • Isotopes have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons ...
... • Isotope has same atomic number but different number of neutrons. • Isotopes have same atomic number but different mass numbers. • Isotopes have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons ...
Structure of the Atom
... • Based on his experimental evidence: – The atom is mostly empty space – All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” – The neutron was discovered by Chadwick in 1932 ...
... • Based on his experimental evidence: – The atom is mostly empty space – All the positive charge, and almost all the mass is concentrated in a small area in the center. He called this a “nucleus” – The neutron was discovered by Chadwick in 1932 ...
Chapter 5 - HCC Learning Web
... For example, iron, the atomic number is 26, the configuration will be, 1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P6 4S2 3d6 QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL OF ATOM In the 1920’s our understanding of electrons in atoms became very sophisticated. Werner Heisenberg suggested the uncertainty principle- that is, it is impossible to sim ...
... For example, iron, the atomic number is 26, the configuration will be, 1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P6 4S2 3d6 QUANTUM MECHANICAL MODEL OF ATOM In the 1920’s our understanding of electrons in atoms became very sophisticated. Werner Heisenberg suggested the uncertainty principle- that is, it is impossible to sim ...
Chemical bonding
... in which atomic symbols represent nuclei and inner-shell electrons, dot-pairs, or dashes between two atomic symbols represent electron pairs in covalent bonds, and dots adjacent to only one atomic symbol represent unshared electrons ...
... in which atomic symbols represent nuclei and inner-shell electrons, dot-pairs, or dashes between two atomic symbols represent electron pairs in covalent bonds, and dots adjacent to only one atomic symbol represent unshared electrons ...
Chapter 3 Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... that a similar model could be applied to all atoms. However, Bohr’s approach _____ _____ _________ the spectra of atoms with _______ _______ _____ __________. Nor did Bohr’s theory explain the ___________ ___________ ___ _______. The Quantum Model of the Atom In 1924, the French scientist Louis de B ...
... that a similar model could be applied to all atoms. However, Bohr’s approach _____ _____ _________ the spectra of atoms with _______ _______ _____ __________. Nor did Bohr’s theory explain the ___________ ___________ ___ _______. The Quantum Model of the Atom In 1924, the French scientist Louis de B ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Introduction to Atoms & Nuclei
... can fit in the 1st shell. 4) The 2nd shell can hold up to 8 electrons. 5) The 3rd shell can hold 18, but the elements in the first few periods only use 8 electrons. ...
... can fit in the 1st shell. 4) The 2nd shell can hold up to 8 electrons. 5) The 3rd shell can hold 18, but the elements in the first few periods only use 8 electrons. ...
Lecture
... the binding energy is(not) great enough to hold the nucleus together. Unstable atoms will lose neutrons or protons as they attempt to become stable. They are called radioactive atoms. What is a radioactive decay? o spontaneous breakdown of an atomic nucleus resulting in the release of nuclear radiat ...
... the binding energy is(not) great enough to hold the nucleus together. Unstable atoms will lose neutrons or protons as they attempt to become stable. They are called radioactive atoms. What is a radioactive decay? o spontaneous breakdown of an atomic nucleus resulting in the release of nuclear radiat ...
ViewpointAPBiology
... Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form ...
... Atomic structure determines behavior of an element Atoms combine by chemical bonding to form ...
Unit 2 Review for Test
... 40. What elements make up a protein? 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule wh ...
... 40. What elements make up a protein? 42. Name the building blocks of lipids. 43. Draw a structural diagram showing a simple representation of a fatty acid.. 44. List some types of lipids. 45. Name the primary use of the type of macromolecule which is a source of energy. 46. Name the macromolecule wh ...
The Structure of the Atom
... A great deal of practical chemical knowledge was accumulated from their D. search for methods of separating metals from ores. E. Raison bun or plum pudding model. F. Earliest suggestion that matter was composed of atoms. G. Particles that have the same electronic configuration. H. Subatomic particle ...
... A great deal of practical chemical knowledge was accumulated from their D. search for methods of separating metals from ores. E. Raison bun or plum pudding model. F. Earliest suggestion that matter was composed of atoms. G. Particles that have the same electronic configuration. H. Subatomic particle ...
Chapter 5 – The Periodic Law 5-1 History of the Periodic Table A
... a list of its observed _______________________ and _______________________ properties. He then arranged them according to various properties and looked for _________________ or ________________________. 2. Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of _______________________ ato ...
... a list of its observed _______________________ and _______________________ properties. He then arranged them according to various properties and looked for _________________ or ________________________. 2. Mendeleev noticed that when the elements were arranged in order of _______________________ ato ...
Atomic Structure File
... Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.3 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and ...
... Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.3 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and ...
Atomic Worksheet
... Where would you find a proton in an atom? ___________________________________ What is the charge of an electron?__________ Where would you find an electron in an atom?_________________________________ What is the charge of a neutron?___________ Where would you find a neutron in an atom? ____________ ...
... Where would you find a proton in an atom? ___________________________________ What is the charge of an electron?__________ Where would you find an electron in an atom?_________________________________ What is the charge of a neutron?___________ Where would you find a neutron in an atom? ____________ ...
File
... - Lothar Meyer of Germany independently presented a similar table in 1870. - Henry Moseley, a British physicist, carried on the work of Mendeleev after his death and arranged the elements according to atomic no. instead of atomic mass. - Indicated in the present day table are the element symbol, ato ...
... - Lothar Meyer of Germany independently presented a similar table in 1870. - Henry Moseley, a British physicist, carried on the work of Mendeleev after his death and arranged the elements according to atomic no. instead of atomic mass. - Indicated in the present day table are the element symbol, ato ...
Review Worksheet
... c) cesium, lead, bismuth, barium 5) Define ionization energy: ________________________________________________________________ Arrange the following elements in order of increasing ionization energy: a) Be, Mg, Sr b) Bi, Cs, Ba c) Na, Al, S ...
... c) cesium, lead, bismuth, barium 5) Define ionization energy: ________________________________________________________________ Arrange the following elements in order of increasing ionization energy: a) Be, Mg, Sr b) Bi, Cs, Ba c) Na, Al, S ...
What is an ion?
... Just as each state has a two-letter abbreviation, each element has a oneor two-letter symbol to make life simple for chemists. ...
... Just as each state has a two-letter abbreviation, each element has a oneor two-letter symbol to make life simple for chemists. ...
Homework #1 Atoms
... 1. The number of ____________ in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic ____________ of that element. Because atoms are electrically neutral, the number of protons and ____________ in an atom are equal. 2. The sum of the _____________ and neutrons is the mass number. 3. Atoms of the same element are i ...
... 1. The number of ____________ in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic ____________ of that element. Because atoms are electrically neutral, the number of protons and ____________ in an atom are equal. 2. The sum of the _____________ and neutrons is the mass number. 3. Atoms of the same element are i ...
Lecture 3 – The Periodic Table
... 1s22s2, respectively. The second ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous unipositive ion in its ground state. For the second ionization process, we write ...
... 1s22s2, respectively. The second ionization energy is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous unipositive ion in its ground state. For the second ionization process, we write ...
Subatomic Particles
... mass of the electron. It was found to be 9.1 x 10-28 g = 1/1837 the mass of 1 H atom. Thomson later turned his attention to another interesting phenomenon. When light of high energy strikes certain metals, negatively charged particles are given off from the metallic surface --> photoelectric effec ...
... mass of the electron. It was found to be 9.1 x 10-28 g = 1/1837 the mass of 1 H atom. Thomson later turned his attention to another interesting phenomenon. When light of high energy strikes certain metals, negatively charged particles are given off from the metallic surface --> photoelectric effec ...
Atomic Number - Mrs. McGee`s Class
... • One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They • are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. • Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. • The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, ...
... • One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They • are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. • Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. • The family of noble gases includes helium, neon, argon, ...
Periodic Table Virtual Activity http://my.uzinggo.com/cplogin/ The
... checkmark. This is a 5 question quiz. Do the quiz. Place your answers and your score here: ___________________________________________________ Part 4: General structure of the periodic table 1. Where are metals and nonmetals located on the periodic table? 2. Why are the elements on the far side (las ...
... checkmark. This is a 5 question quiz. Do the quiz. Place your answers and your score here: ___________________________________________________ Part 4: General structure of the periodic table 1. Where are metals and nonmetals located on the periodic table? 2. Why are the elements on the far side (las ...
Atomic Structure - Madison County Schools
... Electrons are negatively charged particles that surround the atom's nucleus. Electrons were discovered by J. J. Thomson in 1897. Electrons determine properties of the atom. Chemical reactions involve sharing or exchanging electrons. ...
... Electrons are negatively charged particles that surround the atom's nucleus. Electrons were discovered by J. J. Thomson in 1897. Electrons determine properties of the atom. Chemical reactions involve sharing or exchanging electrons. ...























